Abstract
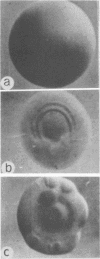
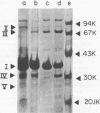
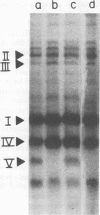
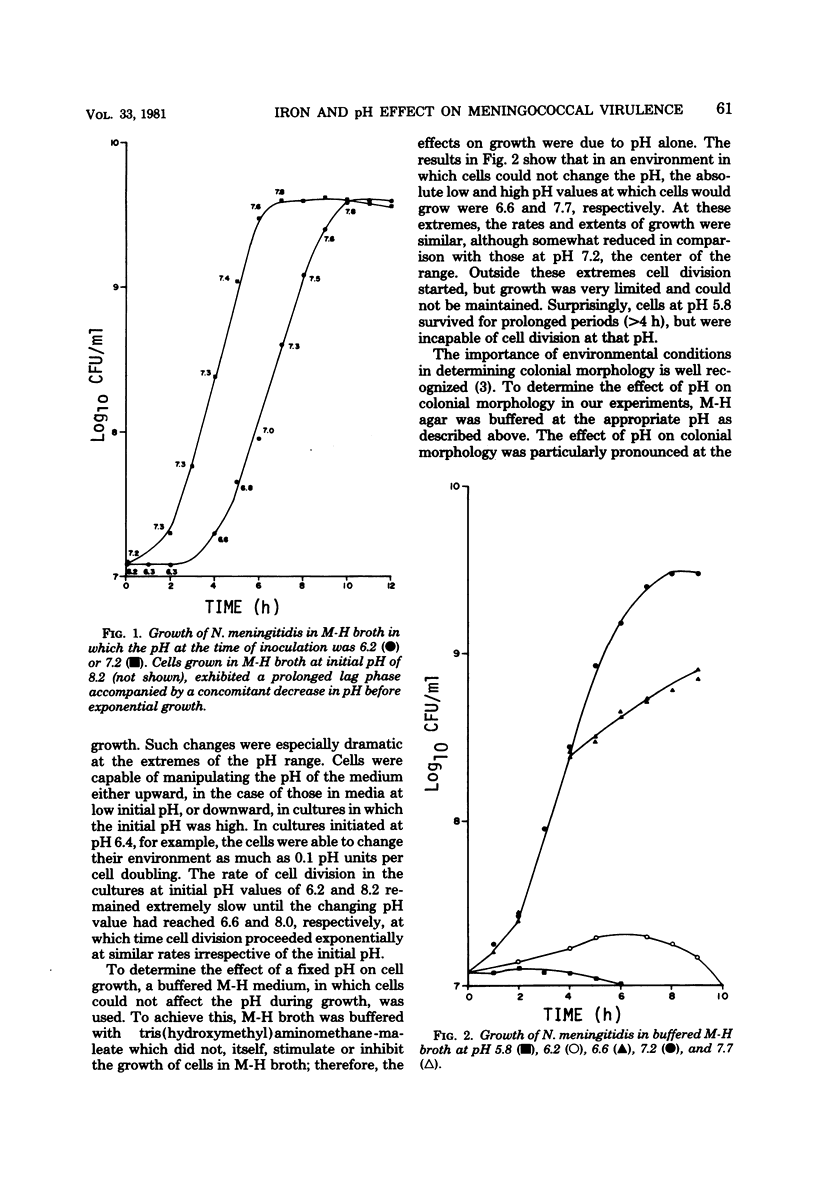
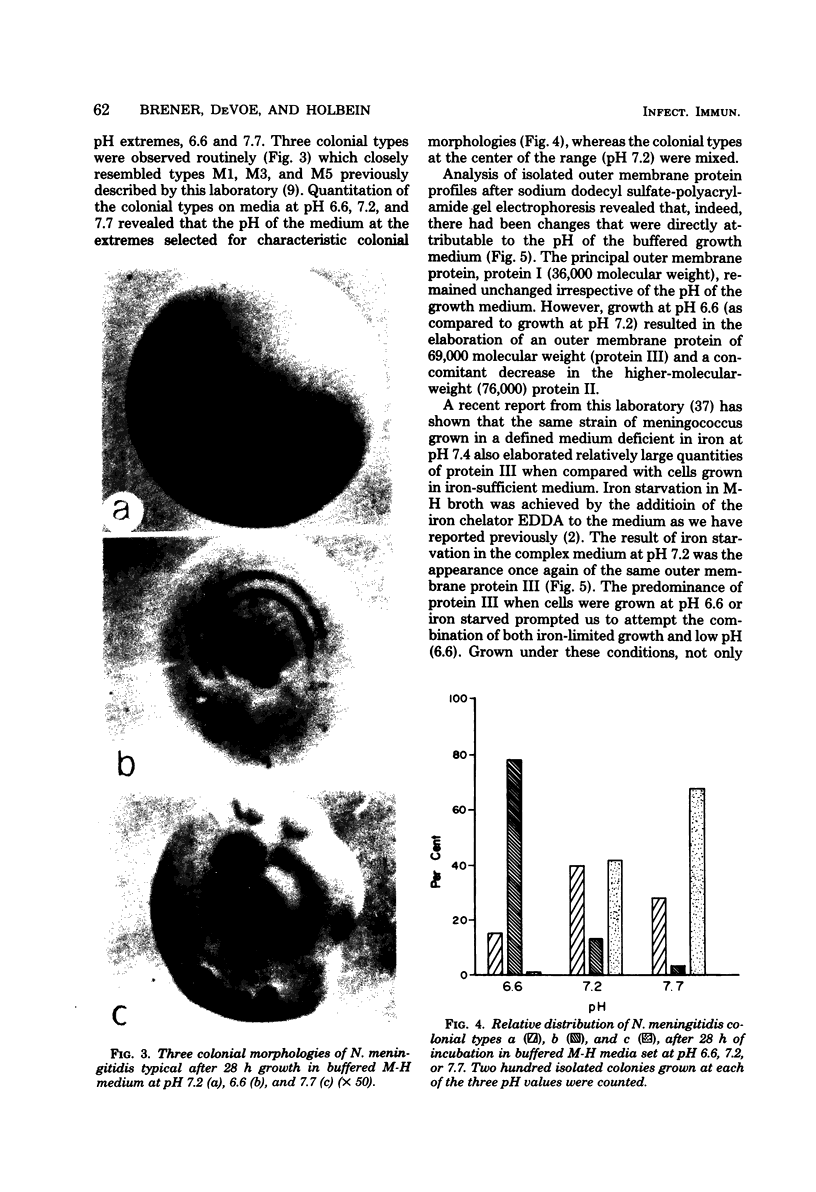
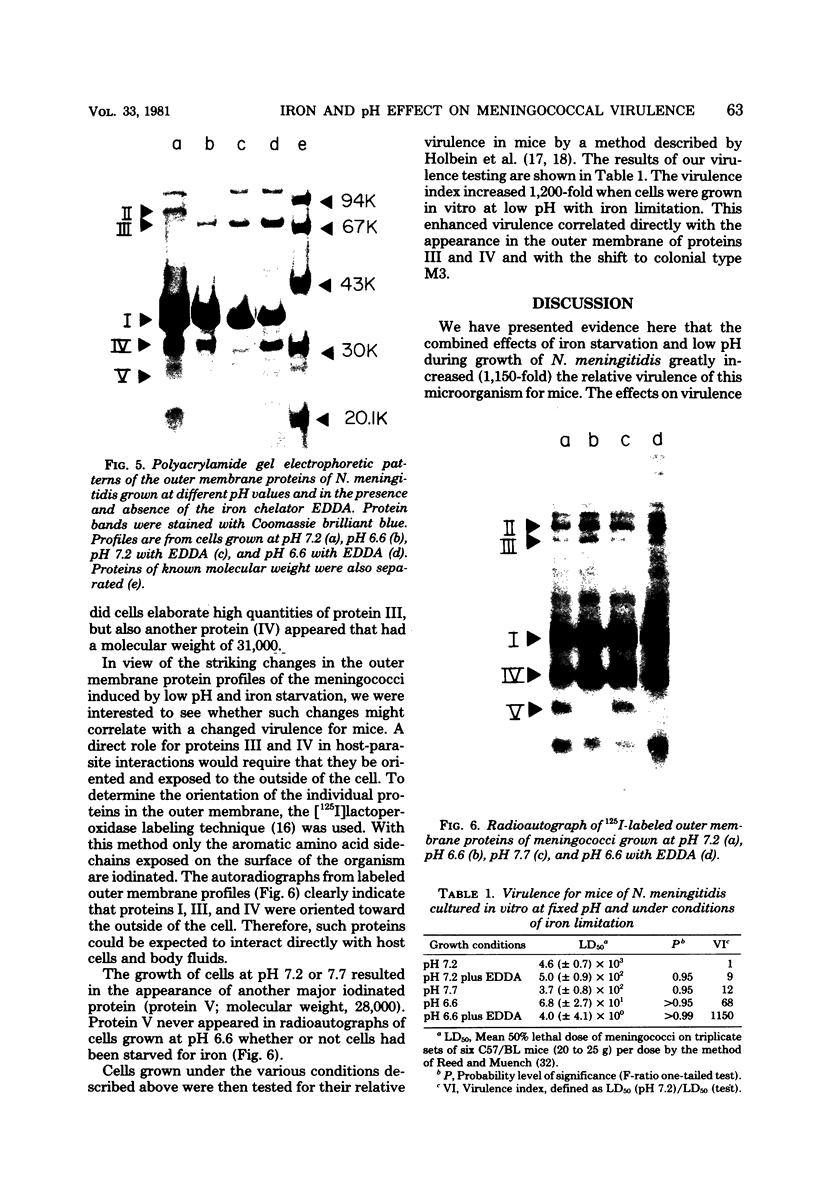
At low pH (6.6) and under conditions of iron limitation, Neisseria meningitidis group B (strain SD1C) exhibited an atypical outer membrane protein profile and an increased relative virulence for the mouse. Cells grown in a buffered medium were effectively deprived of iron by the addition of ethylenediamine-diorthohydroxyphenylacetate. The pH of the medium selected for characteristic colonial morphologies: type M3 predominated at pH 6.6, and type M5 predominated at pH 7.7. A mixed population of M1, M3, and M5 colonies was observed at pH 7.2. Isolated outer membrane proteins were analyzed by sodium dodecyl 99 99 sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and surface exposed proteins were labeled by the [125I]lactoperoxidase method and subsequently identified by autoradiography. Cells grown at pH 6.6 elaborated a major outer membrane protein (protein III; molecular weight, 69,000), which was also present in the outer membrane of iron-limited cells grown at pH 7.2. At pH 7.2 in an iron-sufficient medium, protein III was present only in small quantities in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel was present only in small quantities in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels. A study of the relative virulence (50% lethal dose) of the meningococcus for C57/BL mice revealed that iron-limited cells grown at low pH had an increased relative virulence 1,200-fold (50% lethal dose, 4.0 CFU) greater than that of cells grown in the same medium but at pH 7.2 and with sufficient iron. These studies indicate that pH and iron can be important factors in the determination of meningococcal virulence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald F. S., DeVoe I. W. Iron acquisition by Neisseria meningitidis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):322–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.322-334.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. 3. Correlation of gonococcal colony morphology with infectivity for the chick embryo. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):196–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Role of iron in bacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W. Egestion of degraded meningococci by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):258–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.258-266.