Abstract
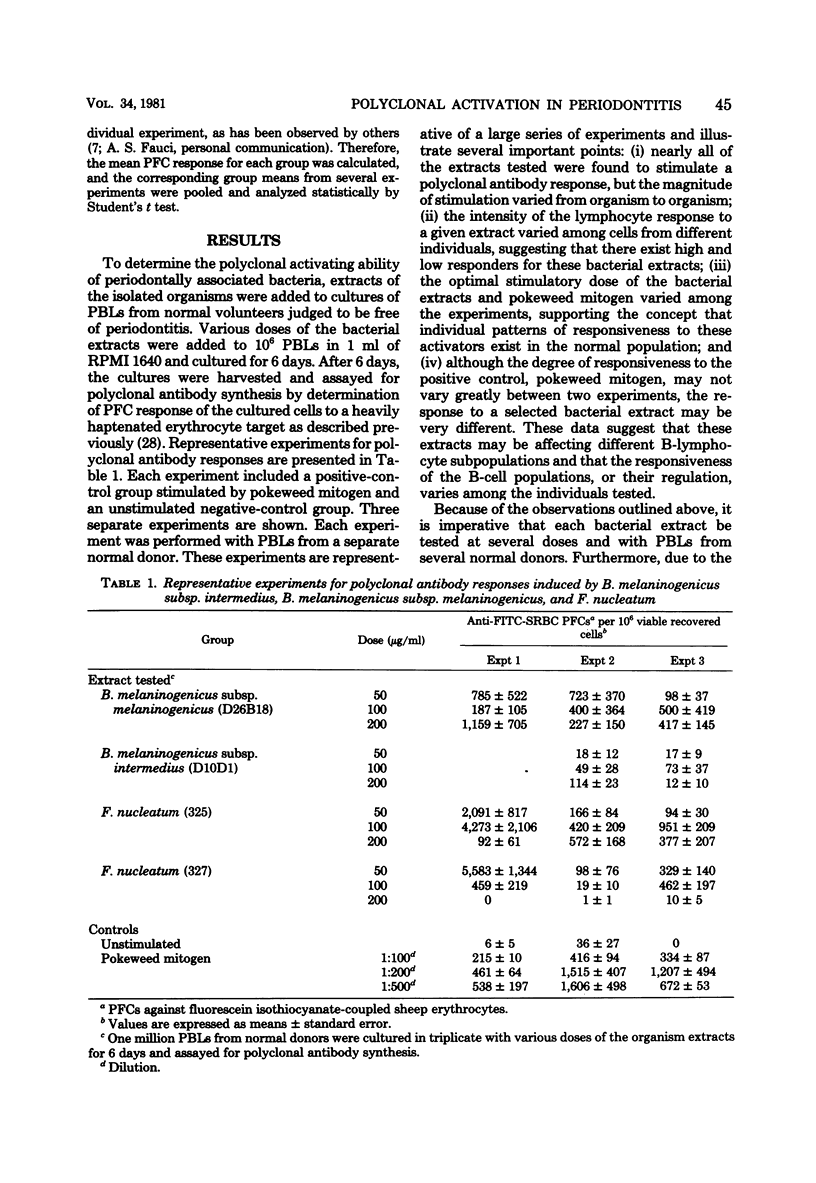
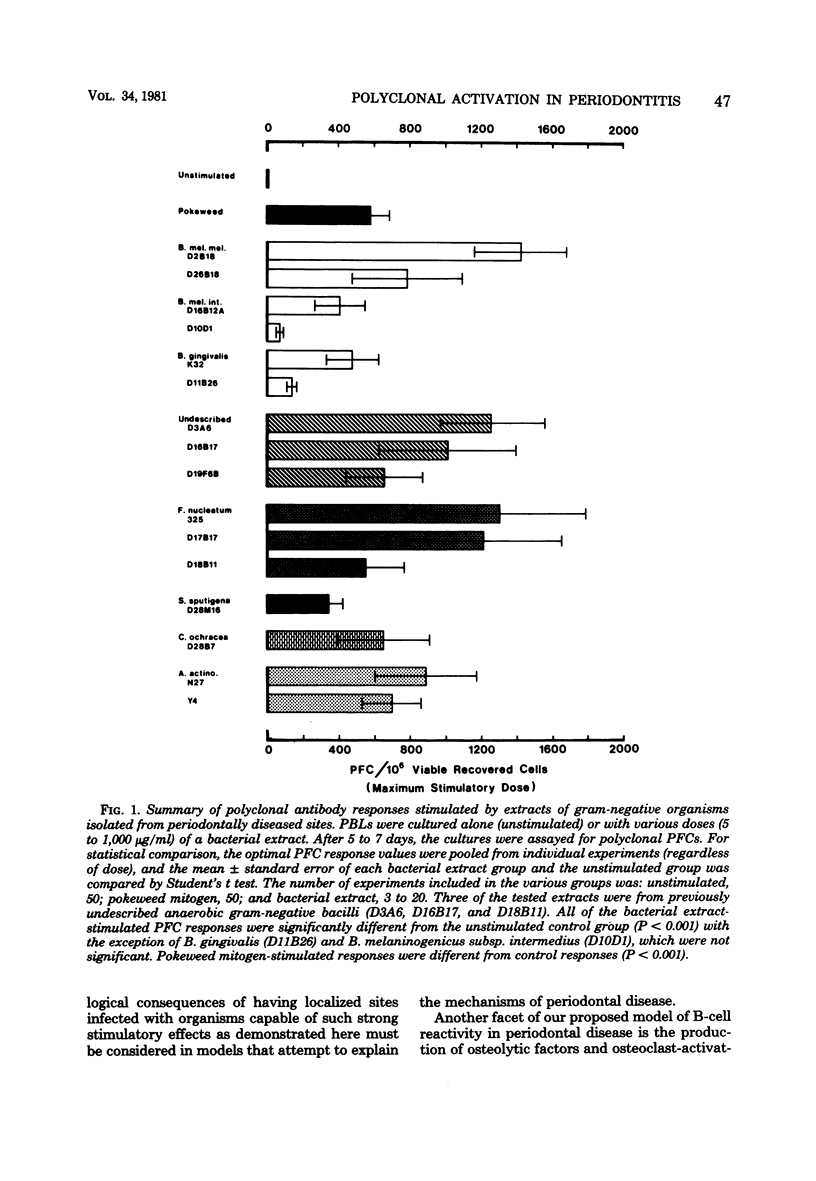
The objective of this research was to determine whether gram-negative bacteria frequently isolated from periodontally diseased sites contained polyclonal B-cell activators. Polyclonal B-cell activation, which results in nonspecific activation of multiple B-cell clones was analyzed by a hemolysis-in-gel assay designed to detect a broad range of antibody specificities. Extracts from numerous bacterial strains, including Bacteroides gingivalis, Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. melaninogenicus, B. melaninogenicus subsp. intermedius, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Selenomonas sputigena, Capnocytophaga ochracea, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, were tested. Extracts of the above organisms were found to stimulate polyclonal antibody responses in cultures of normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes, although the magnitude of stimulation varied among the extracts. Optimal antibody-forming cell responses were found at stimulator doses between 5 and 1,000 micrograms/ml. We conclude that the resident gram-negative subgingival flora associated with periodontal lesions possesses potent polyclonal B-cell activators. These activators may contribute to disease pathogenesis by inducing B lymphocytes to produce antibody, osteolytic factors, or both and possibly other mediators of inflammation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. J., Chan S. P., Socransky S. S., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Importance of Actinomyces and certain gram-negative anaerobic organisms in the transformation of lymphocytes from patients with periodontal disease. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1363–1368. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1363-1368.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banck G., Forsgren A. Many bacterial species are mitogenic for human blood B lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(4):347–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burckhardt J. J., Guggenheim B., Hefti A. Are Actinomyces viscosus antigens B cell mitogens? J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1460–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Trummel C., Horton J., Baker J. J., Oppenheim J. J. Production of osteoclast-activating factor by normal human peripheral blood rosetting and nonrosetting lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Oct;6(10):732–736. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830061014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clagett J. A., Engel D. Polyclonal activation: a form of primitive immunity and its possible role in pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Dev Comp Immunol. 1978 Apr;2(2):235–241. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(78)80066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. Human B cell function in a polyclonally induced plaque forming cell system. Cell triggering and immunoregulation. Immunol Rev. 1979;45:93–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Pratt K. R. Human bone marrow lymphocytes. III. Polyclonal activation of B lymphocytes in human bone marrow measured by a direct plaque-forming cell assay. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1150–1153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Pratt K. R. Polyclonal activation of bone-marrow-derived lymphocytes from human peripheral blood measured by a direct plaque-forming cell assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3676–3679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A. Heterogeneity of B cells: direct evidence of selective triggering of distinct subpopulations by polyclonal activators. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(1-2):55–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb02992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Leikin S., Oppenheim J. J. Human lymphoproliferative reaction to saliva and dental plaque-deposits: an in vitro correlation with periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1972 Sep;43(9):522–527. doi: 10.1902/jop.1972.43.9.522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Raisz L. G., Simmons H. A., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science. 1972 Sep 1;177(4051):793–795. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4051.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. Lymphocyte transformation by sonicates of dental plaque in human periodontal disease. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Sep;16(9):1117–1121. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi L., Lehner T. Stimulation of lymphocyte transformation by bacterial antigens in patients with periodontal disease. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Nov;15(11):1089–1096. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leb L., Grimes E. T., Balogh K., Merritt J. A., Jr Monoclonal macroglobulinemia with osteolytic lesions: a case report and review of the literature. Cancer. 1977 Jan;39(1):227–231. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197701)39:1<227::aid-cncr2820390136>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackler B. F., Altman L. C., Wahl S., Rosenstreich D. L., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Blastogenesis and lymphokine synthesis by T and B lymphocytes from patients with periodontal disease. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):844–850. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.844-850.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackler B. F., Frostad K. B., Robertson P. B., Levy B. M. Immunoglobulin bearing lymphocytes and plasma cells in human periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1977 Jan;12(1):37–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb00107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G., Socransky S. S. Predominant cultivable microbiota in periodontosis. J Periodontal Res. 1977 Mar;12(2):120–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasanen V. J., Mäkelä O. Effect of the number of haptens coupled to each erythrocyte on haemolytic plaque formation. Immunology. 