Abstract
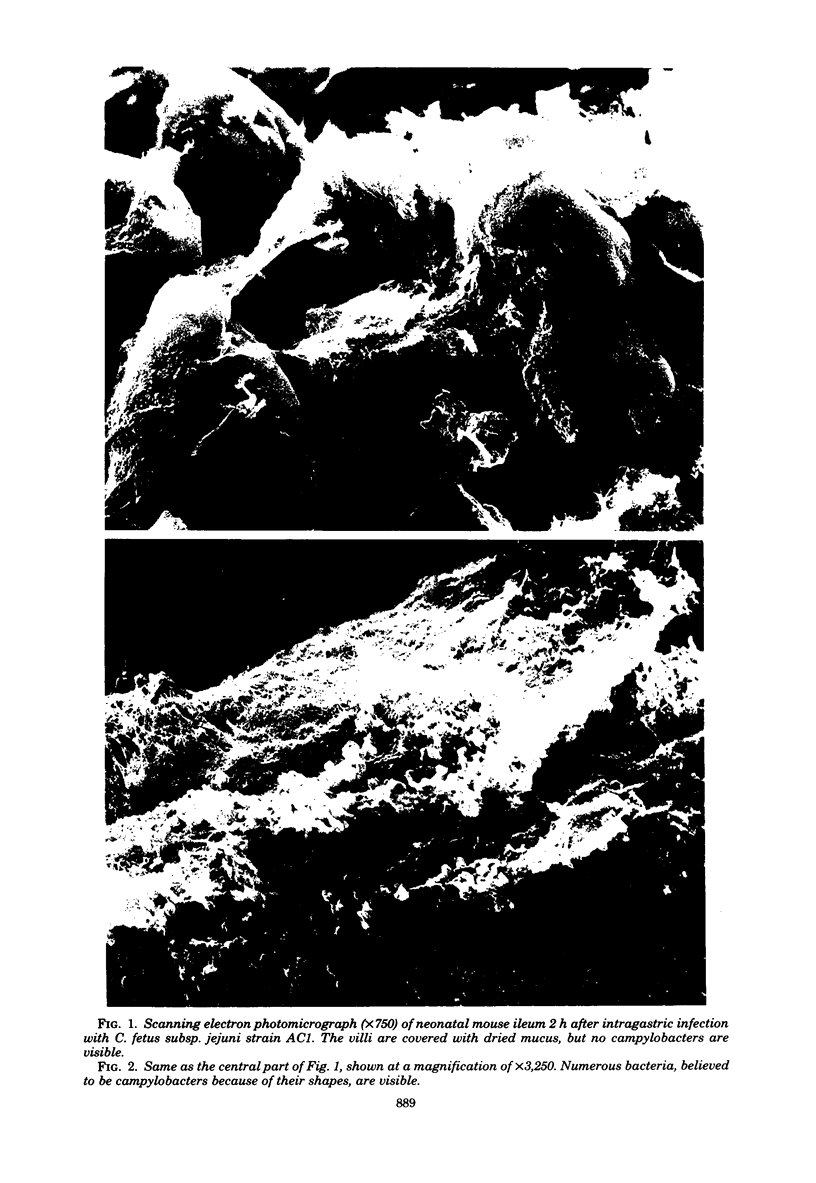
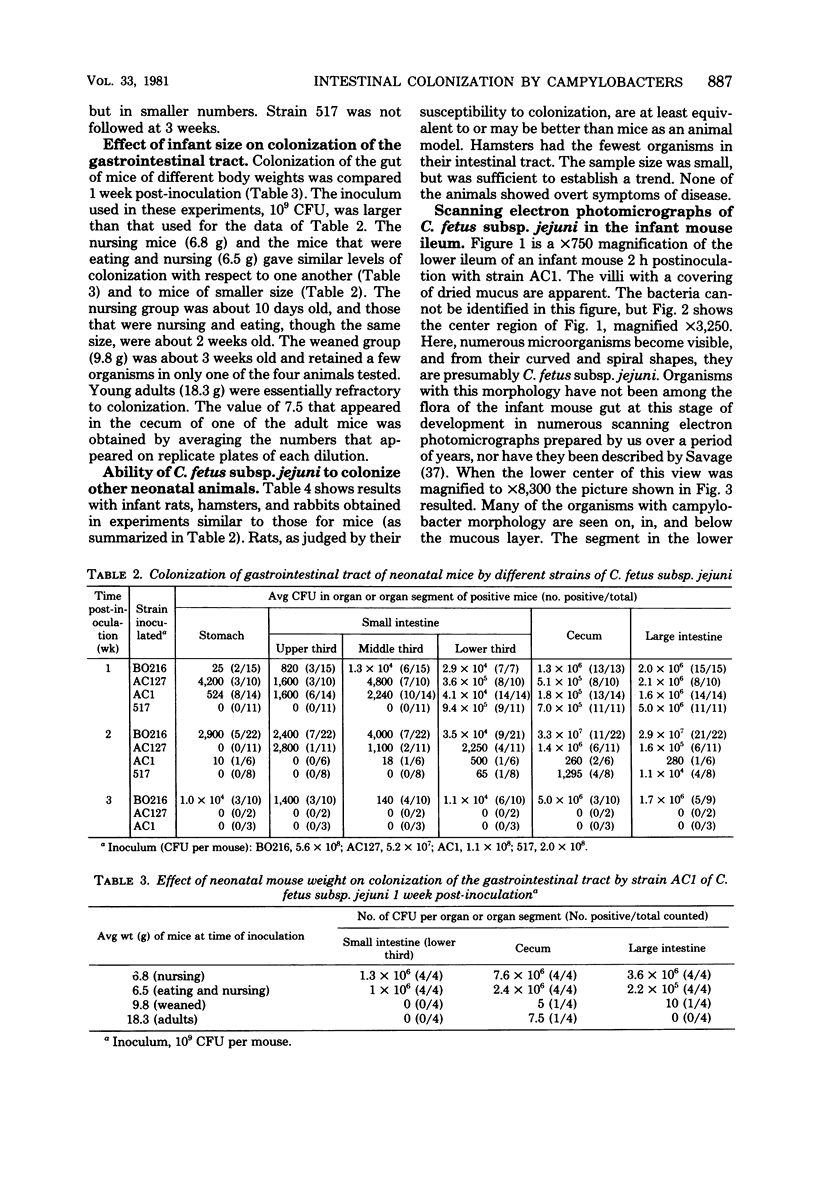
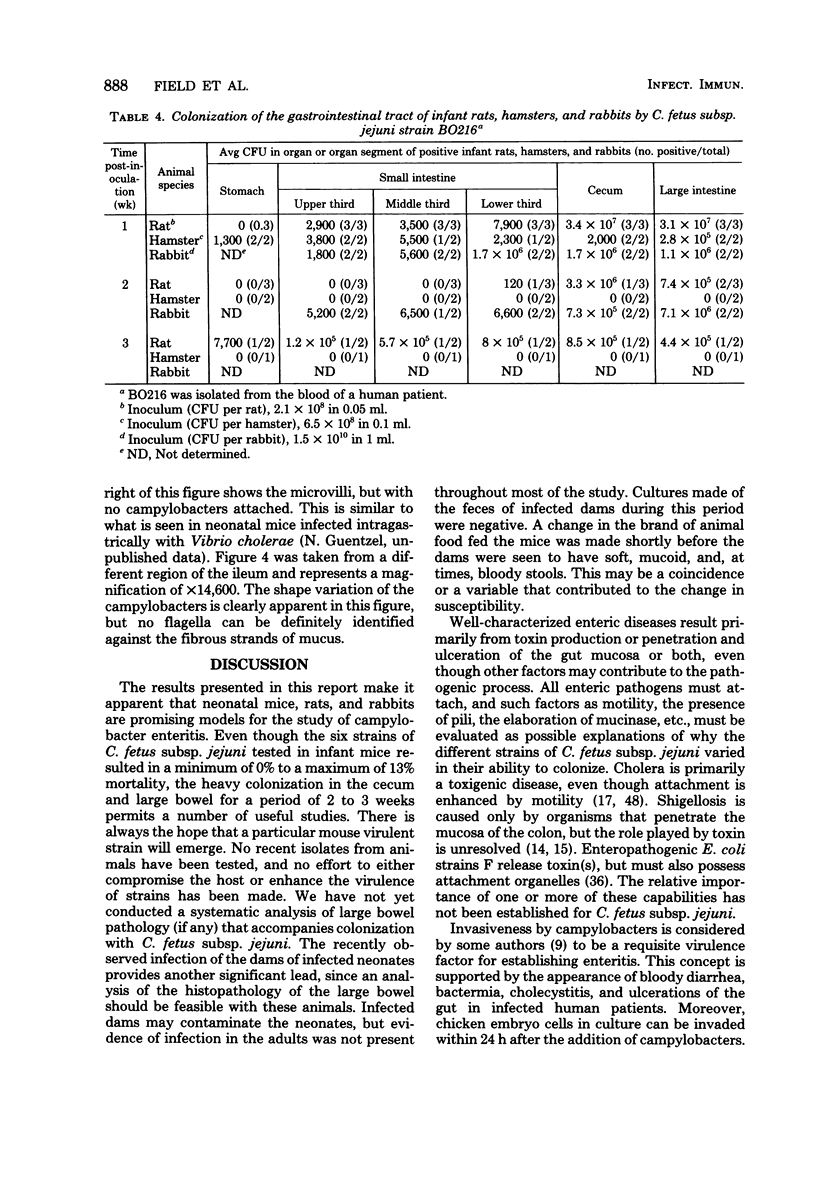
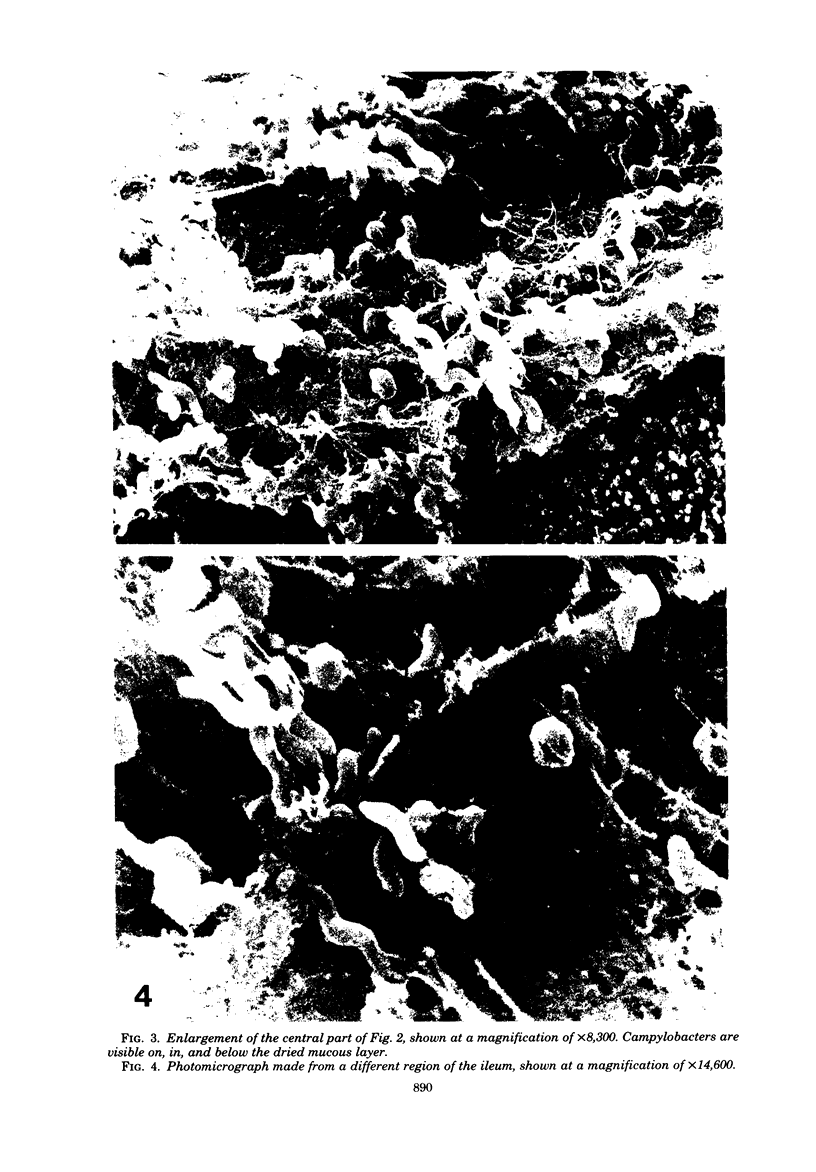
Neonatal mice (2.3 to 2.8 g) were inoculated intragastrically with different human isolates of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. At weekly intervals thereafter, mice were sacrificed and dilution plate counts were performed on segments of the gastrointestinal tract. Mice were uniformly colonized by some strains for 2 weeks, whereas other strains were being cleared at that time. One strain (BO216) persisted in some mice for 3 weeks. The greatest number of organisms (10(7)) was recovered from the cecum and large intestine. The small intestine had from 10(2) to 10(5) colony-forming units. Colonization of the stomach was not found consistently. One strain killed 13% of the infected mice. Deaths occurred between 1 and 5 days postinfection. Two other strains killed a smaller percentage of challenged animals, and two additional strains killed none. Retarded weight gain was noticed in some, but not all, of the infected mice. The intestines of neonatal rats and rabbits were colonized much the same as those of mice, whereas hamsters were resistant to colonization. Preweanling mice, up to about 6.5 to 7.0 g, could be colonized with C. fetus subsp. jejuni after intragastric challenge, but weanling mice of larger weight (9.8 g) and young adult mice (18.3 g) could not. Scanning electron photomicrographs of the lower ileum showed campylobacters in and below the dried mucous gel that lines the intestines. The use of this model for additional studies is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J. Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni: the need for surveillance. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):670–671. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M., Cravens J., Powers B. W., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis associated with canine infection. Lancet. 1978 Nov 4;2(8097):979–981. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92541-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokkenheuser V. D., Richardson N. J., Bryner J. H., Roux D. J., Schutte A. B., Koornhof H. J., Freiman I., Hartman E. Detection of enteric campylobacteriosis in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.227-232.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boncyk L. H., Brack M., Kalter S. S. Hemorrhagic-necrotic enteritis in a baboon (Papio cynocephalus) due to Vibrio fetus. Lab Anim Sci. 1972 Oct;22(5):734–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brougham D. I., Meech Dip Ven R. J. Campylobacter enteritis: a common cause of adult diarrhoea. N Z Med J. 1979 Sep 26;90(644):239–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce D., Ferguson I. R. Campylobacter jejuni in cats. Lancet. 1980 Sep 13;2(8194):595–596. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Dekeyser P., Detrain M., Dehaen F. Related vibrio in stools. J Pediatr. 1973 Mar;82(3):493–495. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mol P., Bosmans E. Campylobacter enteritis in Central Africa. Lancet. 1978 Mar 18;1(8064):604–604. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., SCHNEIDER H. PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY IN LABORATORY ANIMALS. Fed Proc. 1965 Jan-Feb;24:29–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Pope L. M., Cole G. T., Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Persistence and spread of Candida albicans after intragastric inoculation of infant mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):783–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.783-791.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Washington O., Formal S. B. Shigellosis due to Shigella dysenteriae. 1. Relative importance of mucosal invasion versus toxin production in pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):523–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant I. H., Richardson N. J., Bokkenheuser V. D. Broiler chickens as potential source of Campylobacter infections in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 May;11(5):508–510. