Abstract
Background
The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade is an evolutionarily ancient mechanism of signal transduction found in eukaryotic cells. In plants, MAPK cascades are associated with responses to various abiotic and biotic stresses such as plant pathogens. MAPK cascades function through sequential phosphorylation: MAPK kinase kinases (MAPKKKs) phosphorylate MAPK kinases (MAPKKs), and phosphorylated MAPKKs phosphorylate MAPKs. Of these three types of kinase, the MAPKKKs exhibit the most divergence in the plant genome. Their great diversity is assumed to allow MAPKKKs to regulate many specific signaling pathways in plants despite the relatively limited number of MAPKKs and MAPKs. Although some plant MAPKKKs, including the MAPKKKα of Nicotiana benthamiana (NbMAPKKKα), are known to play crucial roles in plant defense responses, the functional relationship among MAPKKK genes is poorly understood. Here, we performed a comparative functional analysis of MAPKKKs to investigate the signaling pathway leading to the defense response.
Results
We cloned three novel MAPKKK genes from N. benthamiana: NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKγ, and NbMAPKKKε2. Transient overexpression of full-length NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ or their kinase domains in N. benthamiana leaves induced hypersensitive response (HR)-like cell death associated with hydrogen peroxide production. This activity was dependent on the kinase activity of the overexpressed MAPKKK. In addition, virus-induced silencing of NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ expression significantly suppressed the induction of programmed cell death (PCD) by viral infection. Furthermore, in epistasis analysis of the functional relationships among NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKγ, and NbMAPKKKα (previously shown to be involved in plant defense responses) conducted by combining transient overexpression analysis and virus-induced gene silencing, silencing of NbMAPKKKα suppressed cell death induced by the overexpression of the NbMAPKKKβ kinase domain or of NbMAPKKKγ, but silencing of NbMAPKKKβ failed to suppress cell death induced by the overexpression of NbMAPKKKα or NbMAPKKKγ. Silencing of NbMAPKKKγ suppressed cell death induced by the NbMAPKKKβ kinase domain but not that induced by NbMAPKKKα.
Conclusions
These results demonstrate that in addition to NbMAPKKKα, NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ also function as positive regulators of PCD. Furthermore, these three MAPKKKs form a linear signaling pathway leading to PCD; this pathway proceeds from NbMAPKKKβ to NbMAPKKKγ to NbMAPKKKα.
Background
Because plants lack an adaptive immune system, appropriate perceptions and responses of individual cells to various environmental stimuli, such as the biotic stress caused by phytopathogenic microorganisms, are critically important. The plant defense response against biotic stress is triggered by the recognition of conserved pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or of pathogen strain-specific factors known as elicitors or effectors [1]. The response triggered by PAMPs is known as the basal defense response, whereas that triggered by specific elicitors is known as the hypersensitive response (HR). In the latter, an effector is recognized by a corresponding plant resistance (R) protein. The HR is frequently accompanied by programmed cell death (PCD), which plays a particularly important role in the defense against biotrophic pathogens but is also an essential function in normal plant development and differentiation [2]. Although many plant components required for the PCD-associated HR have been identified, the entire signaling pathway leading to PCD has not been elucidated.
The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade is a highly evolutionarily conserved signal transduction mechanism found in eukaryotic cells. Subsequent to activation of the cascade by various extracellular stimuli, the signal is transduced intracellularly by sequential phosphorylation. In plants, MAPK cascades are associated with developmental and hormonal responses and with stress responses to abiotic and biotic factors [3]. A MAPK cascade consists of three functionally linked protein kinases: a MAPK is phosphorylated and activated by a MAPK kinase (MAPKK), which is in turn activated by an upstream MAPK kinase kinase (MAPKKK). Typical MAPK substrates are cytoplasmic or nuclear proteins, such as transcription factors [3]. MAPKKKs are the most divergent of these three types of kinases in plants; the Arabidopsis thaliana genome contains approximately 60 MAPKKKs, 10 MAPKKs, and 20 MAPKs [4].
Based on phylogenetic analysis of the amino acid sequences of their catalytic kinase domains, plant MAPKKKs have been classified into three groups: A, B, and C [4]. Group A contains many MAPKKKs involved in PCD and stress and defense responses; e.g., A. thaliana AtMEKK1 is involved in the signaling pathway of basal defense induced by PAMPs [5], and Medicago sativa MsOMTK1 [6] is involved in that of oxidative stress-induced cell death. Group A also includes MAPKKKs that have important functions in HR induction. Silencing of the genes encoding Nicotiana tabacum NPK1 (NtNPK1) and Nicotiana benthamiana MAPKKKα (NbMAPKKKα) suppresses the N gene-mediated HR induced by the helicase domain of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) replicase and Pto-mediated HR induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst) effector avrPto, respectively [7,8]. Recently, N. benthamiana NbMAPKKKε and its tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) ortholog SlMAPKKKε have been implicated in PCD induction in the HR against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens [9]. In addition, silencing of the genes encoding the MAPKK MEK2 and the MAPK SIPK, both of which act downstream of NbMAPKKKα, also attenuates the N gene-mediated HR against TMV [10]. Conversely, silencing of the tomato orthologs of MAPKK MEK1 and MAPK NTF6, both of whose tobacco orthologs act downstream of NtNPK1in tobacco, leads to loss of the Pto-mediated HR in tomato [11]. Therefore, the NtNPK1- and NbMAPKKKα-initiated MAPK cascades are essential for both the N gene-mediated and the Pto-mediated HR, suggesting that at least two distinct MAPK cascades are involved in the regulation of a single HR event [8]. Furthermore, it is now becoming apparent that two distinct MAPK cascades are involved in non-HR environmental responses [12].
Plants generally appear to use the same MAPKK/MAPK sets in different responses to environmental stimuli. The A. thaliana MAPKKs AtMKK4 and AtMKK5 and/or their downstream component MPK6 are involved not only in the signaling pathway for basal defense downstream of AtMEKK1 but also in ethylene production and stomata formation [5,13,14]. Given the relatively limited number of MAPKKs and MAPKs in plants, the diversity of these responses (functions) is assumed to be possible due to the great diversity of MAPKKKs [15,16]. Therefore, comparative functional analysis among MAPKKKs is needed to reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying a variety of responses to environmental stresses.
We previously showed that systemic necrosis, the disease symptom caused by plantago asiatica mosaic virus Li1 (PlAMV-Li1), was accompanied by resistance traits similar to HR. Using tobacco rattle virus (TRV)-based virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) [17], we demonstrated that NbSGT1 and NbRAR1, which are important in the HR, and the MAPK cascade including NbMAPKKKα/NbMEK2, are essential for the induction of PCD-associated systemic necrosis induced by PlAMV-Li1 [18,19]. This result and those described above led us to hypothesize that other MAPKKK genes in addition to NbMAPKKKα are involved in the systemic necrosis induced by PlAMV-Li1.
In the present study, we isolated three novel group A MAPKKK genes from N. benthamiana, a model plant of the family Solanaceae, using an expressed sequence-tag (EST) database. The three cloned genes were designated NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKγ, and NbMAPKKKε2. Further study revealed that NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ are positive regulators of PCD. In addition, the results of epistasis analysis performed using VIGS and agroinfiltration suggest that two of these MAPKKKs (NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ), together with NbMAPKKKα, comprise a linear signaling pathway important in the induction of PCD.
