Abstract
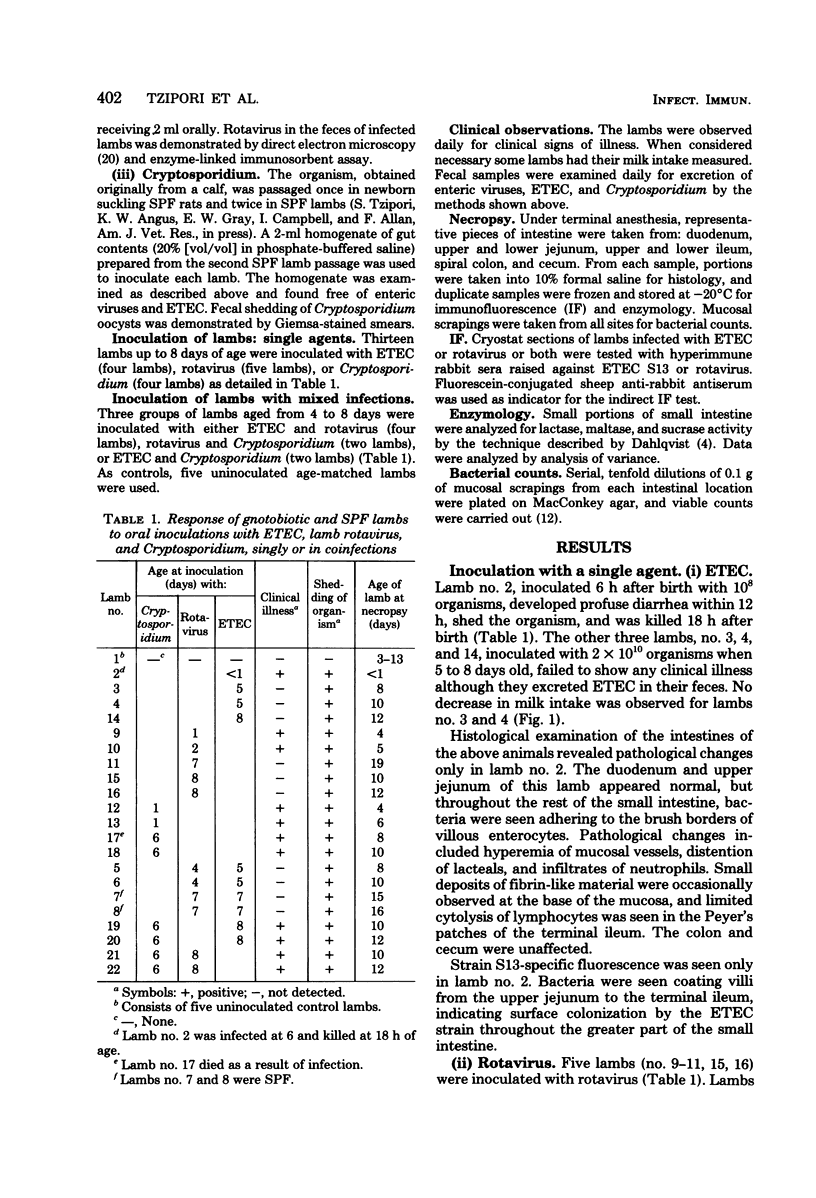
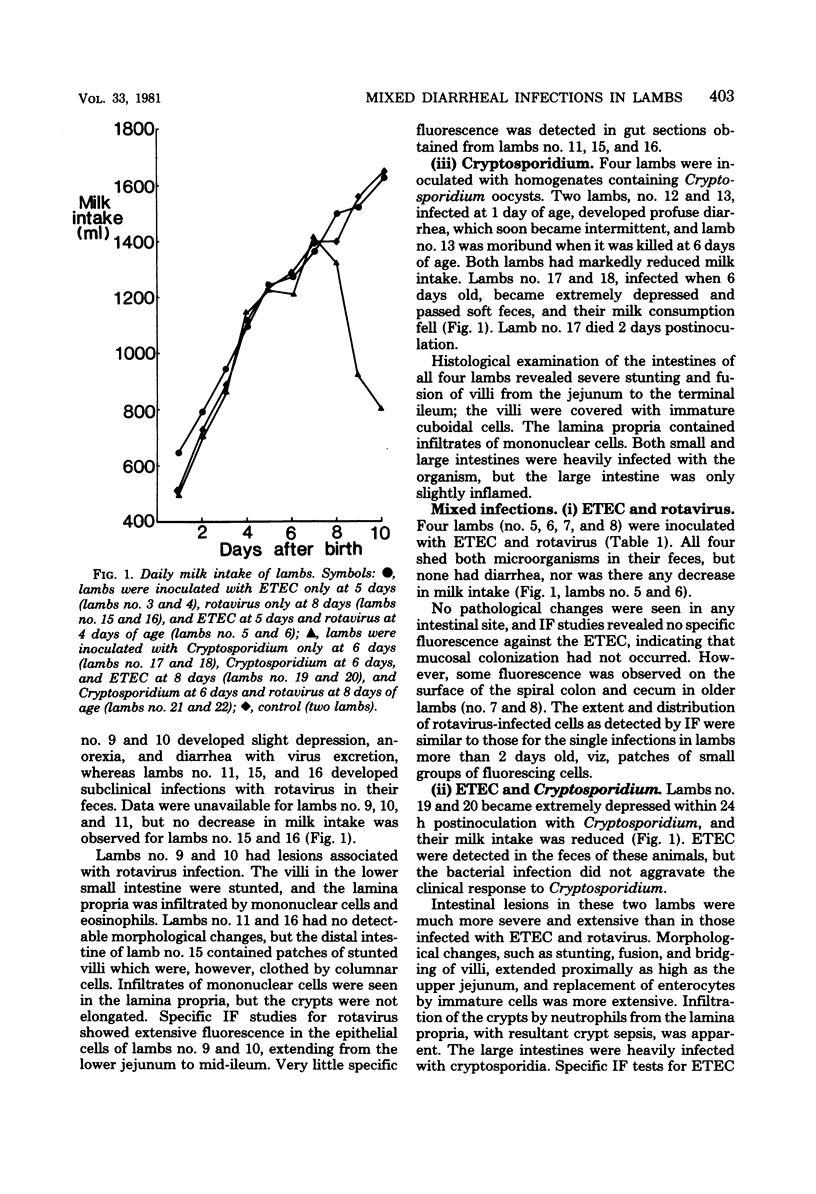
Thirteen gnotobiotic lambs, aged from a few hours to 8 days, were inoculated orally with single infections of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) (four animals), lamb rotavirus (five animals), and Cryptosporidium (four animals). Six gnotobiotic and two specific-pathogen-free lambs were co-inoculated with either rotavirus and ETEC (four animals), rotavirus and Cryptosporidium (two animals), or ETEC and Cryptosporidium (two animals). Lambs 4 days of age and older became only subclinically infected with either rotavirus, ETEC (08:K87:K99 ST+), or both enteropathogens given simultaneously. Six-day-old lambs inoculated with Cryptosporidium became extremely depressed, anorectic, and had intermittent diarrhea. There was no difference in the clinical manifestations, level of disaccharidase activity in the small intestine, or extent of histological damage between lambs inoculated with Cryptosporidium alone or together with either of the other two agents. The results indicate that under the conditions of these experiments, lambs become clinically resistant to infection with ETEC, rotavirus, or both agents together, by 4 days after birth, whereas lambs 2 days old or younger were clinically susceptible to infection by these agents. In contrast, they remained clinically susceptible to infection with Cryptosporidium up to at least 6 days of age. Cryptosporidium infections were not aggravated by coinfection with either ETEC or rotavirus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acres S. D., Laing C. J., Saunders J. R., Radostits O. M. Acute undifferentiated neonatal diarrhea in beef calves. I. Occurence and distribution of infectious agents. Can J Comp Med. 1975 Apr;39(2):116–132. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari M. M., Renshaw H. W., Gates N. L. Colibacillosis in neonatal lambs: onset of diarrheal disease and isolation and characterization of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from enteric and septicemic forms of the disease. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Jan;39(1):11–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg I. E., Peterson A. C., Freeman T. P. Ovine cryptosporidiosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Dec 15;173(12):1586–1587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubourguier H. C., Gouet P., Mandard O., Contrepois M., Bachelerie C. Scanning electron microscopy of abomasium and intestine of gnotoxenic calves infected either with rotavirus, coronarivus or enteropathogenic Escherichia coli or with rotavirus and E. coli. Ann Rech Vet. 1978;9(3):441–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouet P., Contrepois M., Dubourguier H. C., Riou Y., Scherrer R., Laporte J., Vautherot J. F., Cohen J., L'Haridon R. The experimental