Abstract
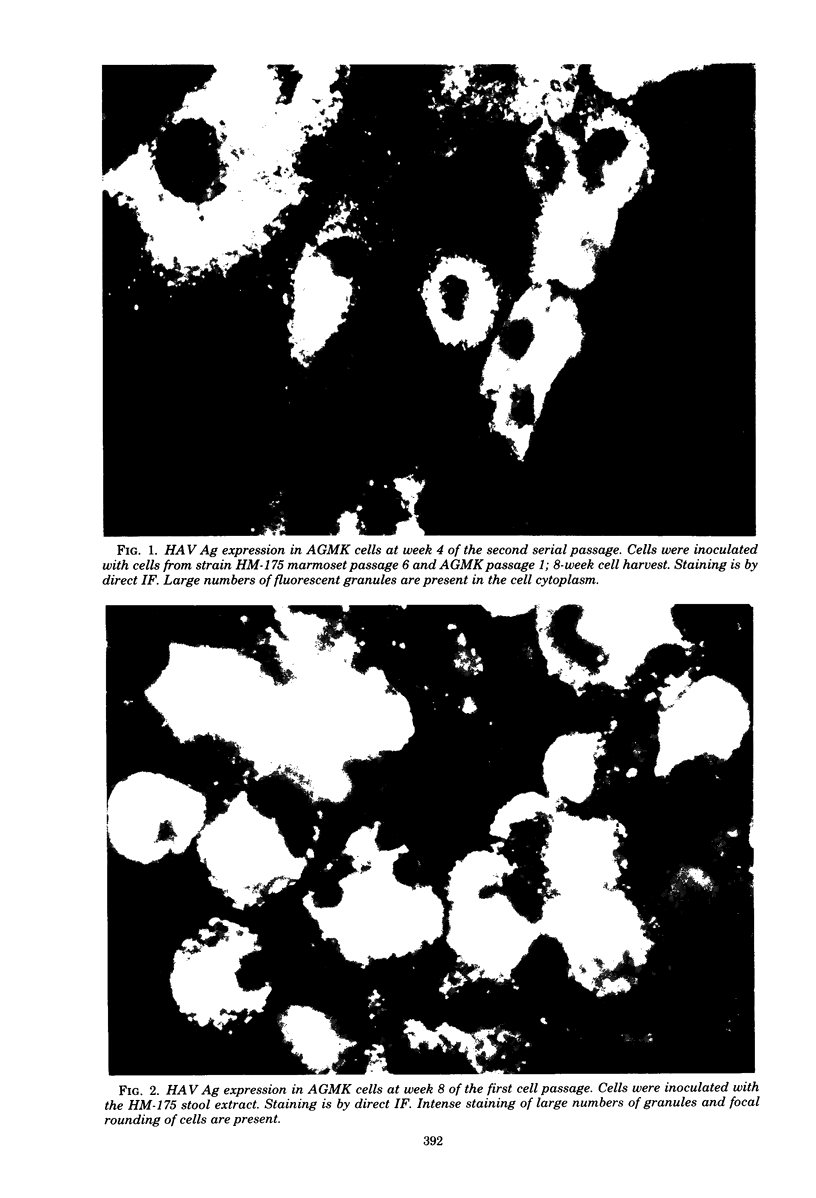
Human hepatitis A virus (HAV) was propagated in primary African Green Monkey (Cercopithecus aethiops) kidney (AGMK) cell cultures. Three strains of HAV were used: MS-1, SD-11, and HM-175. Cells were inoculated with marmoset-passaged material or human clinical specimens and were stained by direct immunofluorescence to establish the identity of the virus. Both clinical samples and marmoset-passaged material produced immunofluorescence. HAV antigen was found scattered throughout the cytoplasm of inoculated cultures. The HM-175 strain produced the most intense immunofluorescence. This strain of HAV had been serially passaged in cell culture seven times. Blocking experiments with paired human sera from naturally acquired HAV infections and hyperimmune chimpanzee serum from an experimentally infected animal established that the immunofluorescence was specific. The viral antigen was found to be exclusively intracellular. The interval to maximum HAV antigen expression was decreased by serial passage. The HAV strain described herein, which was recovered directly from the stool specimen of a patient with HAV in primary AGMK cell culture, may prove useful as a source of antigen for serological tests and as a candidate vaccine strain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boggs J. D., Melnick J. L., Conrad M. E., Felsher B. F. Viral hepatitis. Clinical and tissue culture studies. JAMA. 1970 Nov 9;214(6):1041–1046. doi: 10.1001/jama.214.6.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Hornbeck C. L., Cood E. H., Maynard J. E., Gravelle C. R. CsCl banding of hepatitis A-associated virus-like particles. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):304–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulepis A. G., Locarnini S. A., Ferris A. A., Lehmann N. I., Gust I. D. The polypeptides of hepatitis A virus. Intervirology. 1978;10(1):24–31. doi: 10.1159/000148964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H., Hoofnagle J. H., Barker L. F., London W. T., Popper H., Peterson J. M., Kapikian A. Z. Experimental infection of chimpanzees with hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):532–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Routenberg J. A., Purcell R. H., Hooper R. R., Harrison W. O. Foodhandler-associated outbreak of hepatitis type A. An immune electron microscopic study. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Nov;83(5):647–650. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-5-647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Purceli R. H. Hepatitis A: detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):1026–1028. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S., Giles J. P., Hammond J. Infectious hepatitis. Evidence for two distinctive clinical, epidemiological, and immunological types of infection. JAMA. 1967 May 1;200(5):365–373. doi: 10.1001/jama.200.5.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Salazar F. H., Alexander J. J., Robinson W. S. State of hepatitis B viral DNA in a human hepatoma cell line. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):795–806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.795-806.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen L. R., Drucker J., Lorenz D., Wagner J. A., Gerety R. J., Purcell R. H. Localization of hepatitis A antigen in marmoset organs during acute infection with hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1978 Sep;138(3):369–377. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen L. R., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H., Wagner J. A. Detection of hepatitis A antigen by immunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):524–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.524-530.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Hilleman M. R. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in cell culture in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):213–221. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Wolanski B. S., Miller W. J., Ittensohn O. L., McAleer W. J., Hilleman M. R. Physical, chemical and morphologic dimensions of human hepatitis A virus strain CR326 (38578). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Feb;148(2):532–539. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Moritsugu Y., Dienstag J. L., Routenberg J. A., Boggs J. D. A microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis A antigen and antibody. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Frösner G. G. Characterization and classification of virus particles associated with hepatitis A. I. Size, density, and sedimentation. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.40-47.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Frösner G. G. Characterization and classification of virus particles associated with hepatitis A. II. Type and configuration of nucleic acid. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):48–53. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.48-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]