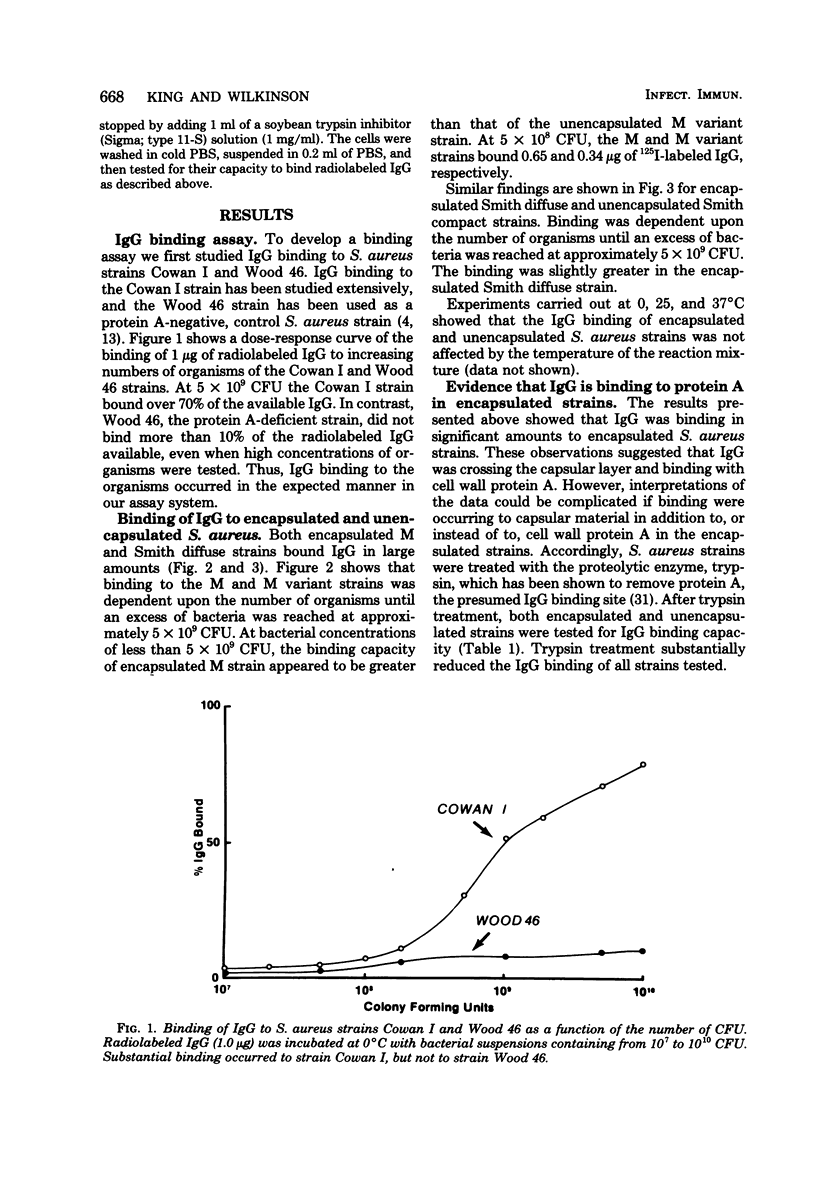
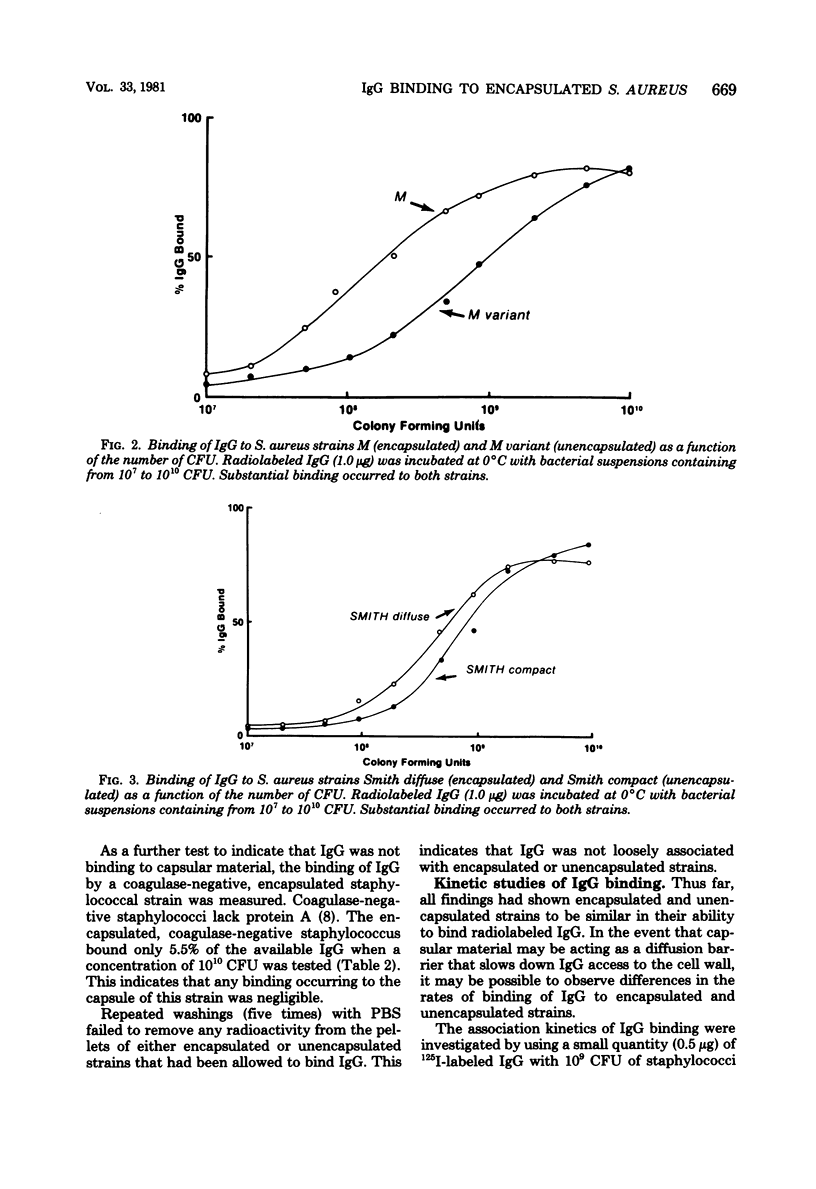
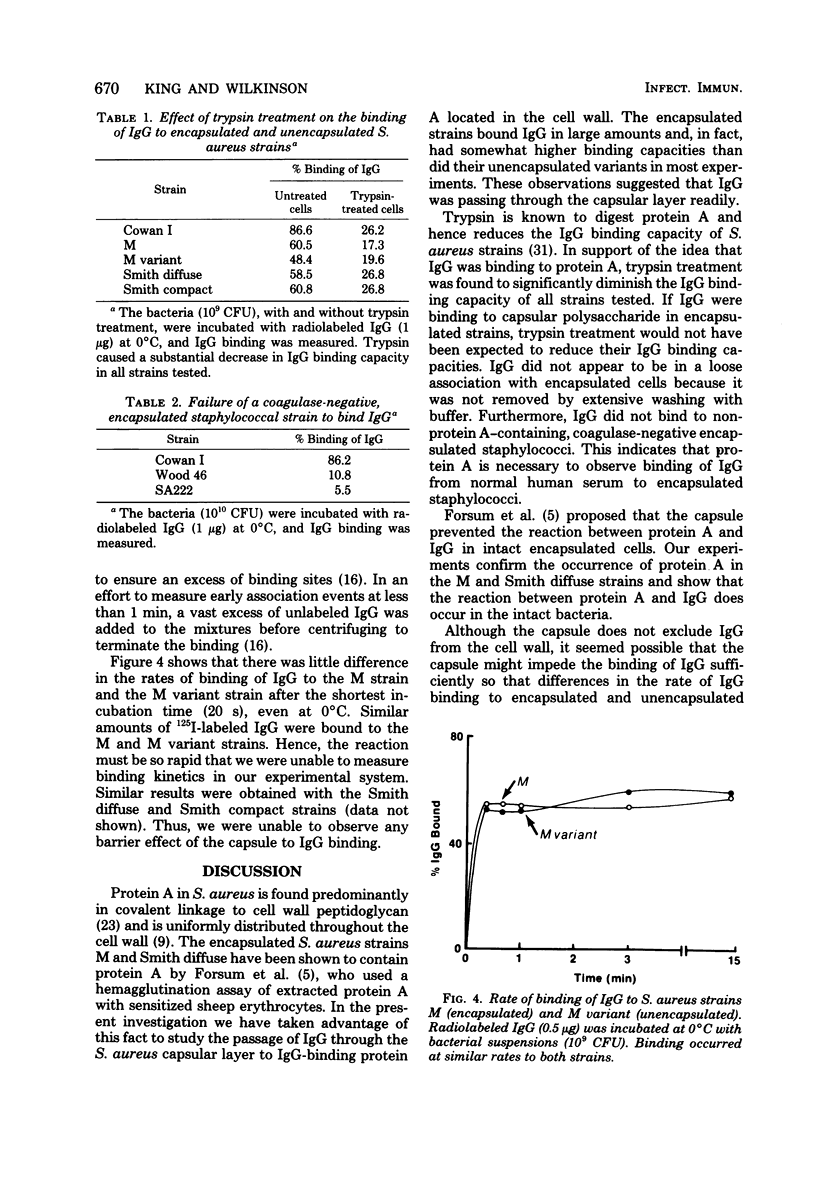
Abstract
Recent studies of the mechanism of resistance to phagocytosis in encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus have suggested that the capsule is readily penetrated by high-molecular-weight proteins such as antibodies and complement components. S. aureus strains contain a cell wall protein, protein A, that reacts with the Fc portion of immunoglobulins. The binding of immunoglobulin G (IgG) to encapsulated and unencapsulated S. aureus strains has been studied to assess the penetrability of the S. aureus capsule by IgG. Encapsulated S. aureus strains M and Smith diffuse bound large amounts of human IgG which were comparable to amounts bound by the unencapsulated strains Cowan I, M variant, and Smith compact. Trypsin treatment of bacteria reduced their ability to bind IgG. Bound IgG was not removed by extensive washing of bacteria with buffer. A non-protein A-containing, coagulase-negative, encapsulated staphylococcal strain did not bind IgG. These observations suggest that IgG is binding to cell wall protein A in encapsulated S. aureus. No differences in the rates of IgG binding by encapsulated and unencapsulated S. aureus strains were observed. It is concluded that the S. aureus capsule is freely permeable to IgG. This is of importance in considerations of the mechanisms of resistance to phagocytosis and antigen masking in encapsulated microorganisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K., STEERE R. L. Restricted diffusion of macromolecules through agar-gel membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 7;59:137–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90704-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEPPELLINI R., LANDY M. Suppression of blood group agglutinability of human erythrocytes by certain bacterial polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1963 Mar 1;117:321–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsum U., Forsgren A., Hjelm E. Role of protein A in the serum-soft agar technique. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):583–586. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.583-586.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Howard C. J. The sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli related to their K antigens. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):331–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramoli J. L., Wilkinson B. J. Characterization and identification of coagulase-negative, heat-stable deoxyribonuclease-positive staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Apr;105(2):275–285. doi: 10.1099/00221287-105-2-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen A, Helgeland S., Grov A. Localization of antigens in thin sections of bacteria by the immuno-peroxidase technique. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Apr;83(2):79–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Influence of the Escherichia coli capsule on complement fixation and on phagocytosis and killing by human phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):82–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI109663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King B. F., Biel M. L., Wilkinson B. J. Facile penetration of the Staphylococcus aureus capsule by lysostaphin. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):892–896. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.892-896.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Frommel D. Definition of staphylococcal protein A reactivity for human immunoglobulin G fragments. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jan;7(1):124–127. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Quantitation of staphylococcal protein A: Determination of equilibrium constant and number of protein A residues on bacteria. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGaw T. G., Kozel T. R. Opsonization of Cryptococcus neoformans by human immunoglobulin G: masking of immunoglobulin G by cryptococcal polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):262–267. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.262-267.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melly M. A., Duke L. J., Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Biological properties of the encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.389-397.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Demonstration of specific binding sites for human serum albumin in group C and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.6-14.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORSKOV I., ORSKOV F., JANN B., JANN K. ACIDIC POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGENS OF A NEW TYPE FROM E. COLI CAPSULES. Nature. 1963 Oct 12;200:144–146. doi: 10.1038/200144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Kim Y., Wilkinson B. J., Schmeling D., Michael A. F., Quie P. G. Dichotomy between opsonization and serum complement activation by encapsulated staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):770–775. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.770-775.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Influence of encapsulation on staphylococcal opsonization and phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):943–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.943-949.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R., Reid K. B. Activation of the complement system by antibody-antigen complexes: the classical pathway. Adv Protein Chem. 1979;33:1–71. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60458-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scribner D. J., Fahrney D. Neutrophil receptors for IgG and complement: their roles in the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):892–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Movitz J., Johansson I. B., Hjelm H. Localization of protein A in the bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct 17;30(1):190–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Bessler W., Fehmel F., Freund-Mölbert E. Bacteriophage particles with endo-glycosidase activity. J Virol. 1971 Sep;8(3):343–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.3.343-346.