Results
Cloning of three novel group A MAPKKK genes from Nicotiana benthamiana
To conduct a comparative analysis of the roles of MAPKKK genes in defense responses, we first sought to clone N. benthamiana MAPKKK genes belonging to group A. Group A includes four subgroups, A1–A4, and contains many genes involved in plant defense responses. To obtain one N. benthamiana MAPKKK gene homolog from each group A subgroup, we selected the following: the Arabidopsis MAPKKK genes AtMEKK1[20], AtMAPKKKγ, and AtMAPKKKε1[21,22] as representatives of the A1, A2, and A4 subgroups, respectively. For the A3 subgroup, which includes NtNPK1 [23] and AtANP1, we were able to amplify N. benthamiana cDNA fragments using NtNPK1-specific primers; the amplified gene turned out to be 98.0% identical in nucleotide sequence to that encoding the NtNPK1 kinase domain, which has been well characterized for its role in defense responses [7]. Therefore, the A3 subgroup was excluded from further study.
Using the nucleotide sequences encoding the highly conserved kinase domains of AtMEKK1 [19], AtMAPKKKγ, and AtMAPKKKε1 as queries for BLAST searches against the N. benthamiana, N. tabacum, and Solanum lycopersicum EST databases, we obtained three EST sequences: N. benthamiana TC15397, N. tabacum BP133312, and S. lycopersicum BI931567, respectively. Based on these sequences, we designed specific primers to isolate full-length N. benthamiana MAPKKK cDNA clones, as described in the Materials and Methods. The cloned N. benthamiana MAPKKK genes are predicted to encode proteins with highly conserved kinase domains and more divergence in other regions, a general feature of plant MAPKKK genes [4].
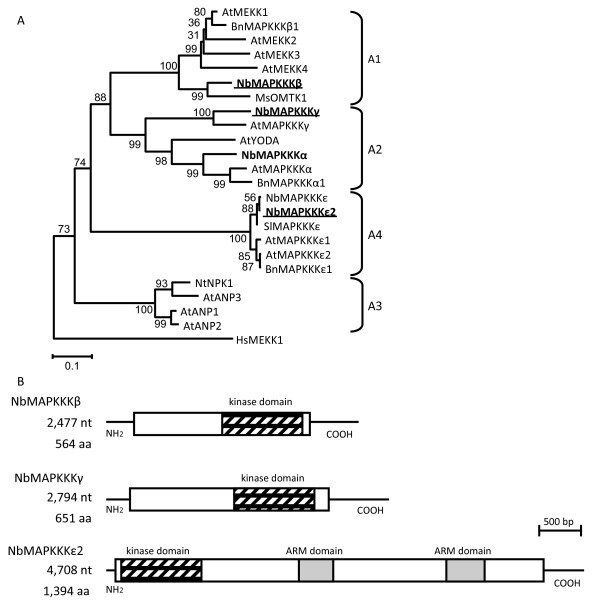
Next, we used the amino acid sequences of the kinase domains of our newly cloned MAPKKKs and those of other previously identified MAPKKKs to construct a phylogenetic tree (Figure 1A). Our newly cloned MAPKKK genes were tentatively designated after the name of the most closely related genes in the phylogenetic tree. Thus, our A2 MAPKKK homolog was designated NbMAPKKKγ after A. thaliana AtMAPKKKγ. At a late phase of this study, an A4 MAPKKK homolog, N. benthamiana NbMAPKKKε, was reported [9]. Although our A4 homolog shares high sequence similarity with NbMAPKKKε, the genes were not identical (96.6% or 95.0% identity at the nucleotide or amino acid level, respectively) and differed in length. Because these results indicated that A4 MAPKKK homologs in N. benthamiana consisted of at least two genes, our A4 homolog was designated NbMAPKKKε2 after NbMAPKKKε. In fact, from the recently released N. benthamiana draft genome sequence (http://solgenomics.net/), only two contigs that show high sequence homology (about ~90%) with NbMAPKKKε2 were retrieved and each of these sequences corresponded to NbMAPKKKε2 and NbMAPKKKε, respectively. Although our A1 MAPKKK homolog was most closely related to MsOMTK1, which was designated after the functional features of its gene products, designating this gene “NbOMTK1” was apparently incorrect, as we do not know if our A1 homologous gene product and MsOMTK1 have a similar function. The next most closely related genes were AtMEKK1 and Brassica napus BnMAPKKKβ1. Therefore, our A1 homolog was designated NbMAPKKKβ after BnMAPKKKβ1, a gene of the A1 subgroup, in accordance with other newly cloned genes NbMAPKKKγ and NbMAPKKKε2. The NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKγ, and NbMAPKKKε2 cDNA sequences determined in this study were deposited in the DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ) under the accession numbers AB649283, AB649284, and AB649285, respectively.
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of plant MAPKKK genes and structural features of novel N. benthamiana MAPKKK genes. A) Phylogenetic tree for the kinase domain-encoding regions of group A MAPKKK genes. Numbers represent bootstrap scores. Names of genes used in this study are shown in boldface. Names of the three novel MAPKKK genes are underlined. B) Diagram of the domain structures of the three novel MAPKKK genes. ORFs are indicated by boxes. The 5′- and 3′-untranslated regions (UTRs) are shown as horizontal lines at the left and right, respectively, of the boxes. Shaded boxes and gray boxes indicate kinase domains and ARM domains, respectively. ORFs and UTRs are drawn to the same scale.
The domain structures of the three novel MAPKKK genes are shown in Figure 1B. The NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKγ, and NbMAPKKKε2 cDNA are 2477, 2794, and 4708 bp in length, respectively, and are respectively predicted to encode proteins of 564, 651, and 1395 amino acids. Kinase domains are found in the C-terminal regions of NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ and the N-terminal region of NbMAPKKKε2. The C-terminal region of NbMAPKKKε2 contains two ARM (armadillo/β-catenin-like repeat) domains. The domain structures of these proteins are similar to those of their respective A. thaliana homologs.
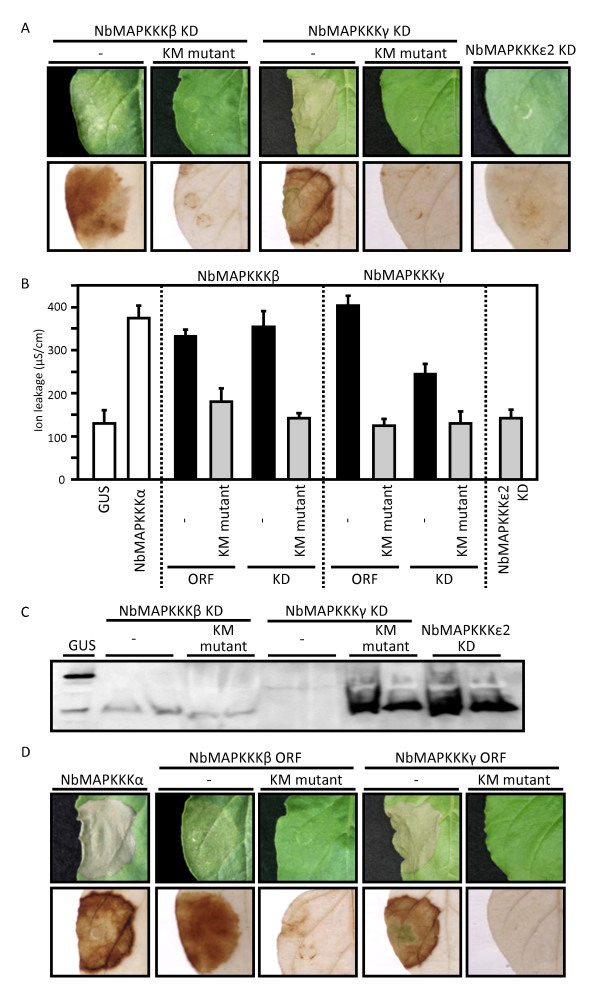
Overexpression of the NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ kinase domains, but not the NbMAPKKKε2 kinase domain, causes cell death
Overexpression of the kinase domain of the tomato homolog of NbMAPKKKα, SlMAPKKKα, in N. benthamiana leaves by agroinfiltration has been reported to induce pathogen-independent cell death [8]. To investigate whether our three newly identified MAPKKKs also possessed cell death-inducing activity, we performed transient overexpression analysis of each kinase domain using agroinfiltration. The transient overexpression of the kinase domains of NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ induced pathogen-independent cell death in the infiltrated area (Figure 2A). In the infiltrated areas, cell death was associated with significant hydrogen peroxide production, which is detected by a characteristic brown color that emerges upon 3,3'-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining. These results were confirmed by measuring the extent of cell death using an ion leakage assay (Figure 2B), which showed significantly increased ion leakage in the NbMAPKKKβ- and NbMAPKKKγ-overexpressing areas. No significant difference in the level of ion leakage was observed for NbMAPKKKβ vs. NbMAPKKKγ. In contrast, overexpression of the kinase domain of NbMAPKKKε2 failed to induce cell death or hydrogen peroxide production and failed to increase the level of ion leakage. Western blot analysis using anti-Myc monoclonal antibody (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) was performed to assess the expression levels of these kinase domains (Figure 2C). Specific signals of NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKε2 kinase domains were detected, but no accumulation of NbMAPKKKγ kinase domain was found. However, we suppose that the NbMAPKKKγ kinase domain was accurately expressed, even at very low levels, because its overexpression rapidly induced cell death. Western blot analysis also showed that the accumulated expression level of NbMAPKKKε2 kinase domain, whose overexpression did not induce cell death, was much greater than the expression levels of the NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ kinase domains. Because these results indicated that NbMAPKKKε2 is not involved in the induction of pathogen-independent cell death, we excluded NbMAPKKKε2 from further analysis.
