Abstract
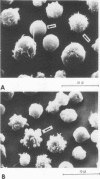
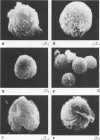
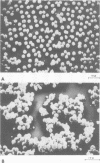
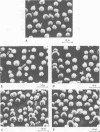
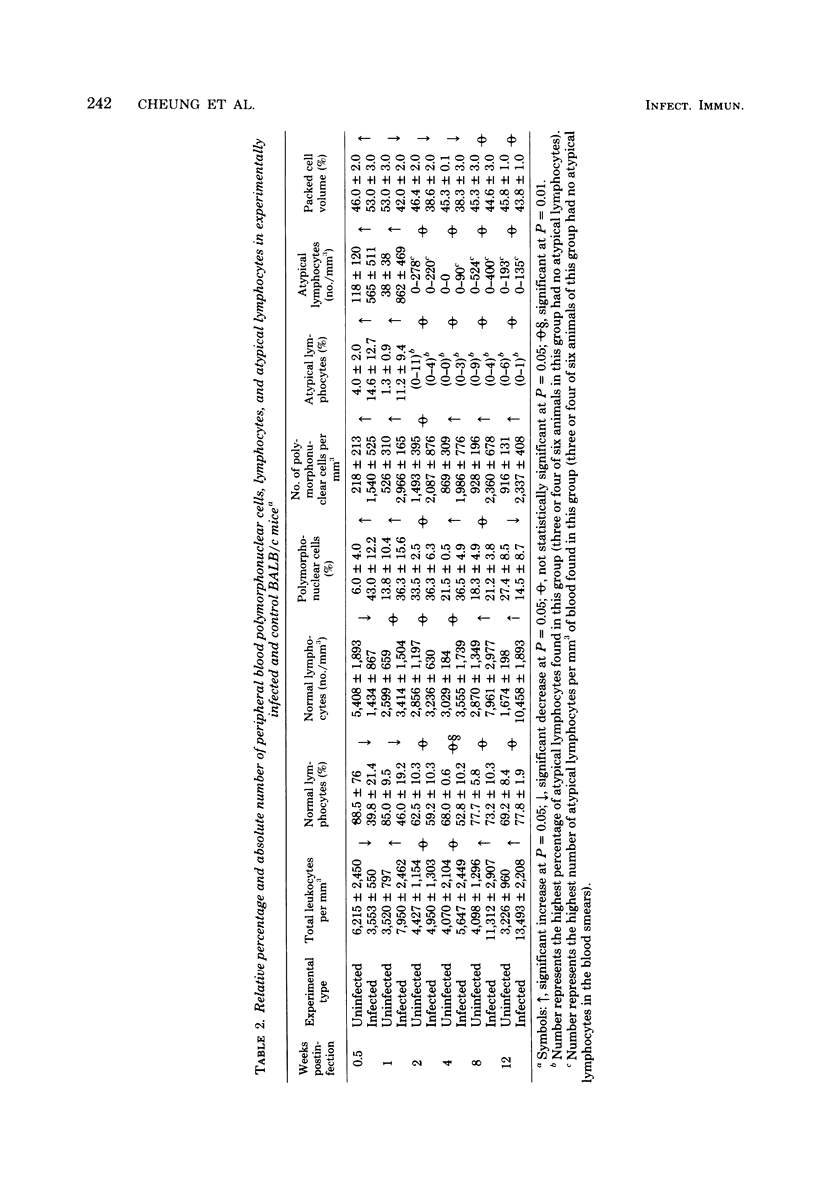
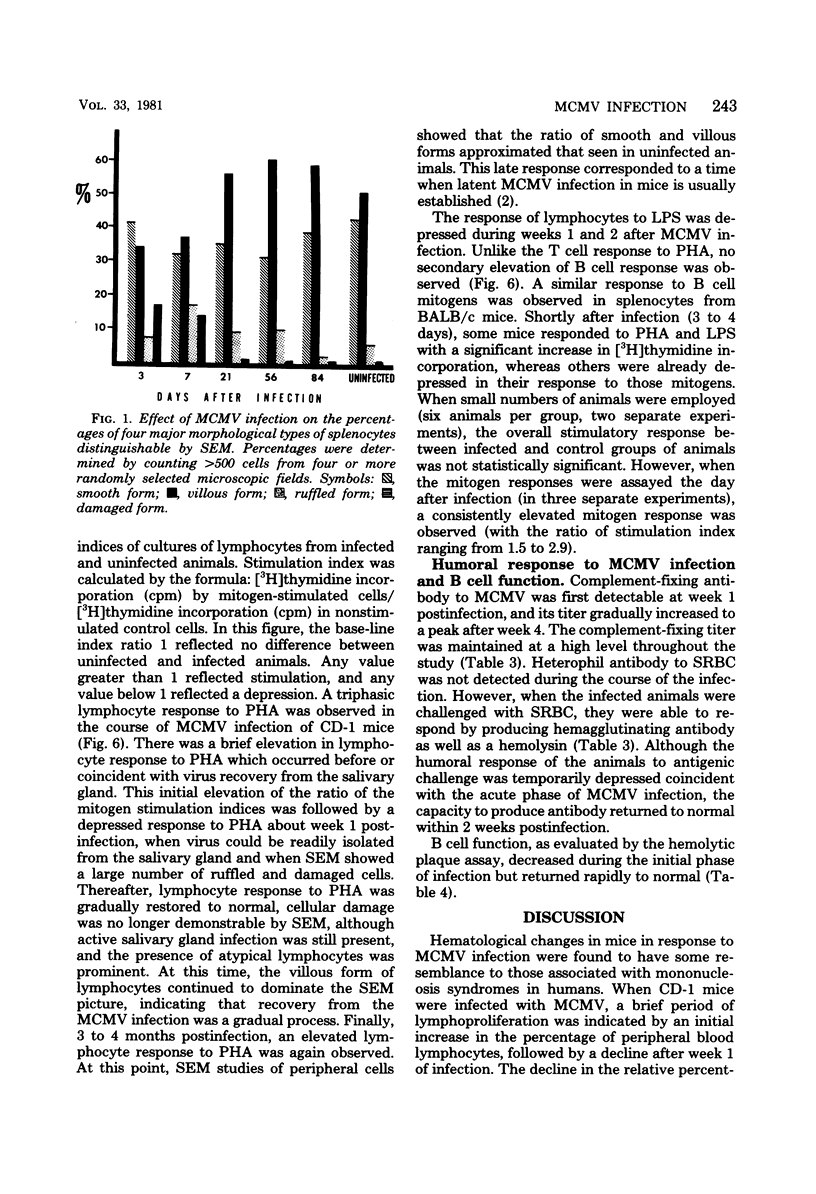
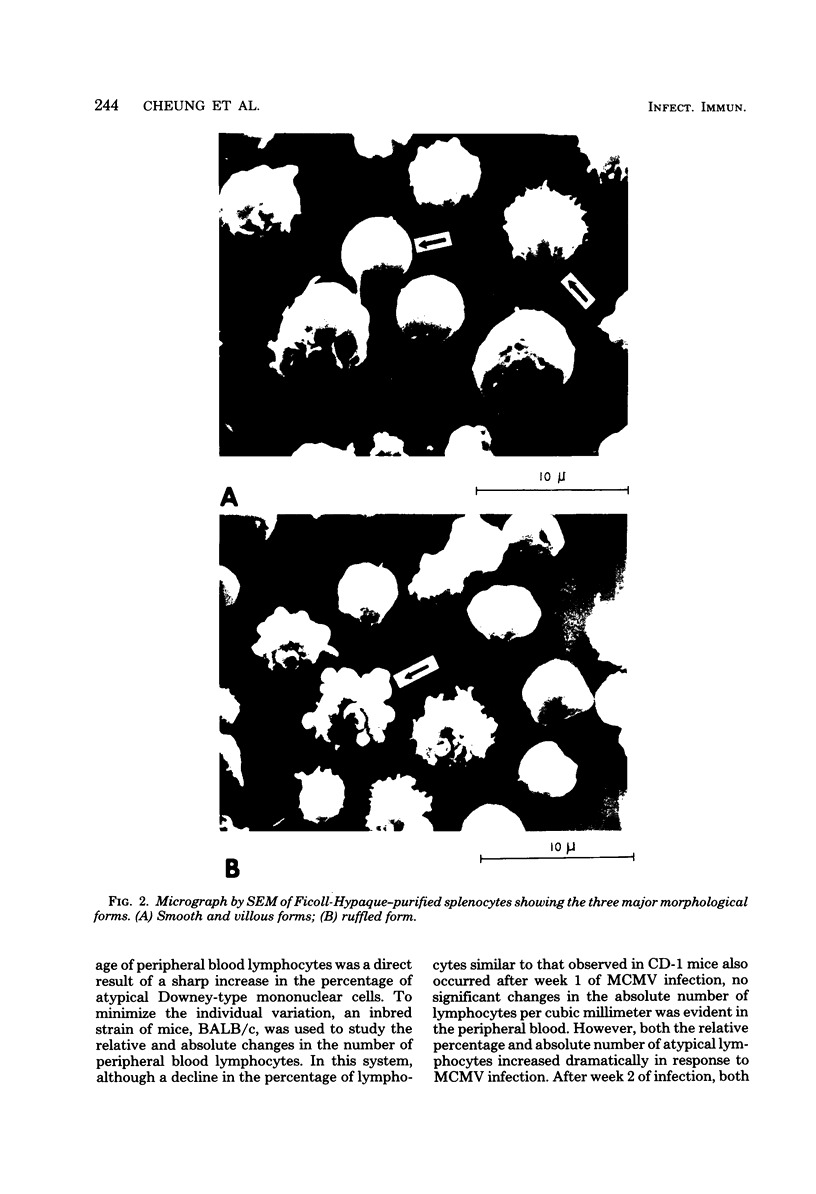
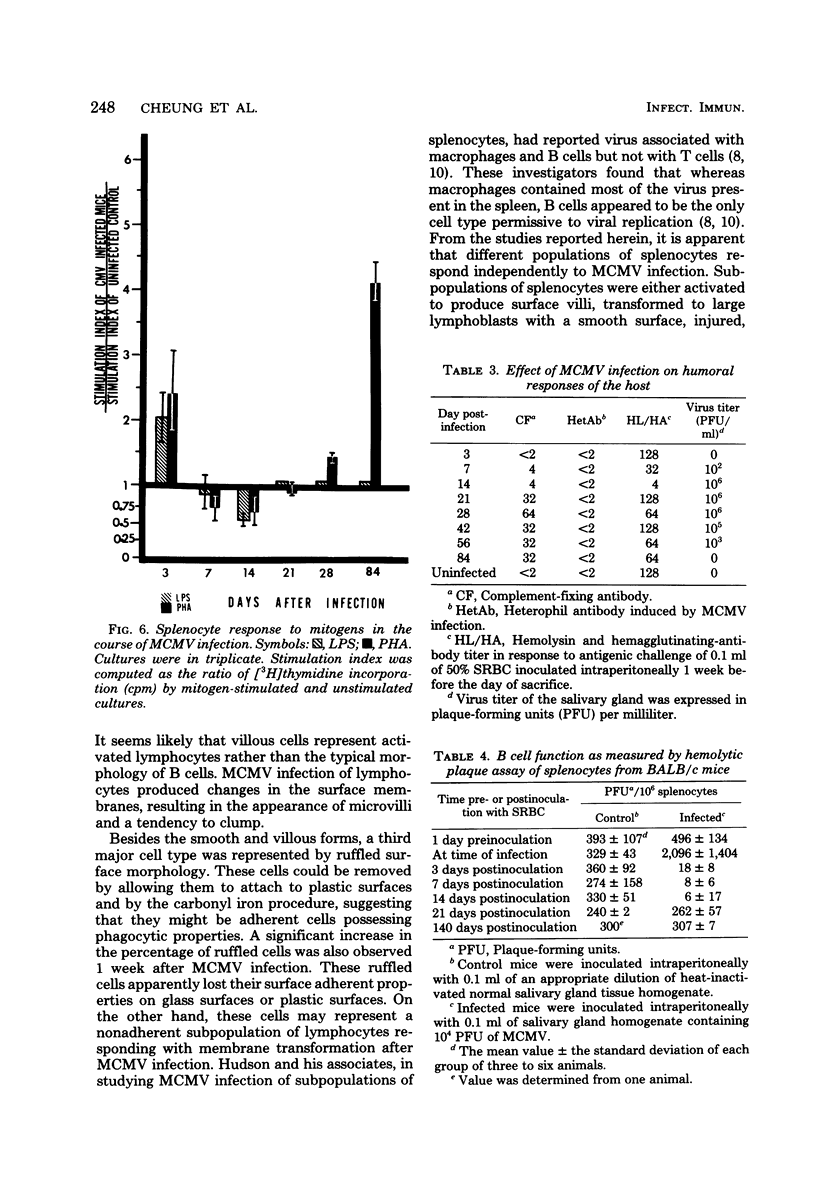
Mice were studied for 3 to 4 months after murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection. Serial hematological parameters were evaluated. It was found that MCMV infection of mice were accompanied by the appearance of many atypical lymphocytes similar to those seen in association with the hematological features of mononucleosis associated with human CMV infection. Certain functions of splenocytes were studied in infected and uninfected animals during the 4 months after MCMV infection. Three periods were identifiable by the functional response of splenocytes during the course of MCMV infection. The initial phase was characterized by an elevated response of splenocytes to a T cell mitogen and a B cell mitogen (phytohemagglutinin and lipopolysaccharide, respectively). The intermediate phase was marked by