Abstract
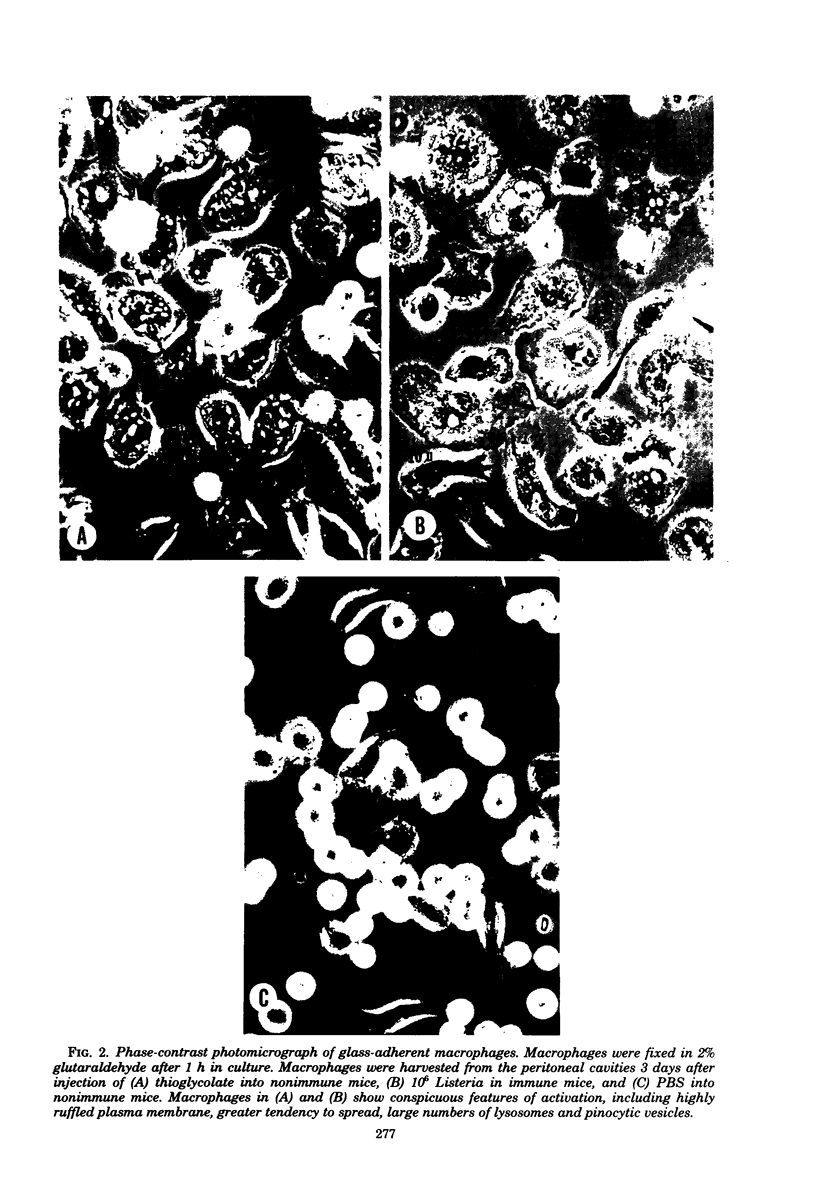
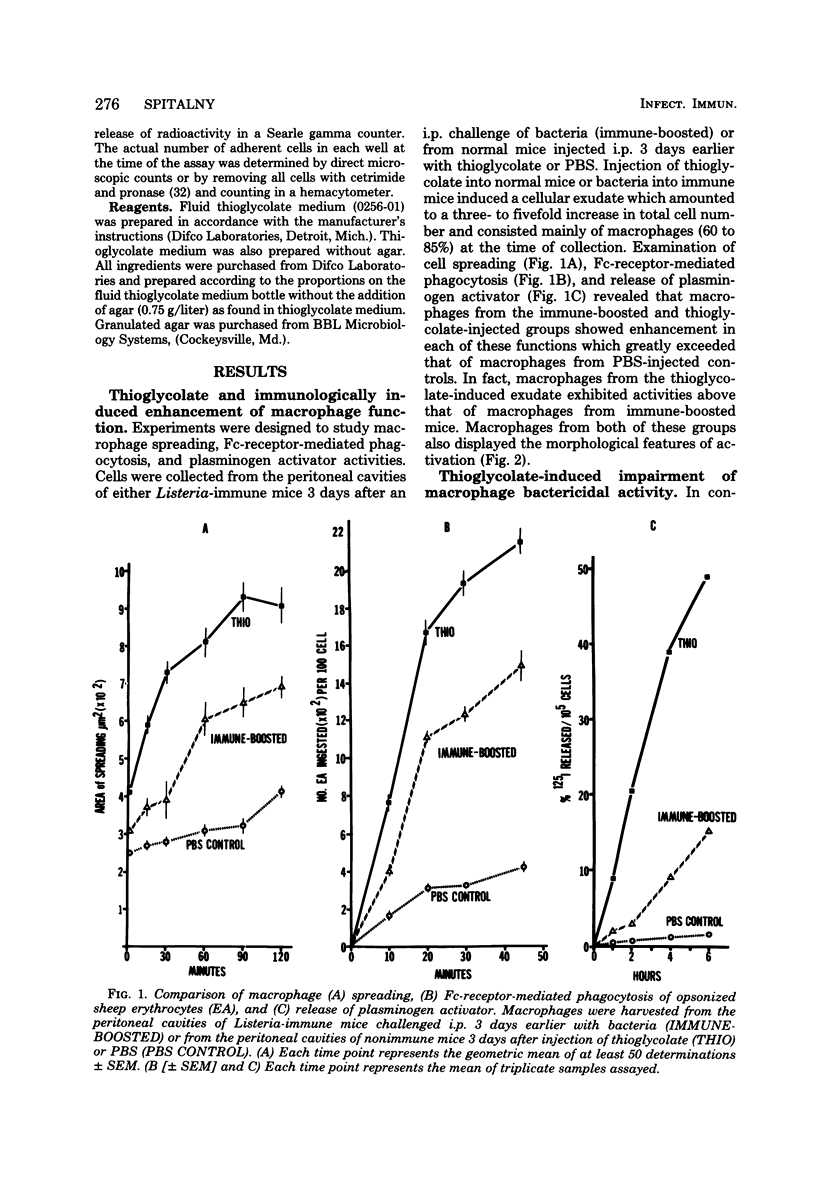
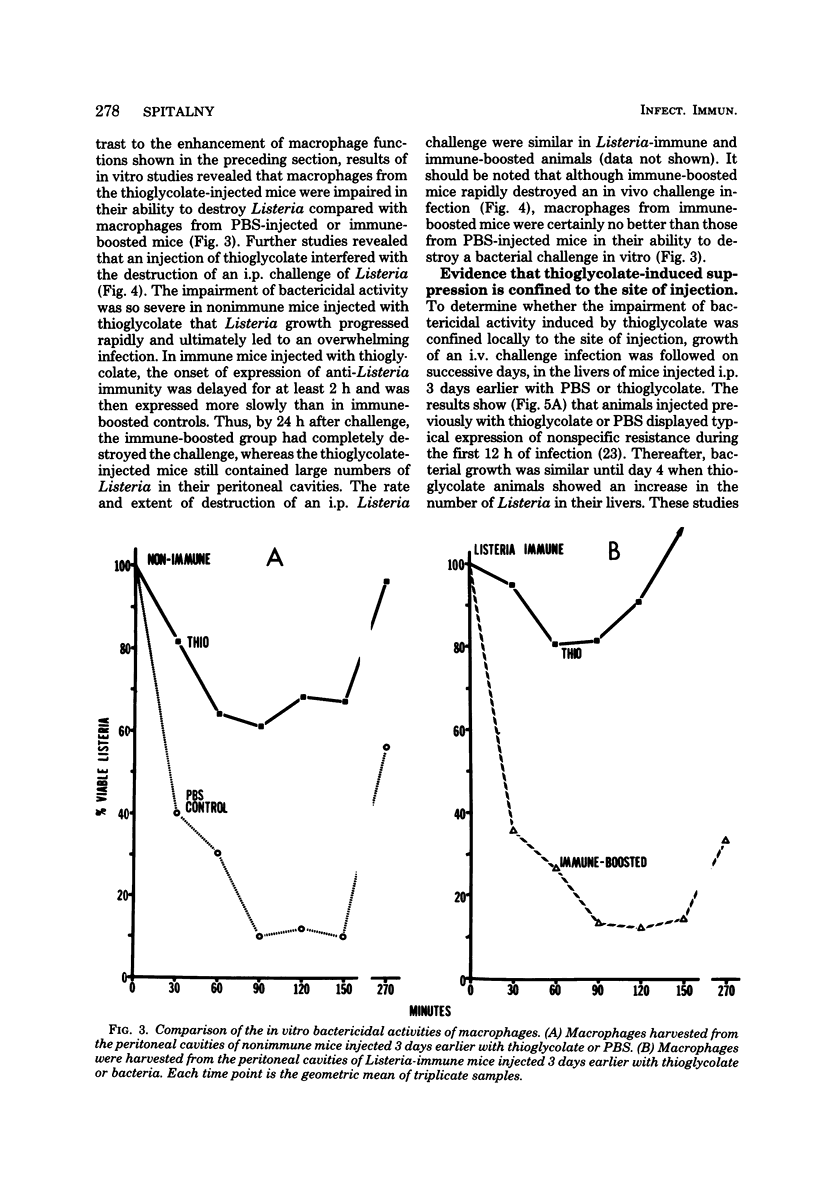
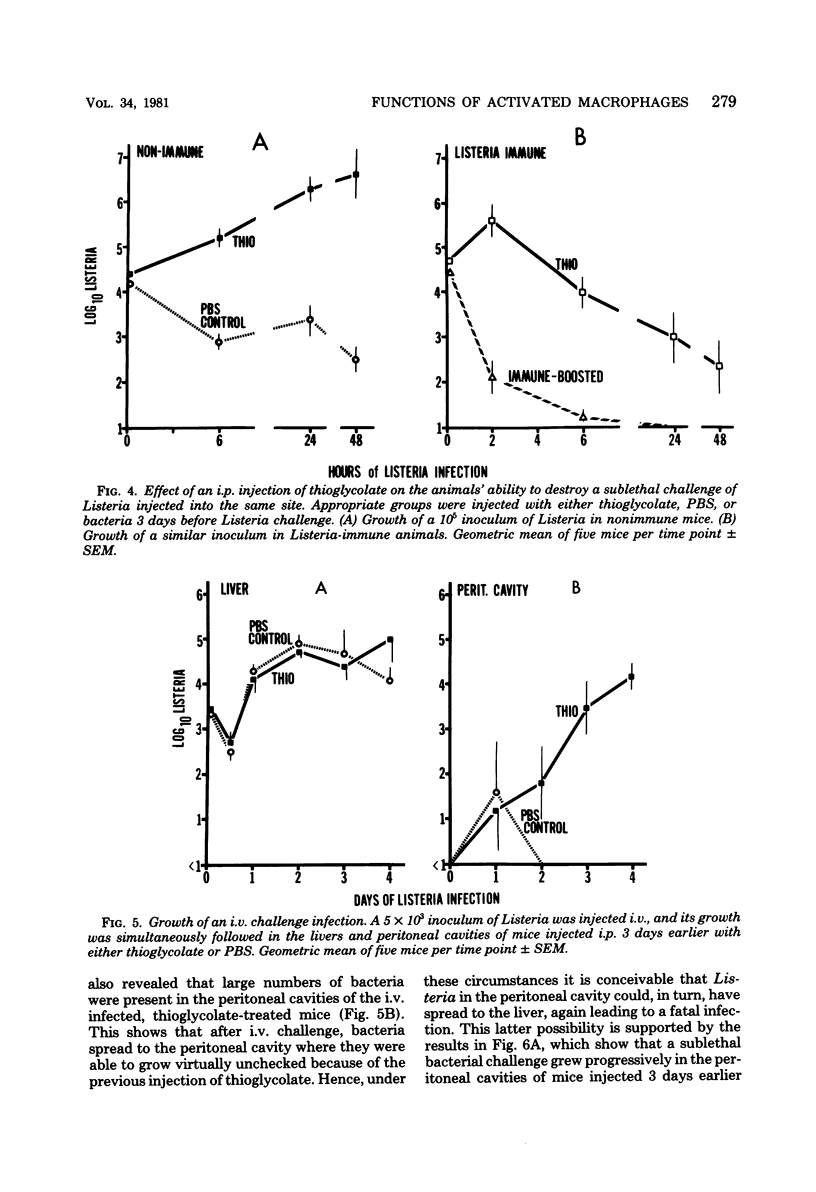
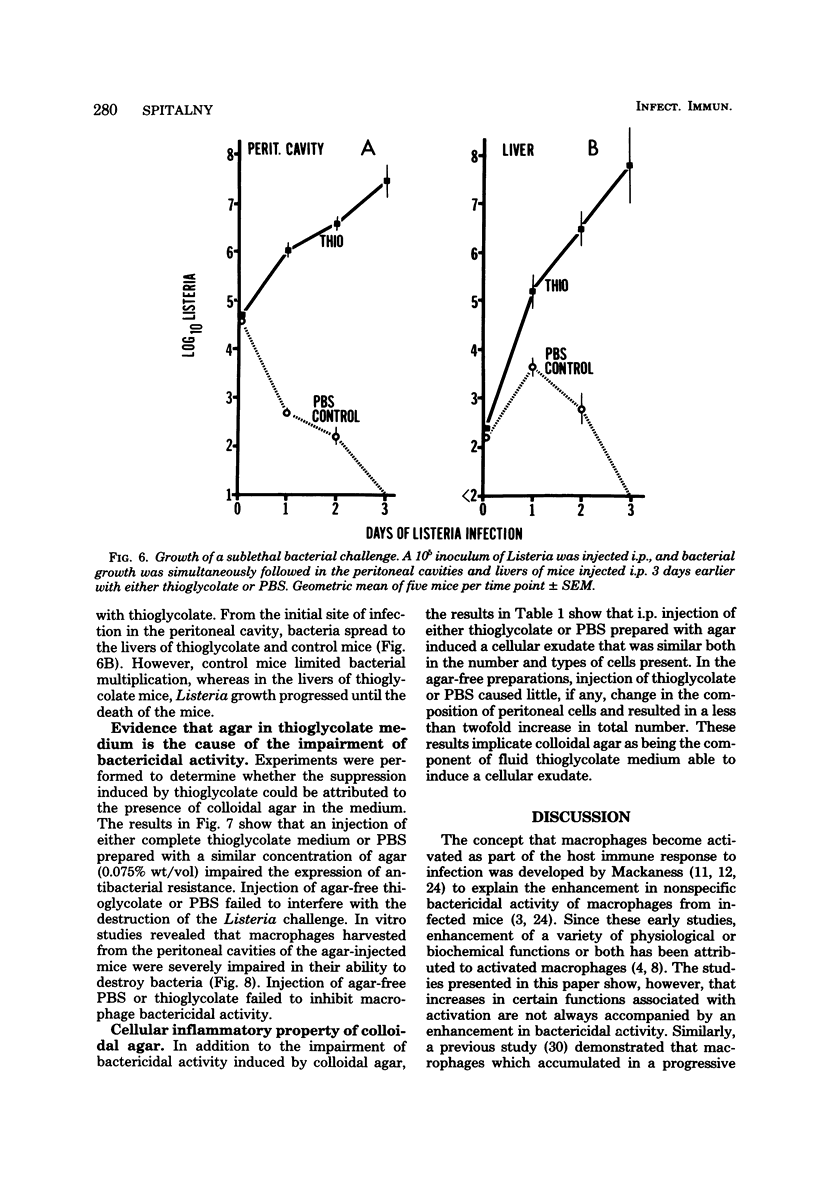
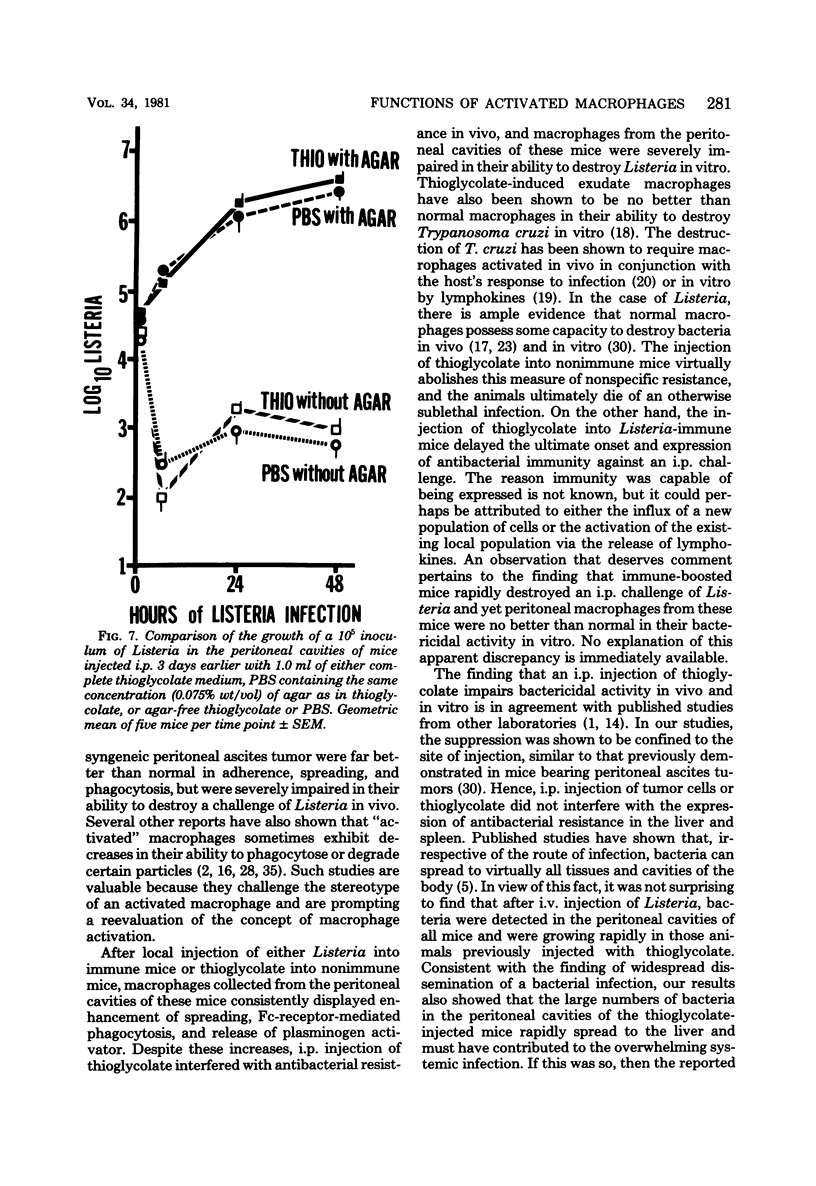