Figure 2.
Overexpression of NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ induces pathogen-independent cell death in N. benthamiana leaves. N. benthamiana leaves were infiltrated with Agrobacterium strains carrying pEarleyGate203 vector [32] derivatives harboring the coding sequences for mutant or full-length MAPKKKs. All experiments, except that shown in Figure 4, were repeated at least three times with similar results. A) Symptoms of infiltrated N. benthamiana leaf areas overexpressing the indicated MAPKKK kinase domain (KDs) or ATP-binding site-deficient (K → M) KD mutants. Images of the same leaves after DAB staining are shown in the lower panels. DAB staining to detect hydrogen peroxide production was performed as previously described [18]. Pictures were taken 5 days post-infiltration (dpi). Each protein was transiently co-expressed with silencing suppressor p19. Agrobacterium cultures were grown to a turbidity (OD600) of 0.5 for use in agroinfiltration. B) Ion leakage in the infiltrated leaf areas overexpressing wild-type or K → M mutant NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ or their wild-type or K → M mutant KDs or NbMAPKKKε2 KD. GUS and NbMAPKKKα were used as internal controls. The ion leakage assay was performed as previously described [18]. Data shown represent means ± standard deviation of at least three independent plants. C) Western blot analysis of Myc-tagged NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ KDs or their K → M mutants or NbMAPKKKε2 KD. Myc-tagged GUS was used as an internal control. Total proteins were extracted from each gene-infiltrated area at 5 dpi. Two replicates are shown for each Myc-tagged construct. D) Symptoms of infiltrated leaf areas overexpressing full-length wild-type or K → M mutant NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ. Images of the same leaves after DAB staining are shown in the lower panels.
Overexpression of full-length, catalytically active NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ causes cell death
To further investigate the involvement of NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ in pathogen-independent cell death, we conducted transient overexpression experiments using their full-length open reading frames (ORFs). As shown in Figure 2D, overexpression of NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ induced cell death. The observed level of ion leakage was similar for overexpression of NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKγ, and NbMAPKKKα, which was used as a positive control (Figure 2B).
Several previous studies have demonstrated that kinase activity is required for the triggering of pathogen-independent cell death by transient overexpression of a component of a MAPK cascade [8,24,25]. To examine whether NbMAPKKKβ- and NbMAPKKKγ-induced cell death also required kinase activity, we constructed full-length and kinase domain MAPKKK mutants deficient in ATP binding. In these mutants, the essential conserved lysine residue (K) in the ATP-binding site of the kinase domain was replaced with a methionine (M) [8]. As shown in Figure 2A and 2D, none of these K → M mutants induced cell death when overexpressed. This result was confirmed by DAB staining (Figure 2A and 2D) and ion leakage assays (Figure 2B). Also, the expression of these kinase domain K → M mutants was confirmed by western blot analysis with anti-Myc monoclonal antibody (Figure 2C). These results indicate that cell death induced by the transient overexpression of N. benthamiana NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ is dependent on their kinase activities.
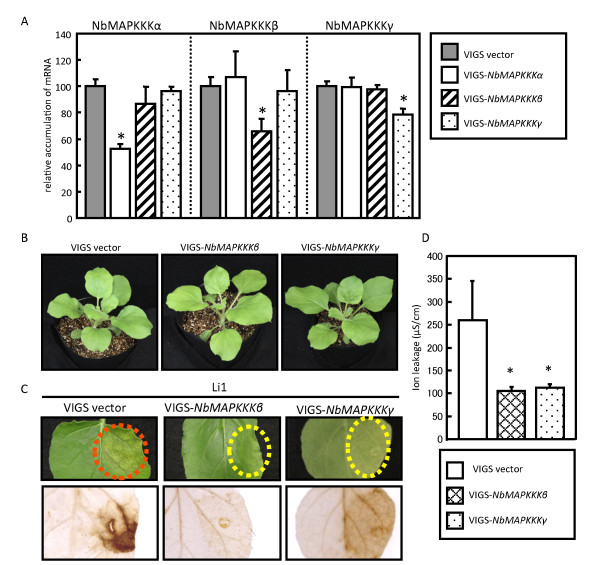
Silencing of NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ suppresses PlAMV-Li1-induced PCD
In light of the above finding that overexpression of full-length NbMAPKKKβ or NbMAPKKKγ or their kinase domains can induce cell death, we expected that silencing of the genes encoding these MAPKKKs would suppress virally induced PCD. Therefore, we used a TRV-based VIGS system [17] to silence NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ. Successful silencing of each gene was confirmed by analyzing the expression of NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKγ, and NbMAPKKKα (control) using real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR analysis (Figure 3A). Also, Southern blot analyses using a kinase domain-specific probe of each gene revealed that NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ exist as single-copy and multiple-copy genes, respectively, in the N. benthamiana genome (Additional file 1: Figure S1). In the N. benthamiana draft genome, two contigs showing high sequence homology (about >90%) with NbMAPKKKγ were obtained, suggesting that there are at least two copies of NbMAPKKKγ homologs. Thus, we assume that a single gene is specifically targeted in NbMAPKKKβ-silenced plants, but one or more highly similar genes might be targeted in NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants. Hereafter, we use the term “NbMAPKKKγ” to indicate NbMAPKKKγ and/or its homologous gene(s) except for transient overexpression experiments. The gene-silenced plants did not display any obvious phenotypic differences compared with non-silenced (VIGS vector) control plants (Figure 3B), suggesting that neither NbMAPKKKβ nor NbMAPKKKγ is involved in normal plant growth and development. In contrast, silencing of NtNPK1, a MAPKKK involved in cell plate formation in plant cytokinesis and in N gene-mediated HR cell death, causes severe stunting of plants [7].
Figure 3.
