Abstract
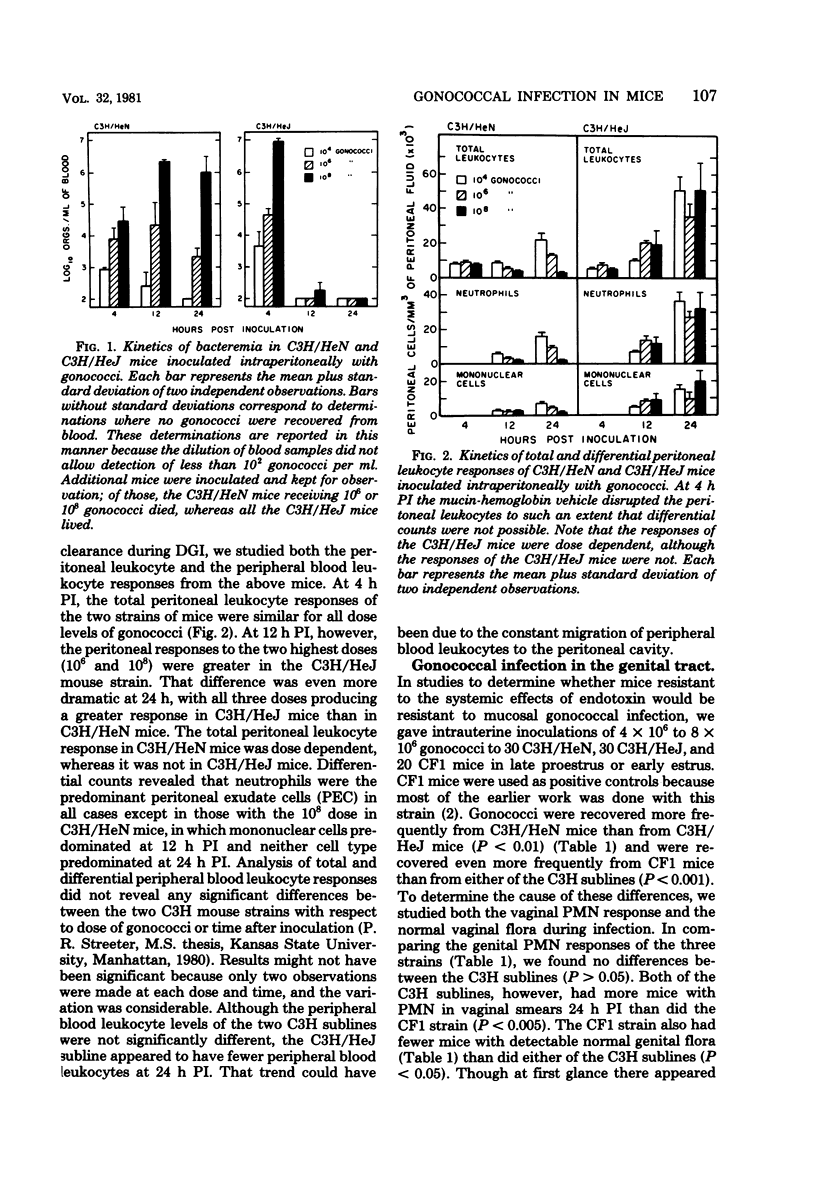
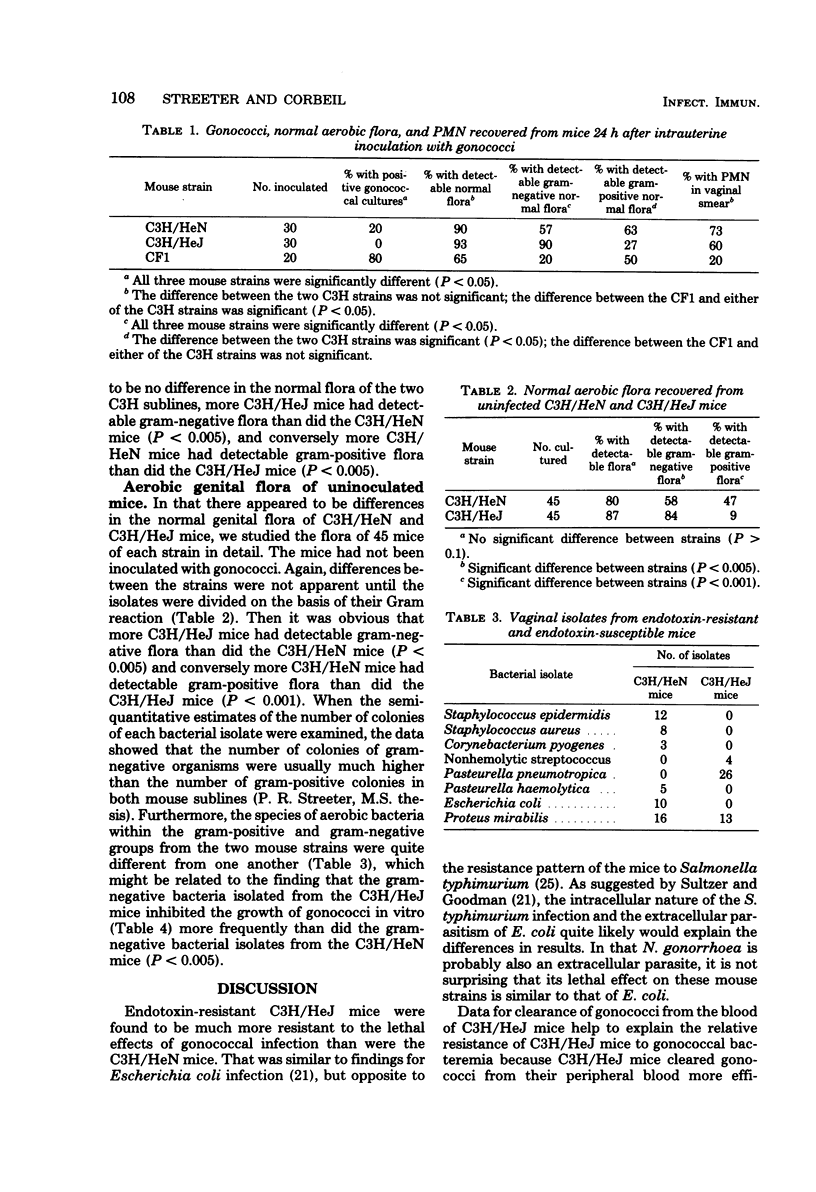
The role of endotoxin responsiveness in defense against gonococcal infection was studied in endotoxin-resistant (C3H/HeJ) and endotoxin-susceptible (C3H/HeN) mice by using a model of disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI) and a model of gonococcal survival in the female genital tract to determine the ability of the mice to eliminate gonococci. The 50% lethal dose in the DGI model was 10(9.6) for C3H/HeJ mice and 10(5.2) for C3H/HeN mice. Levels of bacteremia during infection indicated the C3H/HeJ mice cleared large numbers of gonococci from their peripheral blood by 24 h post-inoculation but that C3H/HeN mice did not. Additionally, the peritoneal leukocyte response after intraperitoneal inoculation of gonococci was greater in C3H/HeJ mice than in C3H/HeN mice, which suggested that the ability to mount an inflammatory response to endotoxin may be important in defense against DGI. Besides being different in susceptibility to DGI, C3H/HeJ mice were found to be more resistant then C3H/HeN mice to genital colonization by gonococci. The resistance of C3H/HeJ mice to genital colonization by gonococci appeared to be due to both the high numbers of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the genital secretion and the predominance of inhibitory gram-negative genital flora in that mouse strain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOOT L. M., MUHLBOCK O., THUNG P. J. Senile changes in the oestrous cycle and in ovarian structure in some inbred strains of mice. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1956 Sep;23(1):8–32. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0230008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Wunderlich A. C., Braude A. I. Technique for transcervical intrauterine inoculation of the mouse. Lab Anim Sci. 1978 Jun;28(3):314–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Wunderlich A. C., Corbeil R. R., McCutchan J. A., Ito J. I., Jr, Braude A. I. Disseminated gonococcal infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):984–990. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.984-990.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode L. M., Jacques A., Mergenhagen S. E., Rosenstreich D. L. Resistance of macrophages from C3H/HeJ mice to the in vitro cytotoxic effects of endotoxin. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. E., Jr, Billings T. E., Hackney J. F., Thayer J. D. Primary isolation of N. gonorrhoeae with a new commercial medium. Public Health Rep. 1967 Apr;82(4):361–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeller G. R., Terry L., Snyderman R. The inflammatory response and resistance to endotoxin in mice. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):116–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Baughn R. E., Musher D. M. Strain-dependent cytotoxic effects of endotoxin for mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):310–319. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.310-319.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Buchanan T. M., Holmes K. K. Gonococci causing disseminated gonococcal infection are resistant to the bactericidal action of normal human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1163–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI108569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic control of leucocyte responses to endotoxin. Nature. 1968 Sep 21;219(5160):1253–1254. doi: 10.1038/2191253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic factors in leucocyte responses to endotoxin: further studies in mice. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):32–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vas S. I., Roy R. S., Robson H. G. Endotoxin sensitivity of inbred mouse strains. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jul;19(7):767–769. doi: 10.1139/m73-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Riblet R. Genetic control of responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice. I. Evidence for a single gene that influences mitogenic and immunogenic respones to lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1147–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


