Abstract
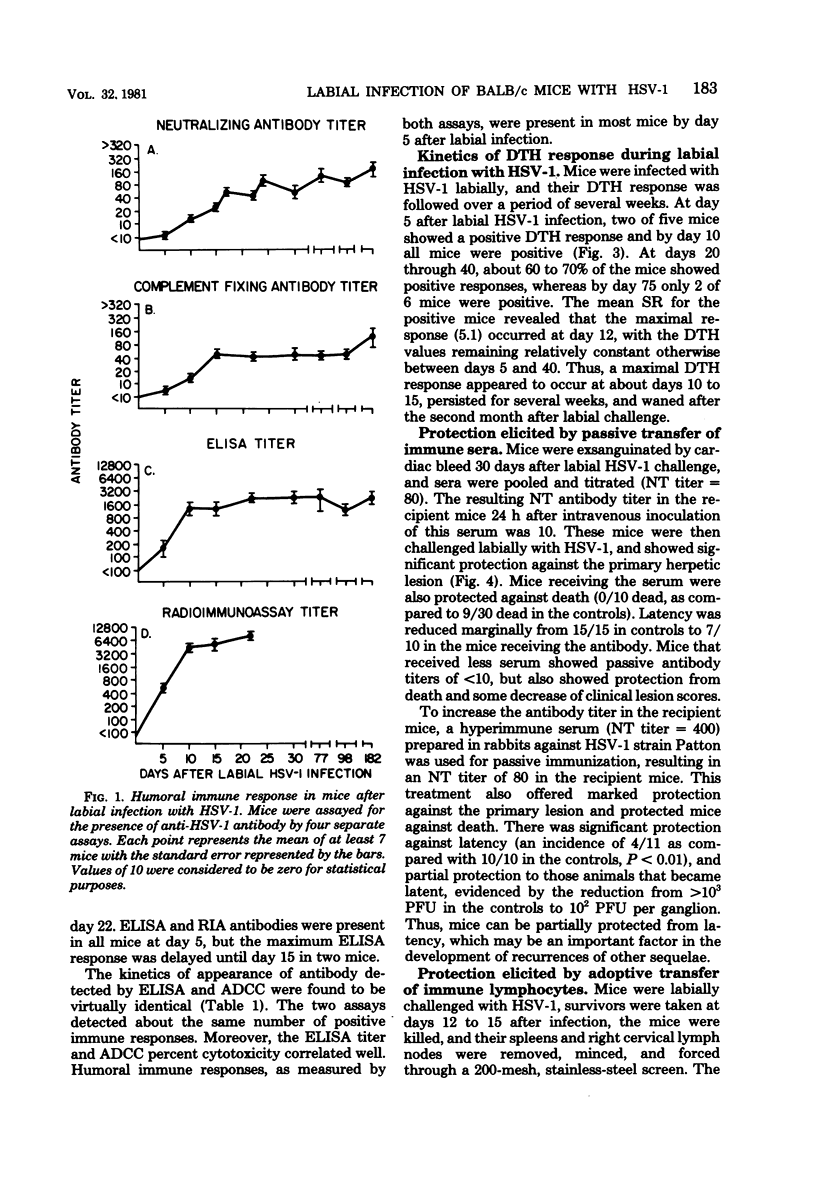
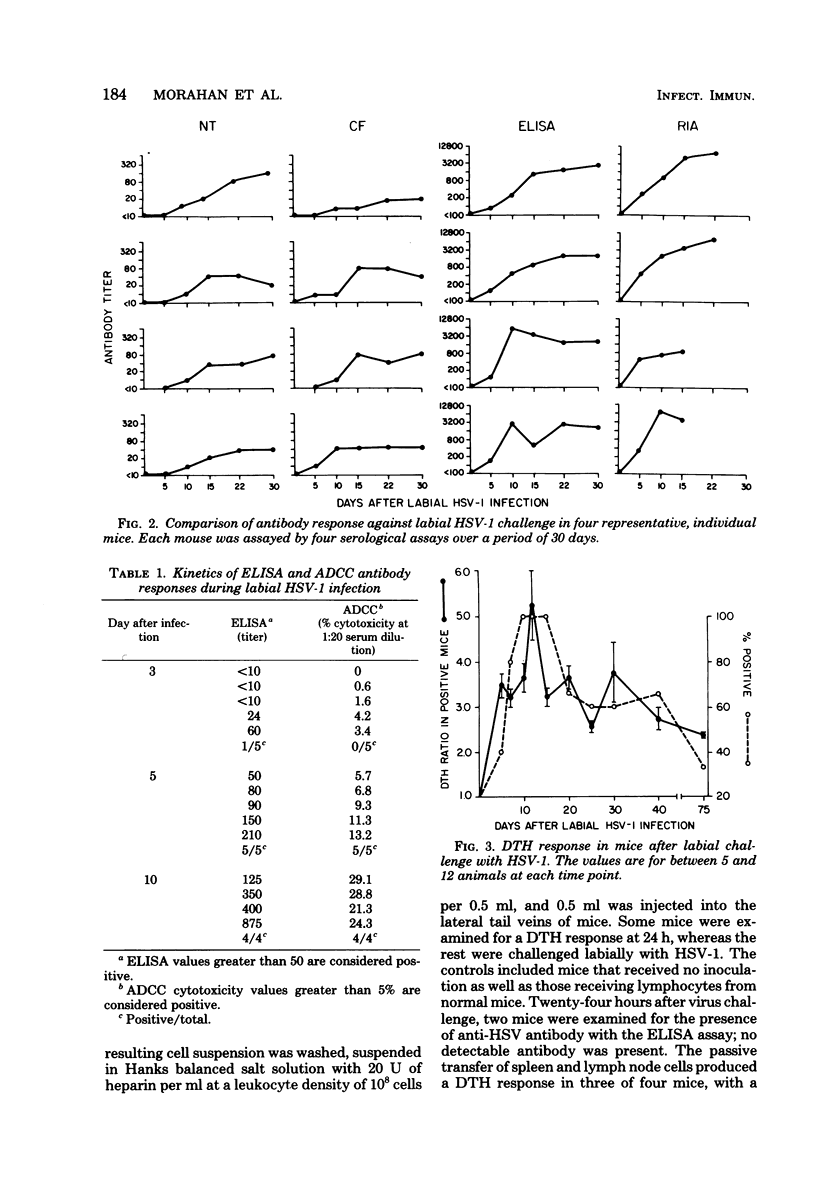
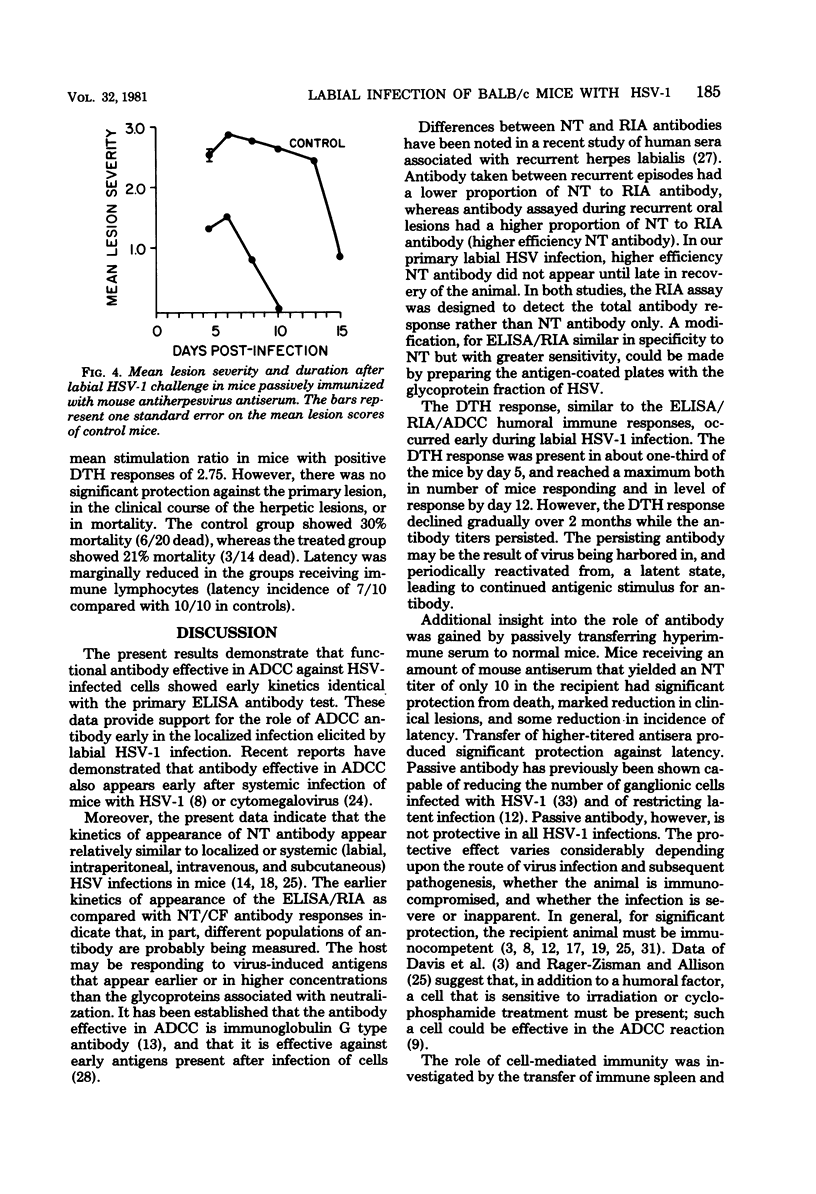
The kinetics of appearance of five humoral antibody responses (micro-neutralization assay [NT], complement fixation [CF], enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay [ELISA], radioimmunoassay [RIA], antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity [ADCC]), were compared during labial infection of BALB/c mice with herpes simplex virus type 1 strain Patton. The ELISA/RIA antibody responses were present in most mice by day 5 after infection, at the beginning of the herpetic lip lesions; antibody effective in ADCC showed identical early kinetics. In contrast, NT/CF antibodies were not detected in most mice until day 10, at the time of resolution of the herpetic lip lesions. The humoral immune responses persisted for at least 6 months after infection. The NT and CF responses were closely correlated in time of appearance and titers (r = 0.9), as were the ELISA and RIA responses (r = 0.99). However, there was little correlation between NT/CF and ELISA/RIA responses (r = 0.02). The kinetics of the delayed type hypersensitivity response showed similar kinetics of appearance to the ELISA/RIA/ADCC humoral responses, and peaked similarly, but waned gradually over 2 months. The importance of antibody in protection against labial herpes simplex virus type 1 infection was demonstrated by the ability of passively transferred convalescent serum (that produced a minimum NT titer of 10 in recipient mice) to protect against development of herpetic lesions and death.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babiuk L. A., Rouse B. T. Immune control of herpesvirus latency. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):267–274. doi: 10.1139/m79-043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. B., Taylor J. A., Oakes J. E. Ocular infection with herpes simplex virus type 1: prevention of acute herpetic encephalitis by systemic administration of virus-specific antibody. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):534–540. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis F. A. Host defense mechanisms against herpes simplex virus. II. Protection conferred by sensitized spleen cells. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):632–638. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes E. L., Taylor W., Mitchison N. A., Simpson E. MHC matching shows that at least two T-cell subsets determine resistance to HSV. Nature. 1979 Jan 4;277(5691):66–68. doi: 10.1038/277067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitces E. N., Morahan P. S., Tew J. G., Murray B. K. Protection from oral herpes simplex virus infection by a nucleic acid-free virus vaccine. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):955–960. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.955-960.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Cahall D. L., Walters D. L., Schaffner V. E. Murine antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected target cells. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Wilton J. M., Shillitoe E. J. Immunological basis for latency, recurrences and putative oncogenicity of herpes simplex virus. Lancet. 1975 Jul 12;2(7924):60–62. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodmell D. L., Notkins A. L. Cellular immunity to herpes simplex virus mediated by interferon. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):764–778. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendall R. R., Klassen T., Baringer J. R. Host defenses in herpes simplex infections of the nervous system: effect of antibody on disease and viral spread. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):305–311. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.305-311.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melewicz F. M., Shore S. L., Ades E. W., Phillips D. J. The mononuclear cell in human blood which mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to virus-infected target cells. II. Identification as a K cell. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):567–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan P. S., Breinig M. C., McGeorge M. B. Immune responses to vaginal or systemic infection of BALB/c mice with herpes simplex virus type 2. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2030–2036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan P. S., Cline P. F., Breinig M. C., Murray B. K. Effect of pyran on latency after herpes simplex virus infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):547–553. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E. Role for cell-mediated immunity in the resistance of mice to subcutaneous herpes simplex virus infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):166–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.166-172.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E., Rosemond-Hornbeak H. Antibody-mediated recovery from subcutaneous herpes simplex virus type 2 infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):489–495. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.489-495.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park N. H., Pavan-Langston D., Hettinger M. E., McLean S. L., Albert D. M., Lin T. S., Prusoff W. H. Topical therapeutic efficacy of 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine and 5-iodo-5'-amino-2',5'-dideoxyuridine on oral infection with herpes simplex virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):575–579. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park N. H., Pavan-Langston D., McLean S. L. Acylovir in oral and ganglionic herpes simplex virus infections. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):802–806. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Schmitz J. Route of infection, systemic host resistance, and integrity of ganglionic axons influence acute and latent herpes simplex virus infection of the superior cervical ganglion. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):373–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.373-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Walz M. A., Wohlenberg C., Notkins A. L. Latent infection of sensory ganglia with herpes simplex virus: efficacy of immunization. Science. 1975 May 30;188(4191):938–940. doi: 10.1126/science.166432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Manischewitz J. E. The role of natural killer cells and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity during murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1549–1554. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Allison A. C. Mechanism of immunologic resistance to herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) infection. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner J. J., Smith K. O. Serum antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 during active oral herpes infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):113–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.113-117.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wardley R. C., Babiuk L. A. The role of antibody dependent cytotoxicity in recovery from herpesvirus infections. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 1;22(1):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Cook M. L. Maintenance of latent herpetic infection: an apparent role for anti-viral IgG. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1685–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Hsiung G. D. Pathogenesis of latent herpes simplex virus infection of the trigeminal ganglion in guinea pigs: effects of age, passive immunization, and hydrocortisone. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):69–74. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.69-74.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz M. A., Yamamoto H., Notkins A. L. Immunological response restricts number of cells in sensory ganglia infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):554–556. doi: 10.1038/264554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