Silencing of NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ suppresses PlAMV-Li1-induced PCD. A) Confirmation of specific MAPKKK gene silencing in gene-silenced plants. The relative quantities of NbMAPKKKα, NbMAPKKKβ, and NbMAPKKKγ mRNA in non-silenced or NbMAPKKKα-, NbMAPKKKβ-, or NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants were measured using real-time RT-PCR. The data for each leaf tissue sample were normalized to the Nb18S rRNA gene expression level in the same sample. Data shown represent means ± standard deviation of at least three independent plants. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences from control plants (P < 0.05). B) Typical phenotypes observed in non-silenced and NbMAPKKKβ- and NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants. Pictures were taken 21 dpi. C) Symptoms in the PlAMV-Li1-infiltrated areas of non-silenced and NbMAPKKKβ- or NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants (upper panels) and DAB staining of the same leaves (lower panels). Red circles indicate cell death; yellow circles indicate no symptoms. Leaves were infiltrated with a PlAMV-Li1-expressing Agrobacterium culture grown to a turbidity (OD600) of 0.05. D) Ion leakage in the PlAMV-Li1-infiltrated areas of non-silenced and NbMAPKKKβ- or NbMAPKKKγ- silenced plants. Data shown represent means ± standard deviation of at least three independent plants. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences from control plants (P < 0.05).
NbMAPKKKβ- and NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants and control non-silenced plants were subsequently inoculated with PlAMV-Li1, which induces PCD-associated necrosis in N. benthamiana. In the PlAMV-Li1-infiltrated areas of non-silenced plants, we observed characteristic necrotic symptoms and brown color staining, indicating the accumulation of hydrogen peroxide. However, in the Li1-infiltrated NbMAPKKKβ-silenced plants, cell death and hydrogen peroxide production were completely compromised. Also, in NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants, cell death and hydrogen peroxide production were suppressed completely and partially, respectively, despite only about 20% decrease in the abundance of NbMAPKKKγ transcripts (Figure 3C). Suppression of cell death in the NbMAPKKKβ- and NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants was confirmed using ion leakage assays (Figure 3D). The suppression of cell death in NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants despite the slight decrease in its mRNA can be explained by a strict requirement of a high level of NbMAPKKKγ protein in cell death. Although it is possible that residual NbMAPKKKγ protein contributes to the decreased level of hydrogen peroxide production, its level might be too low to induce cell death. These results indicate that NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ are involved in hydrogen peroxide production and PCD induced by PlAMV-Li1.
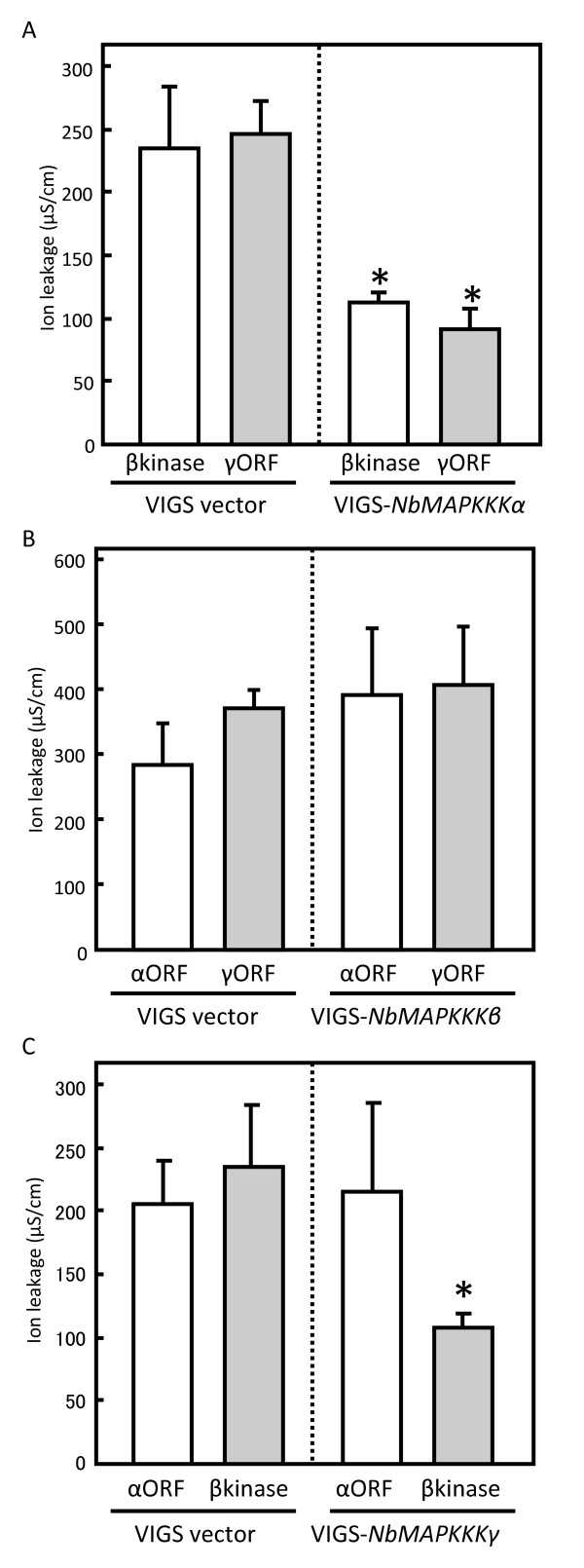
NbMAPKKKα, NbMAPKKKβ, and NbMAPKKKβ form a linear signaling pathway that induces cell death
Together with the findings of our previous study showing that NbMAPKKKα is involved in PlAMV-Li1-induced PCD [19], the above findings demonstrate that NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ are also essential for this virally induced PCD. To determine the relationships among these three genes in the PCD signaling pathway, we designed epistasis experiments combining transient overexpression and silencing of combinations of these genes. In these experiments, plants with a specific VIGS-silenced MAPKKK gene were agroinfiltrated with an Agrobacterium culture expressing a different MAPKKK gene, and the level of ion leakage was measured. Prior to the epistasis experiments, a preliminary experiment was performed to determine the minimum turbidity of Agrobacterium inoculum for each gene sufficient to induce complete cell death. Complete cell death was observed at the following cell densities at OD600: 0.5, NbMAPKKKα; 1.0, NbMAPKKKβ; and 0.05, NbMAPKKKγ. Although each MAPKKK was overexpressed at different concentrations of Agrobacterium inocula, no significant difference in the basal ion leakage level was observed among the different turbidities (ranging from 0.05 to 1.0) of Agrobacterium inocula that expressed the GUS gene in wild-type plants (Additional file 2: Figure S2). For NbMAPKKKβ, cell death induced by both the full-length ORF and kinase domain was slow and weak, but cell death induced by the kinase domain was more often observed than that induced by the full-length ORF. In the ion leakage assay shown in Figure 2B, this tendency was detected, although the difference in cell death induced by the full-length ORF and kinase domain of NbMAPKKKβ was not statistically significant. Previous reports have shown that the substrate specificity of MAPKKK is not affected when only the kinase domain is transiently activated [5,8,26]. Hence, the kinase domain of NbMAPKKKβ was used for further analysis, instead of the full-length ORF.