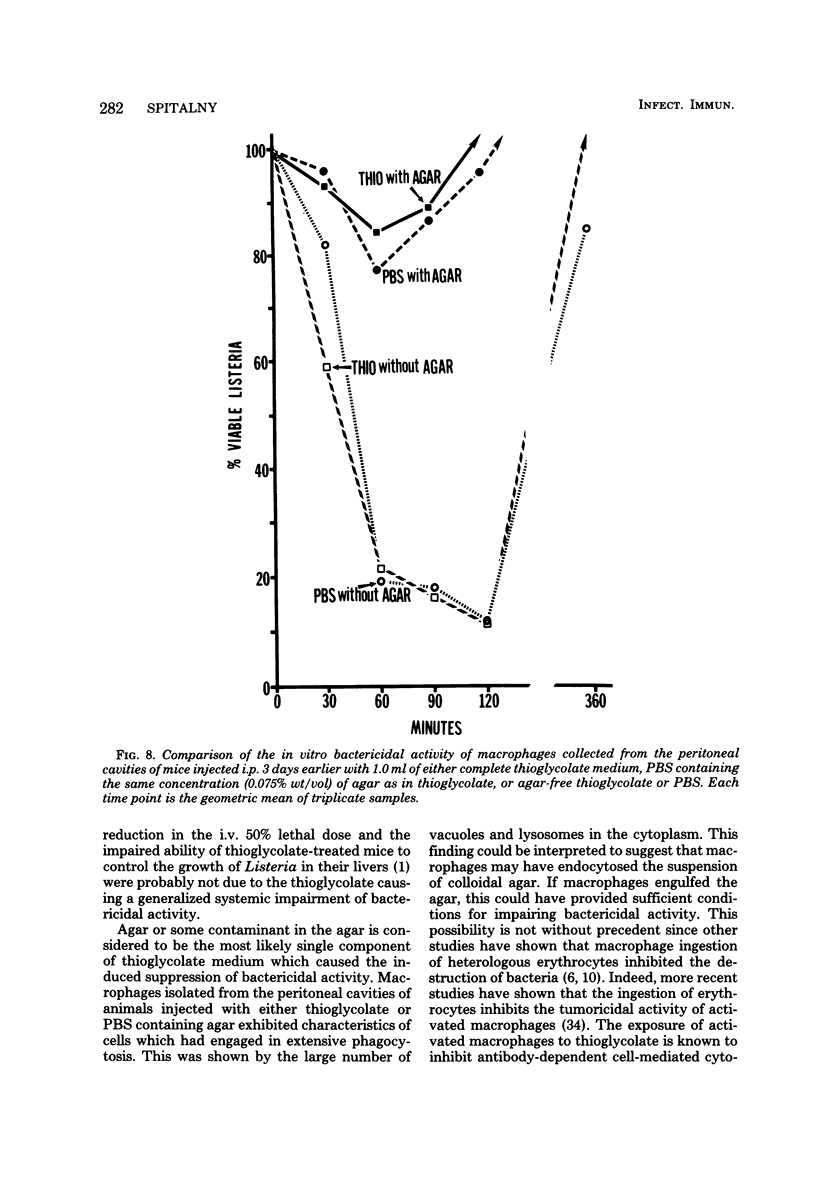
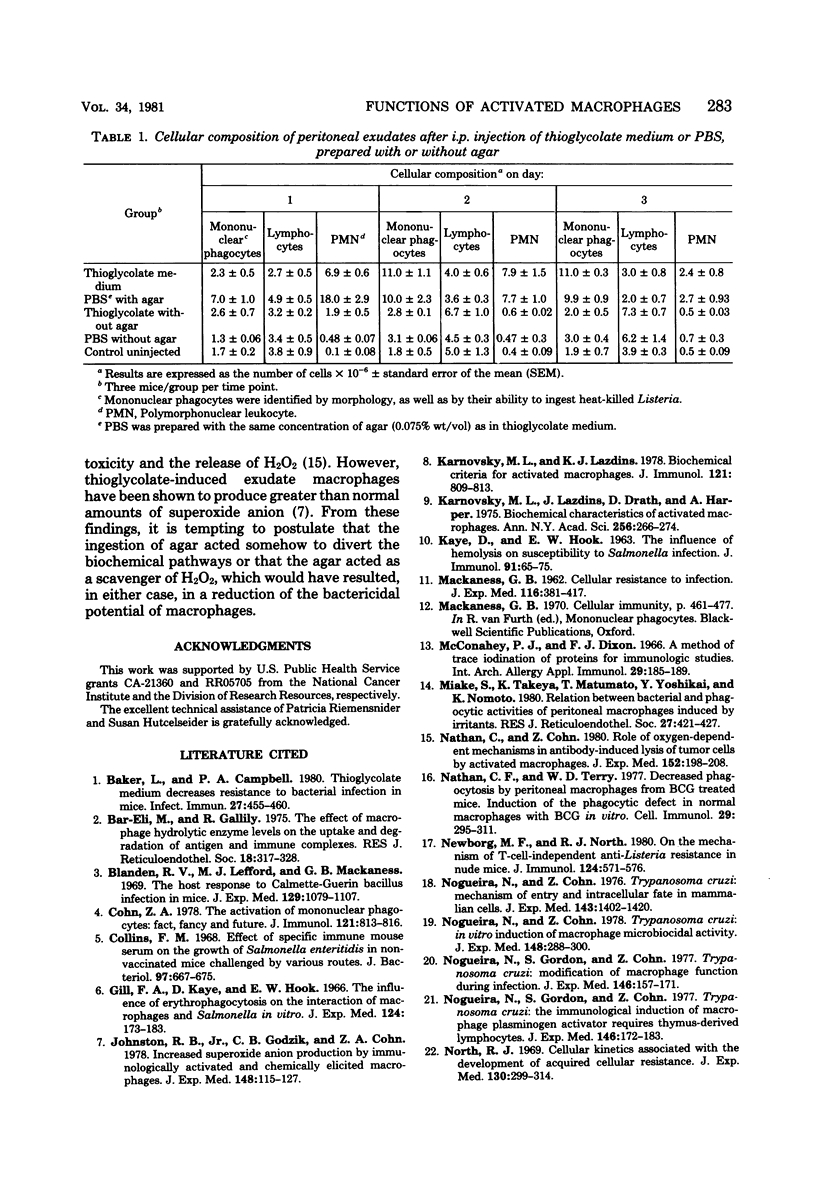
Macrophages displayed increased spreading, increased Fc-receptor-mediated phagocytosis, and increased secretion of plasminogen activator when collected from the peritoneal cavities of either Listeria-immune mice challenged intraperitoneally 3 days earlier with Listeria or nonimmune mice injected intraperitoneally 3 days earlier with fluid thioglycolate medium. In contrast, macrophages from the thioglycolate-induced peritoneal exudates were severely impaired in vitro in their ability to destroy Listeria. Injection of thioglycolate markedly interfered with the destruction of sublethal intraperitoneal challenge of Listeria, which resulted in nonimmune animals dying of an overwhelming systemic infection. In animals immune to Listeria, injection of thioglycolate delayed the onset of the expression of immunity to an intraperitoneal challenge of bacteria. The thioglycolate-induced suppression of bactericidal activity was determined to be confined to the site of injection. Results of experiments indicated that the colloidal agar in thioglycolate medium was the cause of the impairment of macrophage bactericidal activity. In addition to the impairment of bactericidal activity induced by agar, additional studies showed that an intraperitoneal injection of colloidal agar (0.075% wt/vol) by itself was a sufficient inflammatory stimulus for the accumulation of a large number of host phagocytic cells.