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Piliation and colonial morphology among laboratory strains of meningococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):379–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.379-384.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON J. H., CHAPMAN O. D. Fulminating meningococcic infections and the so-called Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1948 Jul;24(4):763–795. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Strain-specific variation in the protein and lipopolysaccharide composition of the group B meningococcal outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):973–981. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.973-981.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green I., Kirkpatrick C. H., Dale D. C. Lactoferrin--specific localization in the nuclei of human polymorphonuclear neutrophilic leukocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1311–1317. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. The surface properties of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: topographical distribution of the outer membrane protein antigens. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Oct;108(2):213–219. doi: 10.1099/00221287-108-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E. Iron-controlled infection with Neisseria meningitidis in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):886–891. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.886-891.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E., Jericho K. W., Likes G. C. Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice: influence of iron, variations in virulence among strains, and pathology. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.545-551.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Reyn A. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Colony variation I. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(5):609–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Peters R., Bernheimer H., Berendsen W. Influence of cultural conditions and mutations on the composition of the outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Sep 23;147(3):251–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00582876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Kihlstrom E., Norqvist A., Davies J., Normark S. Effect of iron on surface charge and hydrophobicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):402–407. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.402-407.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Kihlström E., Norlander L., Norqvist A., Davies J., Normark S. Effect of colony type and pH on surface charge and hydrophobicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.397-401.