As shown in Figure 4A, ion leakage levels induced by transient expression of the NbMAPKKKβ kinase domain or full-length NbMAPKKKγ were lower in NbMAPKKKα-silenced plants than in VIGS vector-only control plants. Cell death induced by both NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ was consistently significantly suppressed in NbMAPKKKα-silenced plants compared to control plants (data not shown). This result suggests that NbMAPKKKα either acts downstream of both NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ in cell death induction or plays an essential role in codependent activation of both NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ. In contrast, the ion leakage levels induced by transient expression of full-length NbMAPKKKα or NbMAPKKKγ were similar in NbMAPKKKβ-silenced plants and control plants (Figure 4B), suggesting that NbMAPKKKα and NbMAPKKKβ are not codependent in their activation; rather, NbMAPKKKβ functions upstream of NbMAPKKKα in the cell death signaling pathway. This result led us to postulate that NbMAPKKKβ functions upstream of NbMAPKKKγ. As expected, in NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants, cell death and the ion leakage level induced by the transient overexpression of the NbMAPKKKβ kinase domain were significantly compromised compared to control plants (data not shown and Figure 4C, respectively). Cell death and the ion leakage induced by transient overexpression of NbMAPKKKα, however, were similar in NbMAPKKKγ-silenced and control plants (data not shown and Figure 4C, respectively), confirming that NbMAPKKKβ functions upstream of NbMAPKKKγ and that NbMAPKKKγ functions upstream of NbMAPKKKα. In this epistasis analysis, ion leakage levels were closely associated with the intensity of cell death at all combinations of these genes. Thus, these three MAPKKK genes form a linear signaling pathway leading to PCD in which NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKα function as the furthest upstream and downstream components, respectively, of the three MAPKKK components.
Figure 4.
Epistasis analysis of the functional relationships among NbMAPKKKα, NbMAPKKKβ, and NbMAPKKKγ. Epistasis analysis was performed by combining functional activation and suppression of specific combinations of MAPKKKs using transient overexpression and VIGS, respectively. Cell death in infiltrated areas was quantified using ion leakage assays at 4 dpi. Data shown represent means ± standard deviation for at least five plants. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences from control plants (P < 0.05). All experiments described in this figure were repeated two times with similar results. A) Cell death in the NbMAPKKKβ kinase domain (βkinase)- or NbMAPKKKγ (γORF)-overexpressing areas of non-silenced and NbMAPKKKα-silenced plants. Agrobacterium cultures expressing βkinase and γORF were grown to a turbidity of 1.0 and 0.05, respectively, for infiltration. B) Cell death in the NbMAPKKKα (αORF)- or γORF-overexpressing areas of non-silenced and NbMAPKKKβ-silenced plants. Agrobacterium cultures expressing αORF and γORF were grown to a turbidity of 0.5 or 0.05, respectively, for infiltration. C) Cell death in the αORF- or βkinase-overexpressing areas of non-silenced and NbMAPKKKγ-silenced plants. Agrobacterium cultures expressing αORF and βkinase were grown to a turbidity of 0.5 or 1.0, respectively, for infiltration.
Discussion
In our previous study [19], we showed that a MAPK cascade including NbMAPKKKα and NbMEK2 is required for both the PCD-associated systemic necrosis induced by PlAMV-Li1 and the Rx-mediated HR against potato virus X. Several studies have demonstrated that at least two MAPK cascades are involved in plant responses to various environmental stimuli [8,12]. The great diversity of plant MAPKKK genes is assumed to underlie the ability of plants to mount specific signaling responses to various environmental stimuli [15,16]. Therefore, to better understand the functions of MAPKKKs in the induction of PCD, we performed a comparative functional analysis of N. benthamiana MAPKKK genes. In the previous and present study, we demonstrated that three of these genes, NbMAPKKKα[19], NbMAPKKKβ, and NbMAPKKKγ (and/or its homologs), function as positive regulators of PlAMV-Li1-induced PCD and are not functionally redundant in the cell death signaling pathway. In the VIGS experiments, not only NbMAPKKKγ but also its homologous gene(s) were presumably knocked down in TRV-NbMAPKKKγ-infected plants. However, only one gene in the A2 subgroup was obtained from the cloning experiments, suggesting that NbMAPKKKγ homologous gene(s), which carries almost the same sequence as NbMAPKKKγ itself, must be effectively knocked down in TRV-NbMAPKKKγ-infected plants. In addition, overexpression of the NbMAPKKKγ full-length ORF and kinase domain could induce rapid cell death. Therefore, NbMAPKKKγ itself could play an important role in the cell death signaling pathway.
We also explored the functional relationship among these three MAPKKK genes by performing an epistasis experiment based on the assumption that if signaling protein A functions upstream of signaling protein B, signaling by activated A will be suppressed by silencing of B expression, whereas signaling by activated B will not be suppressed by silencing of A expression. Our results (Figure 4) demonstrate that NbMAPKKKα, NbMAPKKKβ, and NbMAPKKKγ, which represents NbMAPKKKγ and/or its homologous gene(s), form a linear signaling pathway leading to cell death induction in which NbMAPKKKβ acts upstream of NbMAPKKKγ and NbMAPKKKγ acts upstream of NbMAPKKKα. Results of a similar epistasis analysis have suggested that an NPK1/MEK1/NTF6 MAPK cascade functions downstream of a MAPKKKα/MEK2/SIPK MAPK cascade in the induction of PCD in plants [8]. These results support the possibility that NbMAPKKKα, NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKγ, and NPK1 initiate four distinct MAPK cascades that are coordinately involved in plant cell death. Alternatively, different sets of MAPK cascades might be involved in cell death signaling pathways induced by different plant–microbe interactions. To investigate this issue, further research is needed to determine whether NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ participate in the N gene-mediated HR against TMV or in the Pto-mediated HR against Pst.
In our experiments, the transient overexpression of the NbMAPKKKε2 kinase domain by agroinfiltration did not induce cell death (Figure 2A). However, Melech-Bonfil and associates have shown that the tomato homolog of NbMAPKKKε2, SlMAPKKKε, is required for PCD induction in the HR against Gram-negative bacterial pathogens [9]. Furthermore, they showed that the transient overexpression of the tomato SlMAPKKKε kinase domain in N. benthamiana induces pathogen-independent cell death. A comparison between the amino acid sequences of the kinase domains of NbMAPKKKε2 and SlMAPKKKε indicated only three amino acid differences. These three residues are not highly conserved and are not predicted to be essential for plant kinase catalytic activity, so explaining this functional difference solely by the amino acid sequence level is difficult. Although at first glance, our results seem to contradict theirs, the results cannot be directly compared because three factors in our transient overexpression experiments differed from theirs: promoters, Agrobacterium strains, and species origin of the homologous genes. These three factors, which could influence the expression levels of overexpressed proteins, are critical for the execution of cell death elicited by proteins possessing cell death-inducing activity [27,28]. Moreover, the amount of overexpressed NbMAPKKKε2 kinase domain in our experiment was much more than the amounts of NbMAPKKKβ kinase domain and its K → M mutant or NbMAPKKKγ kinase domain that can induce cell death and was comparable to the amount of the NbMAPKKKγ kinase domain K → M mutant. Therefore, NbMAPKKKε2 might be a less potent inducer of cell death than other MAPKKKs.
Our suggestion that several MAPK cascades function in a linear signaling pathway in the induction of cell death raises a concern about their roles in plant defense responses. To prevent pathogen invasion, plants commonly employ two types of receptors [NBS-LRR (nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat) receptors and RLK (receptor-like kinase)-type receptors] [1] to sense multiple PAMPs or effectors derived from biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. When plants perceive pathogens, the transcription of a common set of genes that act against various types of pathogens is activated [29,30], subsequently producing many defense responses, including cell death and the production of low-molecular-weight signaling compounds such as ethylene and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Activation of the MAPKKKα/MEK2/SIPK cascade can induce production of ethylene and ROS [31,32]. NPK1, which initiates another MAPK cascade, is activated by the ROS produced by the MAPK cascade initiated by MAPKKKα [26]. Similarly, the alfalfa MAPKKK MsOMTK1 is activated by hydrogen peroxide [6]. These results suggest that compounds induced by an upstream-acting MAPK cascade function as signaling molecules that activate a downstream-acting MAPK cascade. In addition, they suggest that the involvement of several MAPK cascades in defense responses enables plants to activate various responses simultaneously or coordinately to combat various types of pathogens.