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Field R. J., Gitlin J. D., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. The opsonic fragment of the third component of human complement (C3). J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1329–1347. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W. Bacterial exopolysaccharides. Adv Microb Physiol. 1972;8:143–213. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolan D. R., Lambert J. M., Boileau G., Fanning T. G., Kenny J. W., Vassos A., Traut R. R. Radioiodination of microgram quantities of ribosomal proteins from polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 15;103(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., van Dijk W. C., van Erne M. E., Peters R., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Quantitation of the third component of human complement attached to the surface of opsonized bacteria: opsonin-deficient sera and phagocytosis-resistant strains. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):808–814. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.808-814.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Human polymorphonuclear leucocyte receptors for staphylococcal opsonins. Immunology. 1977 Aug;33(2):231–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virgilio A R., González P C., Munoz S N., Mendoza G S. Ability of Staphylococcus aureus Cells to Bind Normal Human Immunoglobulin G. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):342–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.342-344.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Holmes K. M. Staphylococcus aureus cell surface: capsule as a barrier to bacteriophage adsorption. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):549–552. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.549-552.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G., Michael A. F. Activation of complement by cell surface components of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):388–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.388-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Cryptic peptidoglycan and the antiphagocytic effect of the Staphylococcus aureus capsule: model for the antiphagocytic effect of bacterial cell surface polymers. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):502–508. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.502-508.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Sisson S. P., Kim Y., Peterson P. K. Localization of the third component of complement on the cell wall of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M: implications for the mechanism of resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1159-1163.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Abramovitz A. S., Tomasz A. Activation of C3 via the alternative complement pathway results in fixation of C3b to the pneumococcal cell wall. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2502–2506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Park J. T. Chemical characterization of a new surface antigenic polysaccharide from a mutant of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):874–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.874-884.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