productive virus replication in the salivary gland, injury to lymphoid elements, a depressed response of splenocytes to mitogens (phytohemagglutinin and lipopolysaccharide), and decreased humoral splenocytes to phytohemagglutinin stimulation was again increased, and a nonproductive latent infection was established. Study by scanning electron microscopy of splenocytes during the course of infection revealed morphological changes which were correlated with functional alterations.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baur P. S., Thurman G. B., Goldstein A. L. Reappraisal of lymphocyte classification by means of surface morphology. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1375–1380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung K. S., Lang D. J. Detection of latent cytomegalovirus in murine salivary and prostate explant cultures and cells. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):568–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.568-574.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung K. S., Lang D. J. Transmission and activation of cytomegalovirus with blood transfusion: a mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):841–845. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criswell B. S., Rich R. R., Dardano J., Kimzey S. L. Scanning electron microscopy of normal and mitogen-stimulated mouse lymphoid cells. Cell Immunol. 1975 Oct;19(2):336–348. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90215-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. D., Fitzwilliam J. F., Cheung K. S., Shelburne J., Lang D. J., Amos D. B. Viral infection-homograft interactions in a murine model. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1303–1312. doi: 10.1172/JCI109251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B., Loh L., Misra V., Judd B., Suzuki J. Multiple interactions between murine cytomegalovirus and lymphoid cells in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):149–159. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B. The murine cytomegalovirus as a model for the study of viral pathogenesis and persistent infections. Arch Virol. 1979;62(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01314900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh L., Hudson J. B. Interaction of murine cytomegalovirus with separated populations of spleen cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):853–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.853-860.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEDEARIS D. N., Jr MOUSE CYTOMEGALOVIRUS INFECTION. 3. ATTEMPTS TO PRODUCE INTRAUTERINE INFECTIONS. Am J Hyg. 1964 Jul;80:113–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polliack A., Hämmerling U., Lampen N., de Harven E. Surface morphology of murine B and T lymphocytes: A comparative study by scanning electron microscopy. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Jan;5(1):32–39. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp C. E., Hewetson J. F. Infectious mononucleosis and the Epstein-Barr virus. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Jan;132(1):78–86. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120260080020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Farrar J. J., Dougherty S. Absolute macrophage dependency of T lymphocyte activation by mitogens. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):131–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]