Conclusions
In this study, we demonstrated that three MAPKKKs in N. benthamiana form a linear signaling pathway leading to PCD, implying that the involvement of multiple MAPK cascades in plant defense responses enables plants to exhibit various reactions simultaneously. Further analysis to identify downstream MAPKK and MAPK genes directly phosphorylated by NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ should help clarify the regulatory mechanisms of cell death involving these MAPKKK genes. Furthermore, to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the sequential activation of each MAPK cascade during plant defense responses, the upstream components or chemical compounds that directly activate these MAPKKKs must be identified.
Methods
Plant materials and virus isolate
N. benthamiana plants were grown in a growth chamber at 25 °C. To virally induce PCD, plants were inoculated with the binary vector pLi1, which contains the full-length cDNA of the Li1 isolate of plantago asiatica mosaic virus (PlAMV) downstream of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35 S promoter [33].
Cloning of MAPKKK genes from N. benthamiana
To retrieve partial MAPKKK cDNA sequences, a BLAST search was performed using the amino acid sequences of the kinase domains of the Arabidopsis MAPKKK genes AtMEKK1, AtMAPKKKγ, and AtMAPKKKε1 as queries against the N. benthamiana, N. tabacum, and S. lycopersicum databases of the Gene Index Project at the Computational Biology and Functional Genomics Laboratory Web site (http://compbio.dfci.harvard.edu/tgi/cgi-bin/tgi/Blast/index.cgi) and the tobacco BY-2 EST clone database of the RIKEN BioResource Center (http://www.brc.riken.go.jp/lab/epd/blast/index.shtml). The consensus nucleotide sequences for the retrieved partial cDNA sequences and query sequences were used to design a pair of specific primers for each of the three MAPKKK genes. Each pair of specific primers was used for RT-PCR amplification of a cDNA fragment from total RNA extracted from N. benthamiana leaves. The RT-PCR products were gel-purified and cloned into the pGEM-T easy vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) for sequencing. New primers were then designed based on the regions of the obtained cDNA sequences that were nonhomologous to the query sequences (to prevent nonspecific amplification) and used for specific 5′- and 3′-rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) using a GeneRacer Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the standard protocol provided by the manufacturer. The sequences of primers used in this study are listed in Table 1. cDNA sequences of these MAPKKK genes were determined from at least three independent clones.
Table 1.
Primers used in this study
| Name | Sequence (5’-3’) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| NbTC9992-1F |
GCTGTCAAAGAAGTGTCATTA |
Specific primer for TC9992 |
| NbTC9992-1280R |
ACCGTTTATTAATCACTATATTGC |
Specific primer for TC9992 |
| NtBP1333-1 F |
CTTAATGGGCAAGCAGCTAATC |
Specific primer for BP133312 |
| NtBP1333-447R |
TCAAGATTGTATGTTGTCTGCTC |
Specific primer for BP133312 |
| LeBI9315-123F |
GTTGCAATTAAACAAGTTTCTCTGGA |
Specific primer for BI931567 |
| LeBI9315-658R |
GGCTGAAGATCATAGTACGG |
Specific primer for BI931567 |
| NbTC9992-458R-5RACE |
GCTTGTCCATAGCCTTGGTTCTTCCT |
5’-RACE for TC9992 |
| NbTC9992-49R-5RACE |
TTTGCCTTCCCCCATCGCCTTGAT |
5’-RACE for TC9992 |
| NbTC9992-F1 |
GGATTGGAAAGGGGGAACCT |
Sequencing |
| NtMAP3Kb-566F |
TCCGCCGGTCATGTCACT |
Sequencing |
| NtBP1333-199R-5RACE |
ACATGGCTGCAGCTGCTTCATATTC |
5’-RACE for BP133312 |
| NtBP1333-91R-nested |
TACTATCCTTCTGCATAACTGACTGCAA |
5’-RACE for BP133312 |
| NtBP1333-333F-5RACE |
GAGAATCTCTCATCAGCCAGATGTTC |
3’-RACE for BP133312 |
| NtBP1333-375F-nested |
CAAACCTGTTGGTGGGGTACGAAT |
3’-RACE for BP133312 |
| NtBP1333-F1 |
AGACGCGCATAATTCGCATC |
Sequencing |
| NtBP1333-R1 |
TGAGCTCTCGTTTGGTAATAAG |
Sequencing |
| LeBI9315-507R-5RACE |
CATCTGCCTCTGTCAACTTTGTTGCA |
5’-RACE for LeBI931567 |
| LeBI9315-165R-nested |
CCTCCTGAGCAATATTCTCCAGAGA |
5’-RACE for LeBI931567 |
| LeBI9315-482F-3RACE |
TGCAACAAAGTTGACAGAGGCAGATG |
3’-RACE for LeBI931567 |
| LeBI9315-564F-nested |
ATGTCGGGAGTATGTGCTGCATCTG |
3’-RACE for LeBI931567 |
| LeBI9315-F1 |
CTGAGAAAGTTCTTGCAAACG |
Sequencing |
| LeBI9315-F2 |
GAACAGATGAATCAGAAGATG |
Sequencing |
| LeBI9315-F3 |
AAAGCACTCCATATAAACACAG |
Sequencing |
| LeBI9315-R1 |
GGTATACATCAAGTCCACCAT |
Sequencing |
| LeBI9315-R2 |
GAGGGAGTATGCTCTCATG |
Sequencing |
| Kp-NbMAPKKKa-1F |
GGGGTACCGAATGCCTGCTTGGTGGGGAA |
Full-length ORF of NbMAPKKKα |
| Xh-NbMAPKKKa-1836R |
GGCTCGAGTGCTAAAGAATTGGTCTTAGTTTTG |
Full-length ORF of NbMAPKKKα |
| Kp-NbMAPKKKb-1F |
CCGGTACCGAATGCATCGATTGCCAGGAATTTTTGC |
Full-length ORF of NbMAPKKKβ |
| EcV-NbMAPKKKb-1695R |
GGGATATCTTTAAAGCCTCTTGCCCAGATTTTG |
Full-length ORF of NbMAPKKKβ |
| Kp-NbMAPKKKg-1F |
GGGGTACCGAATGCGTTGGTGGCAGAACG |
Full-length ORF of NbMAPKKKγ |
| Xh-NbMAPKKKg-1956R |
GGCTCGAGTGCTACCTCTCTAGAGATAAACG |
Full-length ORF of NbMAPKKKγ |
| Kp-NbMAPKKKbkinase-F |
CCGGTACCGAATGTACTGGGACAAAGGTGATCT |
Kinase domain of NbMAPKKKβ |
| EcV-NbMAPKKKbkinase-R |
GGGATATCTTTACACAAAAGGATGCTCCAAGA |
Kinase domain of NbMAPKKKβ |
| Kp-NbMAPKKKgkinase-F |
GGGGTACCGAATGTGGCAAAAAGGGAAGCTTATTG |
Kinase domain of NbMAPKKKγ |
| Xh-NbMAPKKKgkinase-R |
GGCTCGAGTGTTACATAAATCGATGTTCCAATAAC |
Kinase domain of NbMAPKKKγ |
| Kp-NbMAPKKKekinase-F |
GGGGTACCGAATGAAATATATGCTCGGAGATGAG |
Kinase domain of NbMAPKKKε2 |
| Xh-NbMAPKKKekinase-R |
GGCTCGAGTGTTATATCCATGGATGTGAAAGTAG |
Kinase domain of NbMAPKKKε2 |
| NbMAPKKKb-K381M-F |
TTTTGCTGTCATGGAAGTGTCATTACTTGATCA |
K → M mutant of NbMAPKKKβ |
| NbMAPKKKb-K381M-R |
ATGACACTTCCATGACAGCAAAAAAGAAACCG |
K → M mutant of NbMAPKKKβ |
| NbMAPKKKg-K374M-F |
CTGGAGCTTTATGTGCGATGATGGAAGTTGAATT ATTACCGGA |
K → M mutant of NbMAPKKKγ |
| NbMAPKKKg-K374M-R |
TCCGGTAATAATTCAACTTCCATCATCGCACATAA AGCTCCAG |
K → M mutant of NbMAPKKKγ |
| NbMAPKKKa-255F |
GGTTGTTTTGGGATGTGGGGTCAG |
Real-time RT-PCR for NbMAPKKKα |
| NbMAPKKKa-393R |
CAGTGGGCTCAACCTATTATCGCC |
Real-time RT-PCR for NbMAPKKKα |
| NbMAPKKKb-1179F |
CACAAGGCAGATTTTACATGGTTTG |
Real-time RT-PCR for NbMAPKKKβ |
| NbMAPKKKb-1286R |
