Abstract
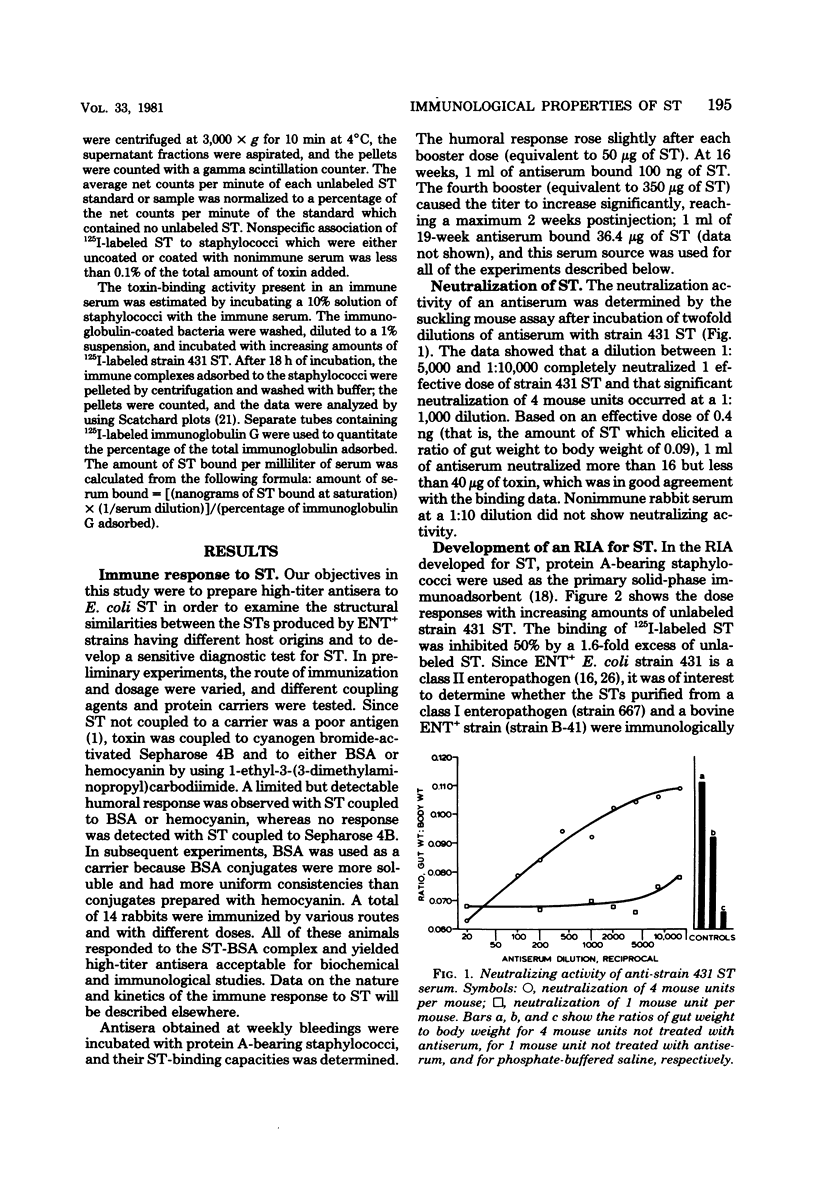
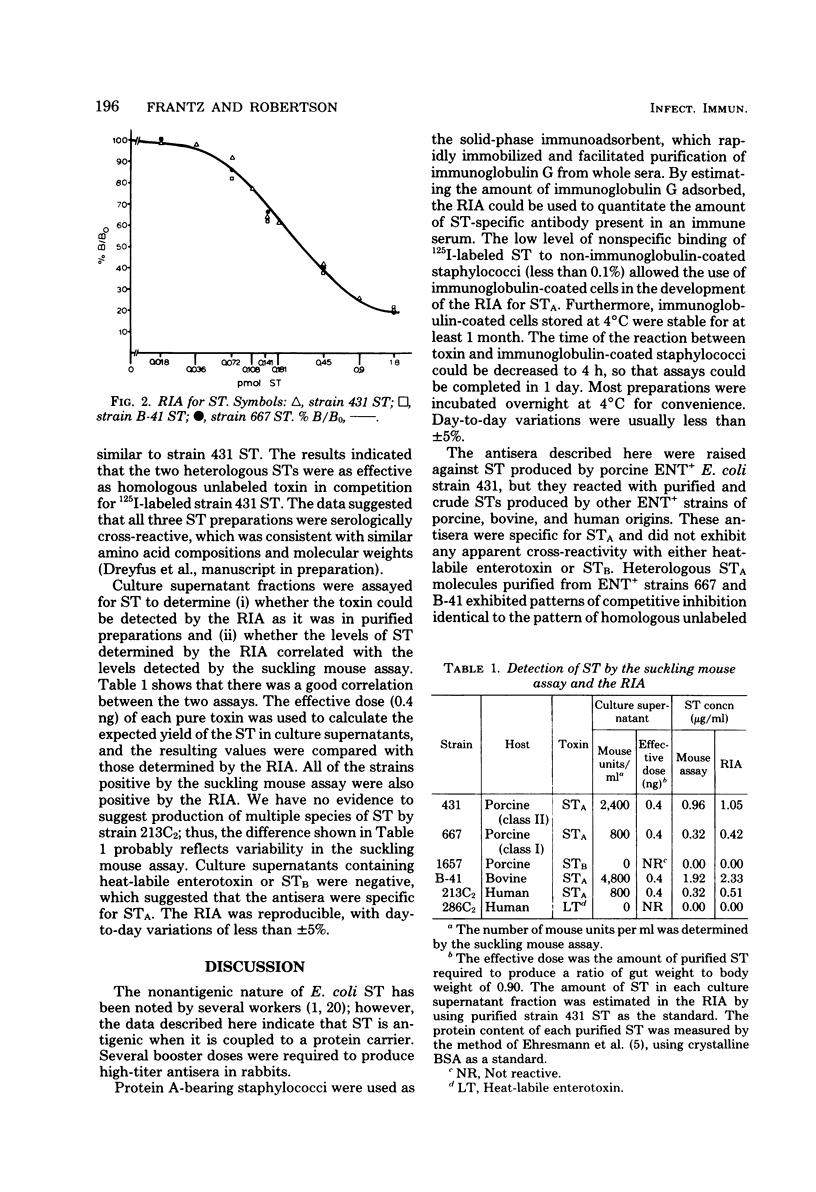
Antiserum was raised against the purified heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain 431, a class II porcine enteropathogen. The antiserum was used to examine the antigenic determinants of STs produced by enterotoxigenic strains of different host origins and develop a sensitive radioimmunoassay specific for ST having biological activity in suckling mice and piglets (STA). The antiserum neutralized one effective dose of toxin at a dilution of 1:5,000 and neutralized approximately 40 microgram of toxin per ml of serum. In the radioimmunoassay, protein A-bearing staphylococci was used as the primary solid-phase adsorbent. The purified STs produced by a class I enteropathogen (strain 667) and by a bovine enterotoxigenic strain (B-41) exhibited patterns of competitive inhibition identical to those of homologous unlabeled strain 431 ST in the radioimmunoassay when specific antibody to strain 431 ST was used. The levels of ST in culture supernatants determined by the suckling mouse assay correlated with the concentrations of toxin measured by the radioimmunoassay. The antiserum was specific for STA produced by enterotoxigenic E. coli of porcine, bovine, and human origins and did not react with heat-labile enterotoxin or with ST that had biological activity in piglets but not in suckling mice (STB). These results suggest that STA molecules having different host origins share at least one antigenic determinant.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. M., Roth F. L., Jr, Tai H. H., Chey W. Y. Radioimmunoassay of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 1;97(2):286–297. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann B., Imbault P., Weil J. H. Spectrophotometric determination of protein concentration in cell extracts containing tRNA's and rRNA's. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):454–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Sack D. A., Rodriguez W., Sack R. B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.541-545.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Limitations of the infant mouse test for Escherichia coli heat stable enterotoxin. Can J Comp Med. 1979 Oct;43(4):371–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Scoot A., Forsyth G. W., McKenzie S. L., Worthington R. W. Evidence for two heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):965–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.965-966.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Cell membrane antigen isolation with the staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1482–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler E. M. Enterotoxic activity of filtrates of escherichia coli in young pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Dec;29(12):2263–2274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-labile enterotoxin produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):586–596. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.586-596.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen G. L., Knoop F. C. Physiochemical properties of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli of human origin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1051–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1051-1053.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Development of resistance with age by swine intestine to effects of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):220–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., Levine M. M., Young C. R., Bergquist E. J., McLaughlin J. C. Increased Escherichia coli enterotoxin detection after concentrating culture supernatants: possible new enterotoxin detectable in dogs but not in infant mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):700–703. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.700-703.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe E., Vennett V. Use of immunoglobulin-loaded protein A-bearing staphylococci as a primary solid phase immunoadsorbent in radioimmunoassay. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):561–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson E., Söderlind O. Comparison of different assays for definition of heat-stable enterotoxigenicity of Escherichia coli porcine strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):6–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.6-15.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., Argenzio R. A. Comparison of enterotoxic activities of heat-stable enterotoxins from class 1 and class 2 Escherichia coli of swine origin. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.245-251.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Greenberg H. B., Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):439–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.439-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