Full text
PDF



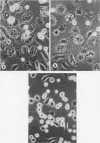
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker L. A., Campbell P. A. Thioglycolate medium decreases resistance to bacterial infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):455–460. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.455-460.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Eli M., Gallily R. The effect of macrophage hydrolytic enzyme levels on the uptake and degradation of antigen and immune complexes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Dec;18(6):317–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Lefford M. J., Mackaness G. B. The host response to Calmette-Guérin bacillus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1079–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. Activation of mononuclear phagocytes: fact, fancy, and future. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in nonvaccinated mice challenged by various routes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.667-675.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill F. A., Kaye D., Hook E. W. The influence of erythrophagocytosis on the interaction of macrophages and salmonella in vitro. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):173–183. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Godzik C. A., Cohn Z. A. Increased superoxide anion production by immunologically activated and chemically elicited macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):115–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAYE D., HOOK E. W. THE INFLUENCE OF HEMOLYSIS OR BLOOD LOSS ON SUSCEPTIBILITY TO INFECTION. J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:65–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L., Lazdins J. K. Biochemical criteria for activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L., Lazdins J., Drath D., Harper A. Biochemical characteristics of activated macrophages. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 13;256:266–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake S., Takeya K., Matsumoto T., Yoshikai Y., Nomoto K. Relation between bactericidal and phagocytic activities of peritoneal macrophages induced by irritants. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Apr;27(4):421–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Terry W. D. Decreased phagocytosis by peritoneal macrophages from BCG-treated mice: induction of the phagocytic defect in normal macrophages with BCG in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 15;29(2):295–311. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90324-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Cohn Z. Role of oxygen-dependent mechanisms in antibody-induced lysis of tumor cells by activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):198–208. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newborg M. F., North R. J. On the mechanism of T cell-independent anti-Listeria resistance in nude mice. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):571–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. A. Trypanosoma cruzi: in vitro induction of macrophage microbicidal activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):288–300. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: mechanism of entry and intracellular fate in mammalian cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1402–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Gordon S., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: modification of macrophage function during infection. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):157–171. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Gordon S., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: the immunological induction of macrophage plasminogen activator requires thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):172–183. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular kinetics associated with the development of acquired cellular resistance. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):299–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Deissler J. F. Nature of "memory" in T-cell mediated antibacterial immunity: cellular parameters that distinguish between the active immune response and a state of "memory". Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):761–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.761-767.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Kirstein D. P. T-cell-mediated concomitant immunity to syngeneic tumors. I. Activated macrophages as the expressors of nonspecific immunity to unrelated tumors and bacterial parasites. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):275–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. T cell dependence of macrophage activation and mobilization during infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):66–71. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.66-71.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The concept of the activated macrophage. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):806–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin J., Remington J. S. Immunity and intracellular infection: resistance to bacteria in mice infected with a protozoan. Science. 1968 Apr 5;160(3823):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3823.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvin S. B., Cheng S. L. Lymphoid Cells in Delayed Hypersensitivity II. In Vitro Phagocytosis and Cellular Immunity. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):548–552. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.548-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass M. J., Lowrey D. S., Hanna M. G., Jr Changes induced by lactic dehydrogenase virus in thymus and thymus-dependent areas of lymphatic tissue. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):877–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalny G. L., North R. J. Subversion of host defense mechanisms by malignant tumors: an established tumor as a privileged site for bacterial growth. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1264–1277. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalny G. L. Suppression of bactericidal activity of macrophages in ascites tumors. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Sep;28(3):223–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. C., Lin H. S., Adles C. Proliferation and colony-forming ability of peritoneal exudate cells in liquid culture. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1114–1132. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Gordon S., Reich E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by stimulated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):834–850. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Hibbs J. B., Jr Endocytosis of red blood cells or haemoglobin by activated macrophages inhibits their tumoricidal effect. Nature. 1977 Sep 15;269(5625):245–247. doi: 10.1038/269245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener E., Bandieri A. Modifications in the handling in vitro of 125I-labelled keyhole limpet haemocyanin by peritoneal macrophages from mice pretreated with the adjuvant Corynebacterium parvum. Immunology. 1975 Aug;29(2):265–274. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]