Abstract
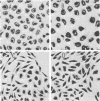
Almost all the cells in populations of mouse fibroblasts (L cells) persistently infected with the 6BC strain of Chlamydia psittaci were immune to superinfection with high multiplicities of C. psittaci, whether or not the L cells contained visible chlamydial inclusions. As ascertained by experiments with 14C-labeled C. psittaci, immunity to superinfection resulted from the failure of added chlamydiae to attach to persistently infected host cells. However, when exogenous C. psittaci was introduced into persistently infected L cells by centrifuging the inoculum onto host cell monolayers or by pretreating the monolayers with diethylaminoethyl-dextran, these chlamydiae produced expected numbers of infectious progeny. Persistently infected L cells were associated in an unknown way with a C. psittaci population that entered the host cells only with the aid of centrifugation or pretreatment with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. Inclusion-free, persistently infected L cells appeared to present at least two separate hindrances to chlamydial activity: blockage of the attachment of exogenous elementary bodies to persistently infected host cells and prevention of the initiation of chlamydial multiplication by means of a normal developmental cycle in the absence of added C. psittaci.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byrne G. I. Kinetics of phagocytosis of Chlamydia psittaci by mouse fibroblasts (L cells): separation of the attachment and ingestion stages. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):607–612. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.607-612.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I. Requirements for ingestion of Chlamydia psittaci by mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):645–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.645-651.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. R. In situ detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by fluorescent Hoechst 33258 stain. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Feb;104(2):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON F. B., QUAN A. L. ISOLATION OF THE TRACHOMA AGENT IN CELL CULTURE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Feb;118:354–359. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P. Competition between Chlamydia psittaci and L cells for host isoleucine pools: a limiting factor in chlamydial multiplication. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):211–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.211-220.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg K. R., Horoschak K. D., Moulder J. W. Toxicity of low and moderate multiplicities of Chlamydia psittaci for mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):531–541. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.531-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K. Interaction between a trachoma strain of Chlamydia trachomatis and mouse fibroblasts (McCoy cells) in the absence of centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.584-591.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Levy N. J., Schulman L. P. Persistent infection of mouse fibroblasts (L cells) with Chlamydia psittaci: evidence for a cryptic chlamydial form. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):874–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.874-883.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rota T. R., Nichols R. L. Infection of cell cultures by trachoma agent: enhancement by DEAE-dextran. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):419–421. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spears P., Storz J. Biotyping of Chlamydia psittaci based on inclusion morphology and response to diethylaminoethyl-dextran and cycloheximide. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):224–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.224-232.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]