Abstract
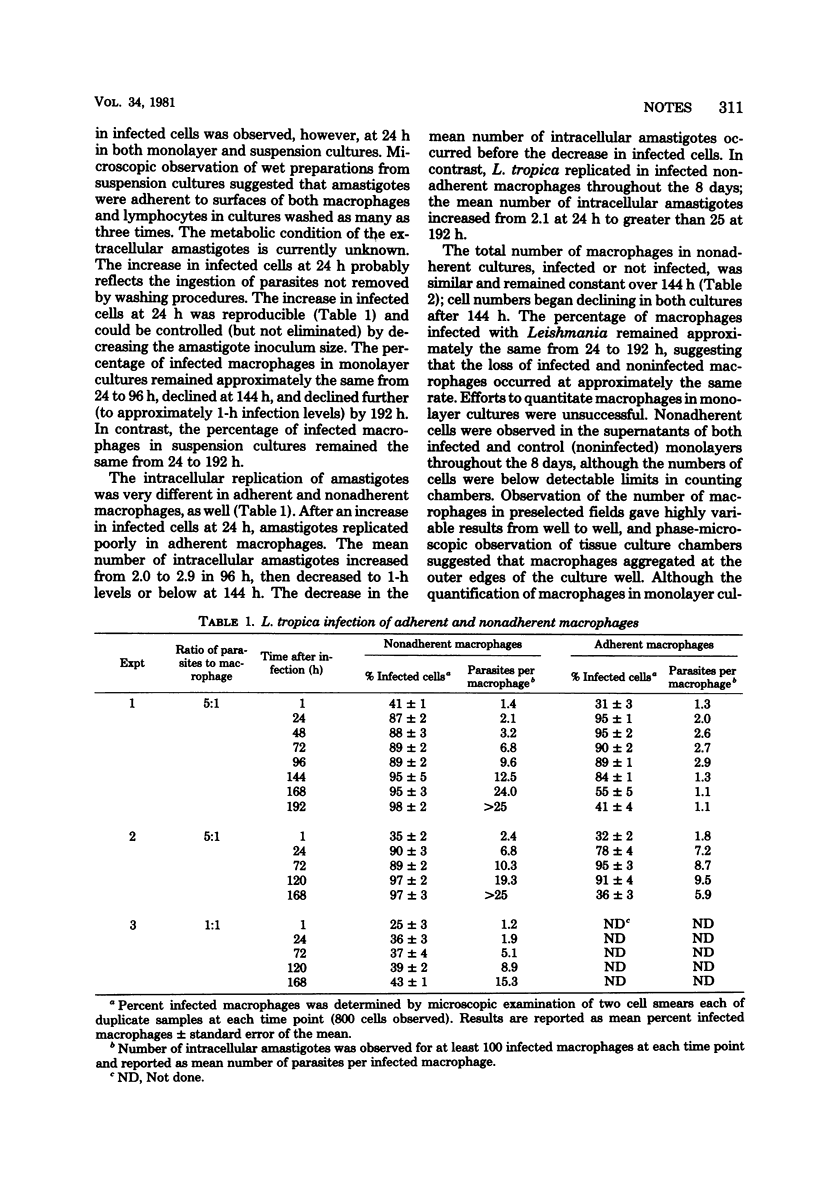
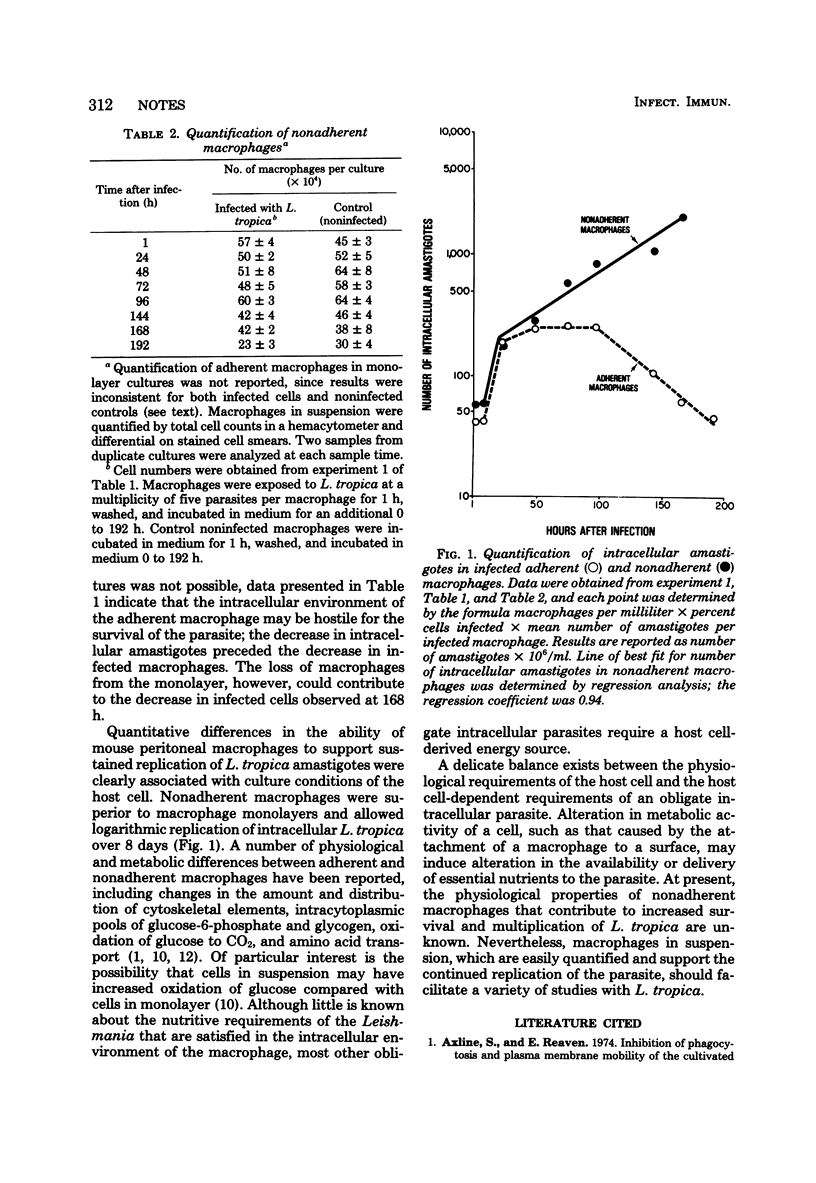
Intracellular replication of Leishmania tropica was assessed in mouse peritoneal macrophage cultures. L. tropica replicated poorly in macrophage monolayers: both the percentage of cells infected and the number of intracellular amastigotes decreased with time in culture. In contrast, nonadherent macrophages supported continuous replication of the parasite, and intracellular amastigotes increased more than 10-fold in these cultures over 8 days.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axline S. G., Reaven E. P. Inhibition of phagocytosis and plasma membrane mobility of the cultivated macrophage by cytochalasin B. Role of subplasmalemmal microfilaments. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):647–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behin R., Mauel J., Biroum-Noerjasin, Rowe D. S. Mechanisms of protective immunity in experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis of the guinea-pig. II. Selective destruction of different Leishmania species in activated guinea-pig and mouse macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):351–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behin R., Mauel J., Sordat B. Leishmania tropica: pathogenicity and in vitro macrophage function in strains of inbred mice. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Aug;48(1):81–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. D., Dwyer D. M., Wyler D. J. Multiplication of Leishmania in human macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):375–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.375-379.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller Y., Mauel J. Studies on the mechanisms of macrophage activation. II. Parasite destruction in macrophages activated by supernates from concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):359–370. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P., Dwyer D. M. Multiplication of a human parasite (Leishmania donovani) in phagolysosomes of hamster macrophages in vitro. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):678–680. doi: 10.1126/science.948742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P. Leishmania infection of human skin fibroblasts in vitro: absence of phagolysosomal fusion after induced phagocytosis of promastigotes, and their intracellular transformation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Nov;27(6):1084–1096. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Burgess A. W. Stimulation by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor of Leishmania tropica killing by macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):1134–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Spira D. T. Growth of Leishmania amastigotes in macrophages from normal and immune mice. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Aug 25;53(1):75–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00383117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdins J. K., Koech D. K., Karnovsky M. L. Oxidation of glucose by mouse peritoneal macrophages: a comparison of suspensions and monolayers. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Nov;105(2):191–196. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauel J., Buchmüller Y., Behin R. Studies on the mechanisms of macrophage activation. I. Destruction of intracellular Leishmania enriettii in macrophages activated by cocultivation with stimulated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):393–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pofit J. F., Strauss P. R. Membrane transport by macrophages in suspension and adherent to glass. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Aug;92(2):249–255. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


