Abstract
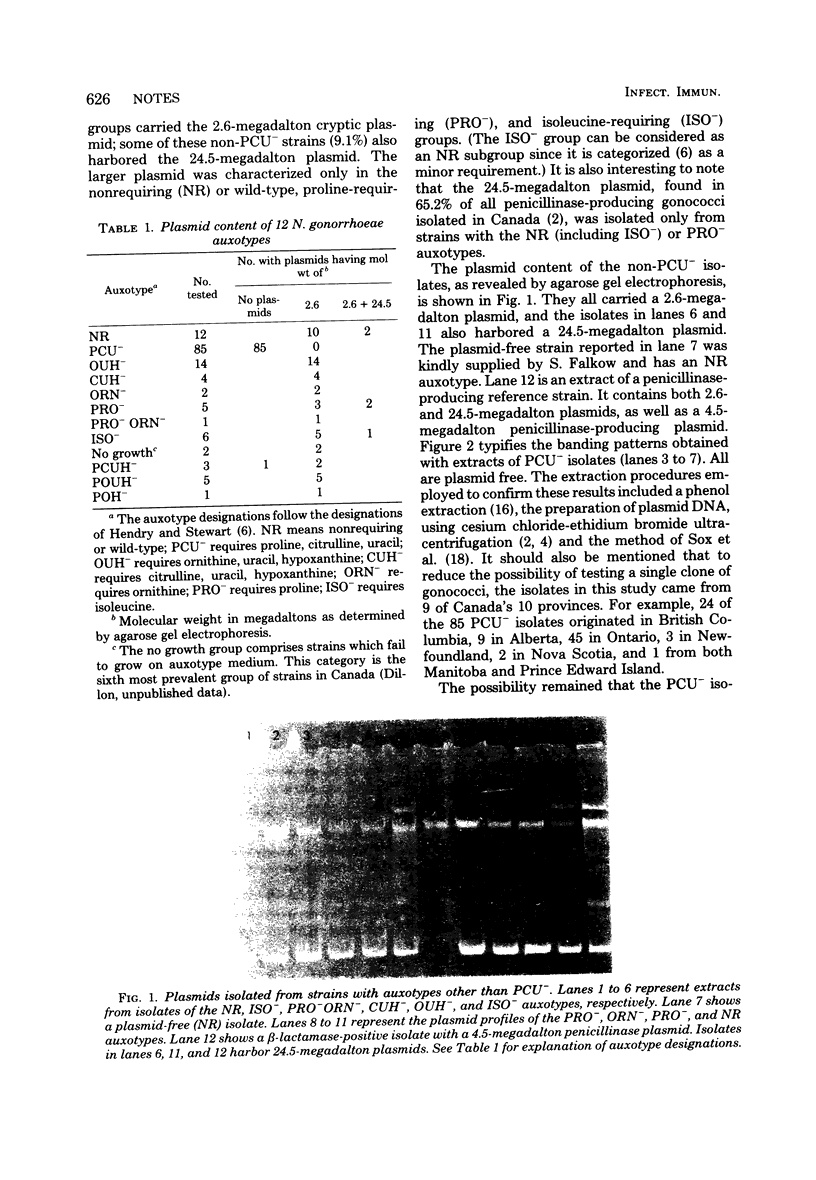
One hundred and forty strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, representing 12 different auxotype groups, were examined for differences in plasmid content. Most auxotype groups harbored a phenotypically cryptic 2,6-megadalton plasmid; a few groups also carried a 24.5-megadalton plasmid which has been previously characterized as a transfer plasmid. However, isolates of the proline-, citrulline-, and uracil-requiring (PCU-) auxotype were consistently free of plasmids. The correlation between auxotype and plasmid content is especially significant since, in Canada, PCU- isolates have the second highest prevalence of all auxotypes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davies J. K., Normark S. A relationship between plasmid structure, structural lability, and sensitivity to site-specific endonucleases in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):251–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00267436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon J. R., Duck P., Thomas D. Y. Molecular and phenotypic characterization of penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae from Canadian sources. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):952–957. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelkirk P. G., Schoenhard D. E. Physical evidence of a plasmid in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):197–200. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in tissue cultures: cellular attachment, entry, and survival. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1141–1146. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1141-1146.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. S., Foster G. C. Electrophoretic comparison of endonuclease-digested plasmids from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1297–1304. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1297-1304.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry A. T., Stewart I. O. Auxanographic grouping and typing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Apr;25(4):512–521. doi: 10.1139/m79-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W., Holmes K. K., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):712–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.712-717.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norlander L., Davies J., Normark S. Genetic exchange mechanisms in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):756–761. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.756-761.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Falkow S. Conjugal transfer of R plasmids in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1977 Apr 14;266(5603):630–631. doi: 10.1038/266630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Piot P., Falkow S. The ecology of gonococcal plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):491–494. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard H. M., Polisky B. Measurement of Plasmid copy number. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:503–513. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox T. E., Mohammed W., Blackman E., Biswas G., Sparling P. F. Conjugative plasmids in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.278-286.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiffler P. W., Lerner S. A., Bohnhoff M., Morello J. A. Plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid in clinical isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1293–1300. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1293-1300.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]