production of diarrhoea in colostrum deprived axenic and gnotoxenic calves with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, rotavirus, coronavirus and in a combined infection of rotavirus and E. coli. Ann Rech Vet. 1978;9(3):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Veldkamp J., Jansen W. H. Improved minca medium for the detection of K99 antigen in calf enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):676–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.676-678.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan E. F., Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S. Studies on the immunity of the calf to colibacillosis--VII: the experimental reproduction of enteric colibacillosis in colostrum-fed calves. Vet Rec. 1977 Nov 26;101(22):443–446. doi: 10.1136/vr.101.22.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., McFerran J. B., Bryson D. G., Logan E. F., Curran W. L. Studies on rotavirus infection and diarrhoea in young calves. Vet Rec. 1976 Sep 18;99(12):229–230. doi: 10.1136/vr.99.12.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Kono M., Underdahl N. R., Twiehaus M. J. Cell culture propagation of neonatal calf diarrhea (scours) virus. Can Vet J. 1971 Mar;12(3):69–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W. Pathogenesis of enteric diseases caused by Escherichia coli. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1974;18(0):179–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Huggins M. B. Experimental infection of calves, piglets and lambs with mixtures of invasive and enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Nov;12(4):507–510. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-4-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Angus K. W., Gray E. W. Rotavirus infection in lambs: pathogenesis and pathology. Arch Virol. 1977;55(4):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01315048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Gray E. W. Detection and transmission of 30 nm virus particles (astroviruses) in faeces of lambs with diarrhoea. Arch Virol. 1977;55(4):287–291. doi: 10.1007/BF01315050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Smith W., Gray E. W., Herring J. A. A rotavirus in lambs with diarrhoea. Res Vet Sci. 1976 Jan;20(1):113–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S. R., Makin T. J., Smith M. L., Krautil F. L. Clinical manifestations of diarrhea in calves infected with rotavirus and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1011–1016. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.6.1011-1016.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Angus K. W., Campbell I., Clerihew L. W. Diarrhea due to Cryptosporidium infection in artificially reared lambs. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.100-105.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