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.5.508-510.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Field L. H., Eubanks E. R., Berry L. J. Use of fluorescent antibody in studies of immunity to cholera in infant mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.539-548.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Lahita R. G., Winn W. C., Jr, Roberts R. B. Campylobacteriosis in man: pathogenic mechanisms and review of 91 bloodstream infections. Am J Med. 1978 Oct;65(4):584–592. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. J., Ganguli L. A. Campylobacter enteritis presenting as an acute abdomen. Postgrad Med J. 1980 Mar;56(653):205–206. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.56.653.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Campylobacter enteritis in children. J Pediatr. 1979 Apr;94(4):527–533. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Fleming P. C. Campylobacter enteritis. Can Med Assoc J. 1979 Jun 23;120(12):1525–1532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosunen T. U., Danielsson D., Kjellander J. Serology of Campylobacter fetus ss. jejuni )"related" campylobacters). Demonstration of strain-specific and interstrain-related antigens by immunoelectrophoresis and co-agglutination. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Aug;88(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. R., Karmali M. A., Newman A. Campylobacter enterocolitis. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Dec;91(6):929–930. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-6-929_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madge D. S. Campylobacter enteritis in young mice. Digestion. 1980;20(6):389–394. doi: 10.1159/000198479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. J., Taylor M., Sangree M. H. Toxic megacolon with campylobacter colitis. Conn Med. 1980 Aug;44(8):496–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalak D. M., Perrault J., Gilchrist M. J., Dozois R. R., Carney J. A., Sheedy P. F., 2nd Campylobacter fetus ss. jejuni: a cause of massive lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Gastroenterology. 