AGCTTGACCGATCCGTTAGCA |
Real-time RT-PCR for NbMAPKKKβ |
| NbMAPKKKg-903F |
CCGTGAGTGTAGTGCTCAGGGTAA |
Real-time RT-PCR for NbMAPKKKγ |
| NbMAPKKKg-984R |
TGCCGTAGGCTGCTGTGATG |
Real-time RT-PCR for NbMAPKKKγ |
| Nb18S-193F |
ATACGTGCAACAAACCCCGAC |
Real-time RT-PCR for Nb18S rRNA |
| Nb18S-280R | TGAATCATCGCAGCAACGG | Real-time RT-PCR for Nb18S rRNA |
ORF and motif analyses were performed using the ORF Finder (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html) and CD-Search (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi) programs, respectively. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using MEGA3.1 based on a multiple alignment created using ClustalW. The MAPKKK gene sequences used in phylogenetic analysis are listed in the GenBank database under the following accession numbers: AtMEKK1 (NM_116919), AtMEKK2 (NM_116917), AtMEKK3 (NM_116916), AtMEKK4 (NM_117272), BnMAPKKKβ1 (AJ010093), AtANP1 (NM_100771), AtANP2 (NM_104370), AtANP3 (NM_111477), NtNPK1 (D26601), AtMAPKKKγ (NM_126084), AtYODA (AY357949), NbMAPKKKα (AY500155), AtMAPKKKα (NM_179472), AtMAPKKKε1 (NM_112199), AtMAPKKKε2 (NM_111677), MsOMTK1 (AJ575100), BnMAPKKKα1 (AJ010091), BnMAPKKKε1 (AJ238845), SlMAPKKKε (GU192457), and NbMAPKKKε (GU205153). Homo sapiens HsMEKK1 (AF042838) was used as an outgroup.
Construction of plasmids for transient expression of wild-type and mutant MAPKKKs and MAPKKK kinase domains and agroinfiltration
The coding regions of NbMAPKKKα, NbMAPKKKβ, and NbMAPKKKγ were amplified by RT-PCR using primer pairs Kp-NbMAPKKKa-1F/Xh-NbMAPKKKa-1836R, Kp-NbMAPKKKb-1F/EcV-NbMAPKKKb-1695R, and Kp-NbMAPKKKg-1F/Xh-NbMAPKKKg-1956R, respectively. The kinase domains of NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKγ, and NbMAPKKKε2 were amplified using primer pairs Kp-NbMAPKKKbkinase-F/EcV-NbMAPKKKbkinase-R, Kp-NbMAPKKKgkinase-F/Xh-NbMAPKKKgkinase-R, and Kp-NbMAPKKKekinase-F/Xh-NbMAPKKKekinase-R, respectively.
Loss-of-function mutants of NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ were obtained by substituting methionine for the essential lysine in the ATP-binding site in the kinase domain. These mutants were obtained by site-directed mutagenesis using primers NbMAPKKKb-K381M-F and NbMAPKKKb-K381M-R for NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKg-K374M-F and NbMAPKKKg-K374M-R for NbMAPKKKγ. Each PCR-amplified MAPKKK gene fragment was subcloned into the pEarleyGate 203 vector under 35 S promoter [34] via the pENTA entry vector [35] with LR Clonase II Enzyme Mix (Invitrogen). GUS gene was also subcloned into the pEarleyGate 203 vector under the 35 S promoter. These plasmid vectors were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105. Agroinfiltration was performed as previously described [27].
Construction of VIGS vectors and VIGS
VIGS was performed as described previously using pTV:00 derivatives and pBintra6 [17]. NbMAPKKKα silencing was induced using pTV:NbMAPKKKα[19]. For NbMAPKKKβ and NbMAPKKKγ silencing, the 390-bp KpnI–PvuII fragment of the 5′-terminal region of the PCR-amplified full-length NbMAPKKKβ ORF and the 576-bp KpnI–EcoRV fragment of the PCR-amplified full-length NbMAPKKKγ ORF were introduced into pTV:00 in the antisense direction to generate pTV:NbMAPKKKβ and pTV:NbMAPKKKγ, respectively. The NbMAPKKKβ ORF was amplified using primers Kp-NbMAPKKKb-1 F and EcV-NbMAPKKKb-1695R, and the NbMAPKKKγ ORF was amplified using primers Kp-NbMAPKKKg-1 F and Xh-NbMAPKKKg-1956R.
Real-time RT-PCR
The methods used for total RNA isolation, cDNA synthesis, and quantitative analysis of gene expression were the same as those previously described [18]. Expression of 18 S rRNA was used as the normalizer. The primers used for real-time RT-PCR were NbMAPKKKa-255F and NbMAPKKKa-393R for NbMAPKKKα, NbMAPKKKb-1179F and NbMAPKKKb-1286R for NbMAPKKKβ, NbMAPKKKg-903F and NbMAPKKKg-984R for NbMAPKKKγ, and Nb18S-193F and Nb280R for Nb18S rRNA.
Abbreviations
HR: Hypersensitive response; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MAPKK: MAPK kinase; MAPKKK: MAPKK kinase; PCD: Programmed cell death; PlAMV: plantago asiatica mosaic virus; Pst: Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato; TMV: tobacco mosaic virus.
Authors’ contributions
MH, KK, YY and SN designed the experiments. MH and KK performed the experiments and analyzed the data together with KM, YO, YY and SN. TS, KI and YT contributed new reagents and analytic tools. MH, KK and SN wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Figure S1. Southern blot analysis of A) NbMAPKKKβ and B) NbMAPKKKγ using kinase domain-specific DNA probes. DNA probes were generated by using the PCR DIG Probe Synthesis Kit (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Each lane was loaded with 5 μg of total genomic DNA digested with each restriction enzyme.
Figure S2. Ion leakage of GUS-infiltrated areas. An Agrobacterium strain expressing the GUS gene using the 35 S promoter was infiltrated at the following turbidities: 0.05, 0.5, and 1.0.
Contributor Information
Masayoshi Hashimoto, Email: ahashi@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Ken Komatsu, Email: akomatsu@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Kensaku Maejima, Email: amaejima@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Yukari Okano, Email: 9889787606@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Takuya Shiraishi, Email: 4199446278@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Kazuya Ishikawa, Email: 3767539939@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Yusuke Takinami, Email: 8276605485@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Yasuyuki Yamaji, Email: ayyamaji@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Shigetou Namba, Email: anamba@mail.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. David Baulcombe (University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK) for tobacco rattle virus vector and silencing suppressor p19 gene. This work supported by grand-in-aid from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and, in part, by a Grand-in-aid for JSPS Fellows, and by the Program for Promotion of Basic Research Activities for Innovative Bioscience (PROBRAIN).
