Abstract
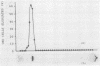
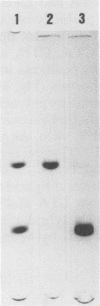
Heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) was purified from cells of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from a patient with traveller's diarrhea. Purified LT was separated into A and B subunits by treatment with 6 M urea solution in 0.1 M propionic acid (pH 4.0). Biologically active toxin was reconstituted from isolated A and B subunits of LT. Hybrid toxins with biological activity were obtained in vitro from the A subunit of cholera enterotoxin and B subunit of LT, and from the A subunit of LT and B subunit of cholera enterotoxin. The hybrid toxins show a similar toxicity to that of the parent toxins from which the A subunits were derived. The in vitro formations of the hybrid toxins were confirmed by polyacrylamide gel disk electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Demonstration of shared and unique immunological determinants in enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):709–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.709-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological cross-reactivity between a heat-labile enterotoxin(s) of Escherichia coli and subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1036-1039.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Yancey R. J., Finkelstein R. A. Properties of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):91–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.91-97.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P. A permeability factor (toxin) found in cholera stools and culture filtrates and its neutralization by convalescent cholera sera. Nature. 1965 Aug 7;207(997):614–616. doi: 10.1038/207614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Amino acid sequence homology between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):499–501. doi: 10.1038/288499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. The molecular nature of heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) of escherichia coli. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):406–407. doi: 10.1038/277406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T. Neutralization of cholera enterotoxin-induced steroidogenesis by specific antibody. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):284–288. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Gorbach S. L. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and serum antitoxin activity by the vascular permeability factor assay. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):731–735. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.731-735.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Boesman M., Neoh S. H., LaRue M. K., Delaney R. Dissociation and recombination of the subunits of the cholera enterotoxin (choleragen). J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera. Preparation and isolation of choleragen and choleragenoid. J Exp Med. 1969 Jul 1;130(1):185–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Banwell J. G., Chatterjee B. D., Jacobs B., Sack R. B. Acute undifferentiated human diarrhea in the tropics. I. Alterations in intestinal micrflora. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):881–889. doi: 10.1172/JCI106560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. A heat-labile enterotoxin from strains of Eschericha coli enteropathogenic for pigs. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):419–426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Immunological study of the heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.564-570.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Shimizu M., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Isolation of a factor causing morphological changes of chinese hamster ovary cells from the culture filtrate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1028-1033.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Taga S., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Modified Elek test for detection of heat-labile enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.1-5.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levner M., Wiener F. P., Rubin B. A. Induction of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxins by an inhibitor of protein synthesis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):132–137. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.132-137.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundell D. H., Anselmo C. R., Wishnow R. M. Factors influencing heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):383–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.383-388.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtomo N., Muraoka T., Tashiro A., Zinnaka Y., Amako K. Size and structure of the cholera toxin molecule and its subunits. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):31–40. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_1.s31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. S., Sagin J. F., Pierzchala W. A., Bonde G., Rubin B. A., Tint H. Activation of Heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin by trypsin. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):41–54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_1.s41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. W., Sack R. B. Immunologic cross-reactions of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):164–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Kavanaugh W. M., Dallas W. S., Falkow S., Konigsberg W. H., Schafer D. E. Sequence homologies between A subunits of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):50–54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto T., Kinoshita Y., Taga S., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Value of passive immune hemolysis for detection of heat-labile enterotoxin produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):768–771. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.768-771.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]