Abstract
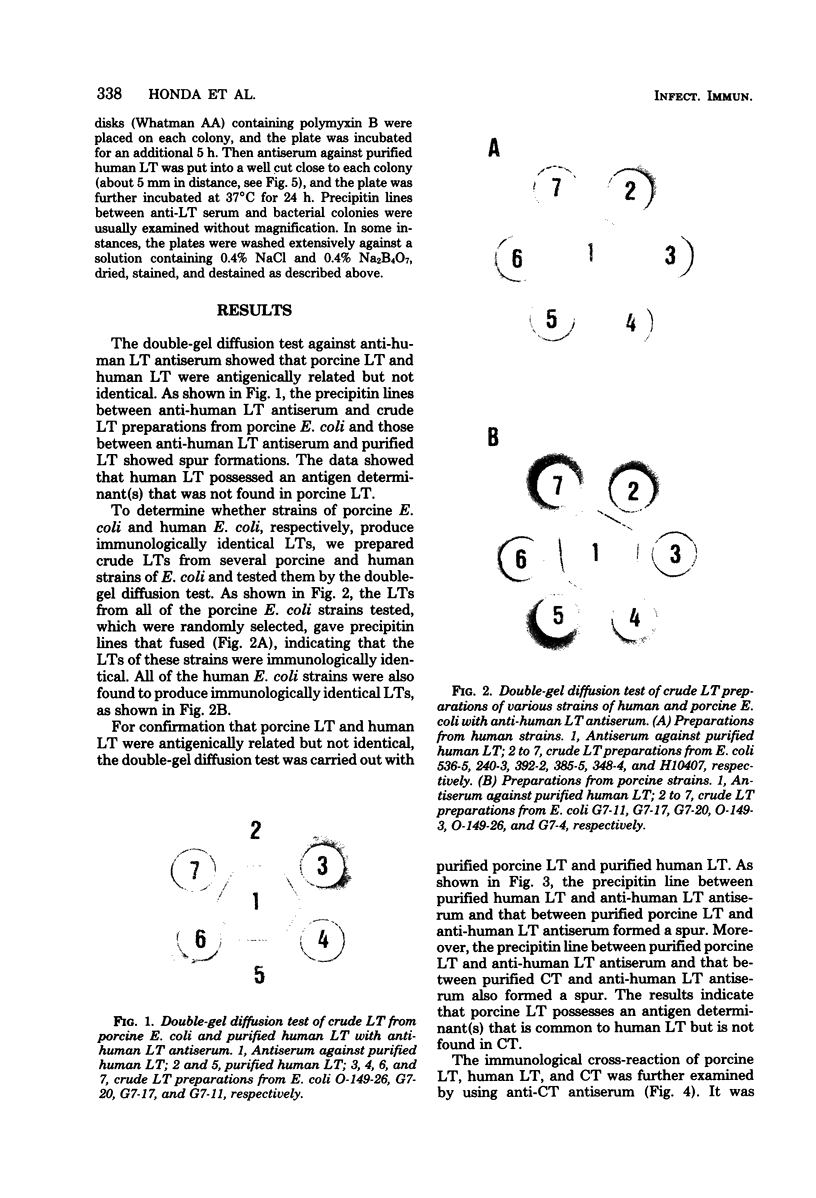
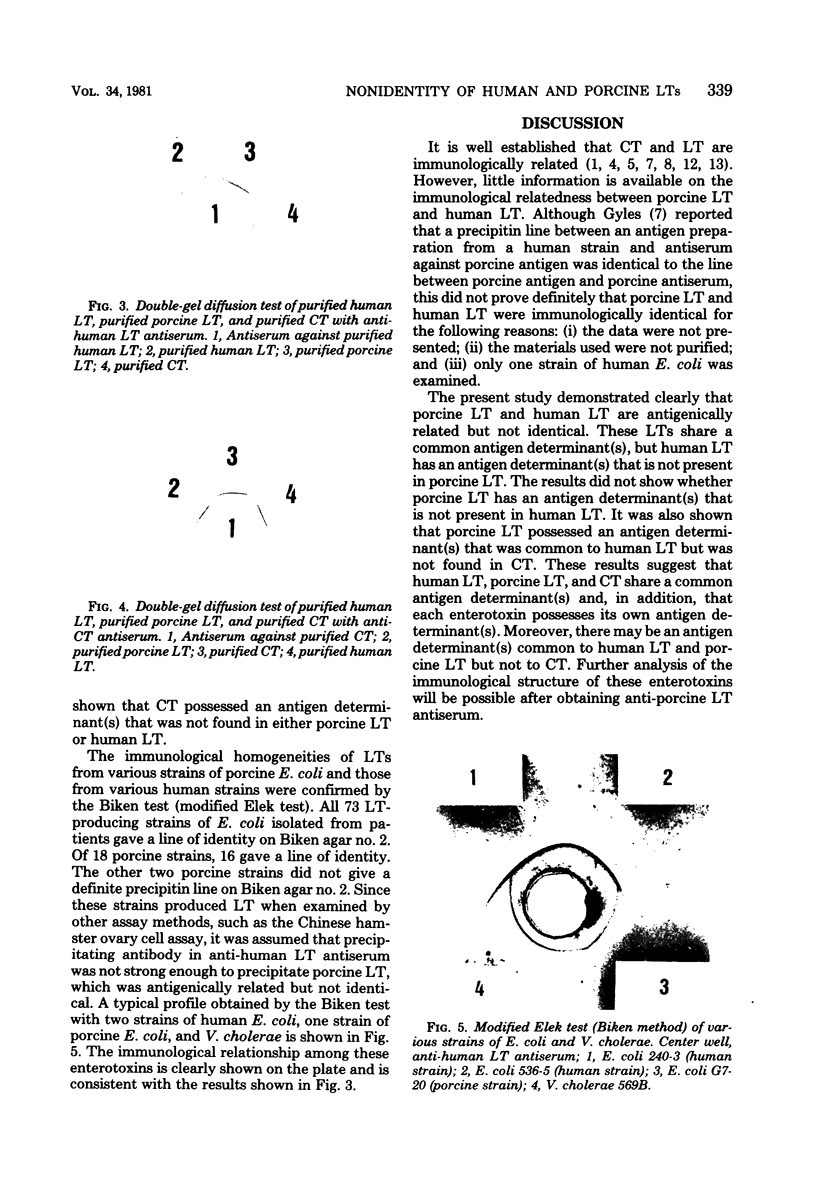
The Ouchterlony double-gel diffusion test demonstrated that heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) from human strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli was antigenically related but not identical to that from porcine E. coli. All human strains examined produced immunologically identical LTs, and all porcine strains examined produced immunologically identical LTs. The Biken test (modified Elek test), developed for detection of E. coli LT (Honda et al., J. Clin. Microbiol. 13: 1-5, 1981), was useful for confirmation of these results.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological cross-reactivity between a heat-labile enterotoxin(s) of Escherichia coli and subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1036-1039.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Amino acid sequence homology between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):499–501. doi: 10.1038/288499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T. Neutralization of cholera enterotoxin-induced steroidogenesis by specific antibody. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):284–288. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Gorbach S. L. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and serum antitoxin activity by the vascular permeability factor assay. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):731–735. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.731-735.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera. Preparation and isolation of choleragen and choleragenoid. J Exp Med. 1969 Jul 1;130(1):185–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Immunological study of the heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.564-570.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Taga S., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Modified Elek test for detection of heat-labile enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.1-5.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. W., Sack R. B. Immunologic cross-reactions of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):164–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Kavanaugh W. M., Dallas W. S., Falkow S., Konigsberg W. H., Schafer D. E. Sequence homologies between A subunits of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):50–54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Honda T., Taga S., Miwatani T. In vitro formation of hybrid toxins between subunits of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and those of cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.341-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]