References
- Jones JD, Dangl JL. The plant immune system. Nature. 2006;444(7117):323–329. doi: 10.1038/nature05286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers HJ. Cell death and organ development in plants. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005;71:225–261. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(05)71007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez MC, Petersen M, Mundy J. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. pp. 621–649. [DOI] [PubMed]
- MAPKGroup. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci. 2002;7(7):301–308. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02302-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J. MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature. 2002;415(6875):977–983. doi: 10.1038/415977a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagami H, Kiegerl S, Hirt H. OMTK1, a novel MAPKKK, channels oxidative stress signaling through direct MAPK interaction. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(26):26959–26966. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312662200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin H, Axtell MJ, Dahlbeck D, Ekwenna O, Zhang S, Staskawicz B, Baker B. NPK1, an MEKK1-like mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase, regulates innate immunity and development in plants. Dev Cell. 2002;3(2):291–297. doi: 10.1016/S1534-5807(02)00205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Pozo O, Pedley KF, Martin GB. MAPKKKα is a positive regulator of cell death associated with both plant immunity and disease. EMBO J. 2004;23(15):3072–3082. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melech-Bonfil S, Sessa G. Tomato MAPKKKε is a positive regulator of cell-death signaling networks associated with plant immunity. Plant J. 2010;64(3):379–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin H, Liu Y, Yang KY, Kim CY, Baker B, Zhang S. Function of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in N gene-mediated resistance in tobacco. Plant J. 2003;33(4):719–731. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekengren SK, Liu Y, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Martin GB. Two MAPK cascades, NPR1, and TGA transcription factors play a role in Pto-mediated disease resistance in tomato. Plant J. 2003;36(6):905–917. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo SD, Cho YH, Tena G, Xiong Y, Sheen J. Dual control of nuclear EIN3 by bifurcate MAPK cascades in C2H4 signalling. Nature. 2008;451(7180):789–795. doi: 10.1038/nature06543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y, Zhang S. Phosphorylation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase by MPK6, a stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinase, induces ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2004;16(12):3386–3399. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H, Ngwenyama N, Liu Y, Walker JC, Zhang S. Stomatal development and patterning are regulated by environmentally responsive mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2007;19(1):63–73. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.048298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S, Klessig DF. MAPK cascades in plant defense signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2001;6(11):520–527. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(01)02103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley KF, Martin GB. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2005;8(5):541–547. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2005.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliff F, Martin-Hernandez AM, Baulcombe DC. Tobacco rattle virus as a vector for analysis of gene function by silencing. Plant J. 2001;25(2):237–245. doi: 10.1046/j.0960-7412.2000.00942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu K, Yamaji Y, Ozeki J, Hashimoto M, Kagiwada S, Takahashi S, Namba S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of seven Japanese isolates of Plantago asiatica mosaic virus (PlAMV): a unique potexvirus with significantly high genomic and biological variability within the species. Arch Virol. 2008;153(1):193–198. doi: 10.1007/s00705-007-1078-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu K, Hashimoto M, Ozeki J, Yamaji Y, Maejima K, Senshu H, Himeno M, Okano Y, Kagiwada S, Namba S. Viral-induced systemic necrosis in plants involves both programmed cell death and the inhibition of viral multiplication, which are regulated by independent pathways. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2010;23(3):283–293. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-23-3-0283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoguchi T, Irie K, Hirayama T, Hayashida N, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Matsumoto K, Shinozaki K. A gene encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is induced simultaneously with genes for a mitogen-activated protein kinase and an S6 ribosomal protein kinase by touch, cold, and water stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93(2):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouannic S, Champion A, Segui-Simarro JM, Salimova E, Picaud A, Tregear J, Testillano P, Risueno MC, Simanis V, Kreis M. et al. The protein kinases AtMAP3Kε1 and BnMAP3Kε1 are functional homologues of S. pombe cdc7p and may be involved in cell division. Plant J. 2001;26(6):637–649. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaiwongsar S, Otegui MS, Jester PJ, Monson SS, Krysan PJ. The protein kinase genes MAP3Kε1 and MAP3Kε2 are required for pollen viability in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2006;48(2):193–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banno H, Hirano K, Nakamura T, Irie K, Nomoto S, Matsumoto K, Machida Y. NPK1, a tobacco gene that encodes a protein with a domain homologous to yeast BCK1, STE11, and Byr2 protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13(8):4745–4752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren D, Yang KY, Li GJ, Liu Y, Zhang S. Activation of Ntf4, a tobacco mitogen-activated protein kinase, during plant defense response and its involvement in hypersensitive response-like cell death. Plant Physiol. 2006;141(4):1482–1493. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.080697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S, Liu Y. Activation of salicylic acid-induced protein kinase, a mitogen-activated protein kinase, induces multiple defense responses in tobacco. Plant Cell. 2001;13(8):1877–1889. doi: 10.1105/TPC.010044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovtun Y, Chiu WL, Tena G, Sheen J. Functional analysis of oxidative stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97(6):2940–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.6.2940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu K, Hashimoto M, Maejima K, Shiraishi T, Neriya Y, Miura C, Minato N, Okano Y, Sugawara K, Yamaji Y, Namba S. A necrosis-inducing elicitor domain encoded by both symptomatic and asymptomatic Plantago asiatica mosaic virus isolates, whose expression is modulated by virus replication. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011;24(4):408–420. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-10-0279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Dorey S, Swiderski M, Jones JD. Expression of RPS4 in tobacco induces an AvrRps4-independent HR that requires EDS1, SGT1 and HSP90. Plant J. 2004;40(2):213–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro L, Zipfel C, Rowland O, Keller I, Robatzek S, Boller T, Jones JD. The transcriptional innate immune response to flg22. Interplay and overlap with Avr gene-dependent defense responses and bacterial pathogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2004;135(2):1113–1128. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.036749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao Y, Xie Z, Chen W, Glazebrook J, Chang HS, Han B, Zhu T, Zou G, Katagiri F. Quantitative nature of Arabidopsis responses during compatible and incompatible interactions with the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Cell. 2003;15(2):317–330. doi: 10.1105/tpc.007591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim CY, Liu Y, Thorne ET, Yang H, Fukushige H, Gassmann W, Hildebrand D, Sharp RE, Zhang S. Activation of a stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade induces the biosynthesis of ethylene in plants. Plant Cell. 2003;15(11):2707–2718. doi: 10.1105/tpc.011411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y, Ren D, Pike S, Pallardy S, Gassmann W, Zhang S. Chloroplast-generated reactive oxygen species are involved in hypersensitive response-like cell death mediated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Plant J. 2007;51(6):941–954. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozeki J, Takahashi S, Komatsu K, Kagiwada S, Yamashita K, Mori T, Hirata H, Yamaji Y, Ugaki M, Namba S. A single amino acid in the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Plantago asiatica mosaic virus contributes to systemic necrosis. Arch Virol. 2006;151(10):2067–2075. doi: 10.1007/s00705-006-0766-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley KW, Haag JR, Pontes O, Opper K, Juehne T, Song K, Pikaard CS. Gateway-compatible vectors for plant functional genomics and proteomics. Plant J. 2006;45(4):616–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himeno M, Maejima K, Komatsu K, Ozeki J, Hashimoto M, Kagiwada S, Yamaji Y, Namba S. Significantly low level of small RNA accumulation derived from an encapsidated mycovirus with dsRNA genome. Virology. pp. 69–75. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Southern blot analysis of A) NbMAPKKKβ and B) NbMAPKKKγ using kinase domain-specific DNA probes. DNA probes were generated by using the PCR DIG Probe Synthesis Kit (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Each lane was loaded with 5 μg of total genomic DNA digested with each restriction enzyme.
Figure S2. Ion leakage of GUS-infiltrated areas. An Agrobacterium strain expressing the GUS gene using the 35 S promoter was infiltrated at the following turbidities: 0.05, 0.5, and 1.0.