1969 Mar;16(3):399–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patters M. R., Genco R. J., Reed M. J., Mashimo P. A. Blastogenic response of human lymphocytes to oral bacterial antigens: comparison of individuals with periodontal disease to normal and edentulous subjects. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1213–1220. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1213-1220.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringdén O., Rynnel-Dagö B., Kunori T., Smith C. I., Hammarström L., Freijd A., Möller E. Induction of antibody synthesis in human B lymphocytes by different polyclonal B cell activators: evaluation by direct and indirect PFC assays. Immunol Rev. 1979;45:195–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Wahl S. M., McMaster P. R. The role of B lymphocytes in cell-mediated immunity II. Delayed hypersensitivity induced by dinitrophenyl-ficoll in dinitrophenyl-keyhole limpet hemocyanin-immunized guinea pigs. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jun;38(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rynnel-Dagö B., Ringdén O., Alfredsson H., Möller E. The use of bacteria for the functional characterization of human lymphocyte subpopulations in various lymphoid organs. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(5):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour G. J., Greenspan J. S. The phenotypic characterization of lymphocyte subpopulations in established human periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1979 Jan;14(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1979.tb00216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Subgingival microflora and periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):351–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. The predominant cultivable microflora of advanced periodontitis. Scand J Dent Res. 1977 Jan-Feb;85(2):114–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1977.tb00541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Bick P. H., Miller G. A., Ranney R. R., Rice P. L., Lalor J. H., Tew J. G. Polyclonal B-cell activation: severe periodontal disease in young adults. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Jul;16(3):354–366. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Microbiology of periodontal disease -- present status and future considerations. J Periodontol. 1977 Sep;48(9):497–504. doi: 10.1902/jop.1977.48.9.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Palenstein Helderman W. H. Total viable count and differential count of vibrio (campylobacter) sputorum, fusobacterium nucleatum, selenomonas sputigena, bacteroides ochraceus and veillonella in the inflamed and non inflamed human gingival crevice. J Periodontal Res. 1975 Nov;10(5):294–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1975.tb00037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


