Abstract
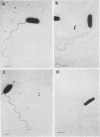
Flagella were isolated from virulent Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1, 2, and 3. Antiserum made against purified serogroups 1 flagellin agglutinated live, flagellated serogroups 1, 2, and 3 but not heat-killed or nonflagellated bacteria. A single line of identity was seen in immunodiffusion slides between the flagella isolated from the three serogroups and antibody to flagellin isolated from serogroups 1, 2, and 3. Indirect immunoperoxidase staining showed that antibody to flagellin isolated from serogroup 1 organisms reacted with flagella on serogroup 1, 2, and 3 bacteria. Indirect immunoperoxidase staining was also showed that antibody to flagellin isolated from serogroup 1 L. pneumophila did not react with the serogroup-specific cell surface antigen, thus demonstrating that the flagella- and the serogroup-specific antigen are separate antigens. The amino acid content of the flagella from the three serogroups was essentially the same, with aspartate, glutamate, alanine, and threonine comprising 41% of the total. Thirty-five percent of the amino acids were hydrophobic, and there were not detectable amounts of cysteine, tryptophan, or tyrosine.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohn W. A fixation method for improved antibody penetration in electron microscopical immunoperoxidase studies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Apr;26(4):293–297. doi: 10.1177/26.4.77869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W., Roth I. L., Callaway C. S., Bump J. L., Thomason B. M., Weaver R. E. Flagella on Legionnaires' disease bacteria: ultastructural observations. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Nov;93(5):711–714. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-5-711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W., Thomason B. M., Hébert G. A. Flagella on Legionnaires' disease bacteria in the human lung. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Nov;93(5):715–716. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-5-715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Pittman B., Harris P. P., Hebert G. A., Thomason B. M., Thacker L., Weaver R. E. Detection of Legionnaires disease bacteria by direct immunofluorescent staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):329–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.329-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott J. A., Johnson W., Helms C. M. Ultrastructural localization and protective activity of a high-molecular-weight antigen isolated from Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):822–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.822-824.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farshy C. E., Klein G. C., Feeley J. C. Detection of antibodies to legionnaires disease organism by microagglutination and micro-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):327–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.327-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Weaver R. E., Mackel D. C., Smith H. W. Primary isolation media for Legionnaires disease bacterium. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.320-325.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Genetics and chemistry of bacterial flagella. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Dec;33(4):454–475. doi: 10.1128/br.33.4.454-475.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W., Elliott J. A., Helms C. M., Renner E. D. A high molecular weight antigen in Legionnaires' disease bacterium: isolation and partial characterization. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):638–641. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W., Pesanti E., Elliott J. Serospecificity and opsonic activity of antisera to Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):698–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.698-704.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Chang Y. H. Hydrolysis of proteins with p-toluenesulfonic acid. Determination of tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCDONOUGH M. W. AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF ANTIGENICALLY DISTINCT SALMONELLA FLAGELLAR PROTEINS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:342–355. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J., Brown D. M., Glazer A. N. The formation of bacterial flagella. 3. Characterization of the subunits of the flagella of Bacillus subtilis and Spirillum serpens. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W., Sommers H. M., Fikes B. J., Sasseville K. R., Yungbluth M. M., Wolf J. S. Legionella pneumophila serogroup six: isolation from cases of legionellosis, identification by immunofluorescence staining, and immunological response to infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.395-401.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Lattimer G. L., Page L. A., Fiset P. Legionnaires' disease: antigenic peculiarities, strain differences, and antibiotic sensitivities of the agent. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):260–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers F. G., Greaves P. W., Macrae A. D. Flagella and fimbriae on Legionella organisms. Lancet. 1979 Oct 6;2(8145):753–754. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90691-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers F. G., Greaves P. W., Macrae A. D., Lewis M. J. Electron microscopic evidence of flagella and pili on Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1184–1188. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomason B. M., Chandler F. W., Hollis D. G. Flagella on Legionnaires' disease bacteria: an interim report. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):224–226. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINTRAUB M., RAYMOND S. ANTISERUMS PREPARED WITH ACRYLAMIDE GEL USED AS ADJUVANT. Science. 1963 Dec 27;142(3600):1677–1678. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3600.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Fikes B. J., Cruce D. D. Indirect immunofluorescence test for serodiagnosis of Legionnaires disease: evidence for serogroup diversity of Legionnaires disease bacterial antigens and for multiple specificity of human antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):379–383. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.379-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Schalla W. O., Arko R. J., Bullard J. C., Feeley J. C. Immunochemical, serologic, and immunologic properties of major antigens isolated from the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Observations bearing on the feasibility of a vaccine. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):634–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]