1980 Oct;79(4):742–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Sorger S., Lackman L., Sinai R. E., Marks M. I. Campylobacter gastroenteritis in children. J Pediatr. 1979 Apr;94(4):589–591. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepersack F., Prigogyne T., Butzler J. P., Yourassowsky E. Campylobacter jejuni post-transfusional septicaemia. Lancet. 1979 Oct 27;2(8148):911–911. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92738-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope L. M., Cole G. T., Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Systemic and gastrointestinal candidiasis of infant mice after intragastric challenge. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):702–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.702-707.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter I. A., Reid T. M. A milk-borne outbreak of Campylobacter infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Jun;84(3):415–419. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Barker I. K. Campylobacter colitis in gnotobiotic dogs. Vet Rec. 1980 Sep 27;107(13):314–315. doi: 10.1136/vr.107.13.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Karmali M. A. Attempts to transmit campylobacter enteritis to dogs and cats. Can Med Assoc J. 1978 Nov 4;119(9):1001–1002. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringertz S., Rockhill R. C., Ringertz O., Sutomo A. Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni as a cause of gastroenteritis in Jakarta, Indonesia. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):538–540. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.538-540.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. A., Edgar W. J., Gibson G. L., Matchett A. A., Robertson L. Campylobacter enteritis associated with consumption of unpasteurised milk. Br Med J. 1979 May 5;1(6172):1171–1173. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6172.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Factors involved in colonization of the gut epithelial surface. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978 Oct;31(10 Suppl):S131–S135. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/31.10.S131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Turnbull G. L., Walker R. E., Young S. E. Campylobacter jejuni enteritis transmitted from cat to man. Lancet. 1980 May 31;1(8179):1188–1188. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91644-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele T. W., McDermott S. Campylobacter enteritis in South Australia. Med J Aust. 1978 Oct 21;2(9):404–406. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1978.tb76814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner E. I., Bullin C. H. Campylobacter enteritis. Br Med J. 1977 Aug 27;2(6086):579–579. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6086.579-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribe G. W., Frank A. Campylobacter in monkeys. Vet Rec. 1980 Apr 19;106(16):365–366. doi: 10.1136/vr.106.16.365-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribe G. W., Mackenzie P. S., Fleming M. P. Incidence of thermophilic Campylobacter species in newly imported simian primates with enteritis. Vet Rec. 1979 Oct 6;105(14):333–333. doi: 10.1136/vr.105.14.333-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson L. A., Brooks H. J., Scrimgeour G. Campylobacter enteritis and Yersinia enterocolitica infection in New Zealand. N Z Med J. 1979 Sep 26;90(644):240–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa S. Large outbreak of campylobacter enteritis among schoolchildren. Lancet. 1980 Jul 19;2(8186):153–153. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Willis D. L., Berry L. J. Role of motility in experimental cholera in adult rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):387–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.387-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