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald I. J., Adams G. A. Influence of cultural conditions on the lipopolysaccharide composition of Neisseria sicca. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Feb;65(2):201–207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh M. A., Earhart C. F. Effect of iron of the relative abundance of two large polypeptides of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 3;70(1):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C. EFFECTS OF ENVIRONMENT ON THE COMPOSITION OF BACTERIAL CELLS. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1963;17:61–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.17.100163.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Tempest D. W. Phenotypic variability of the envelope proteins of Klebsiella aerogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):361–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Blake M., Gotschlich E. C. Intra-strain heterogeneity of gonococcal pili is related to opacity colony variance. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):716–725. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal color and opacity variants: virulence for chicken embryos. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.359-364.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. IV. Differences in outer membrane proteins due to strain and cultural differences. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):454–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.454-464.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Trivett T., DeVoe I. W. Energy-independent uptake of iron from citrate by isolated outer membranes of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):547–553. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.547-553.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. The involvement of lactoferrin in the hyposideremia of acute inflammation. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1068–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H. Novel iron uptake system specified by ColV plasmids: an important component in the virulence of invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):925–932. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.925-932.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Mandrell R. E. Outer-membrane protein and lipopolysaccharide serotyping of Neisseria meningitidis by inhibition of a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.424-433.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]