Abstract
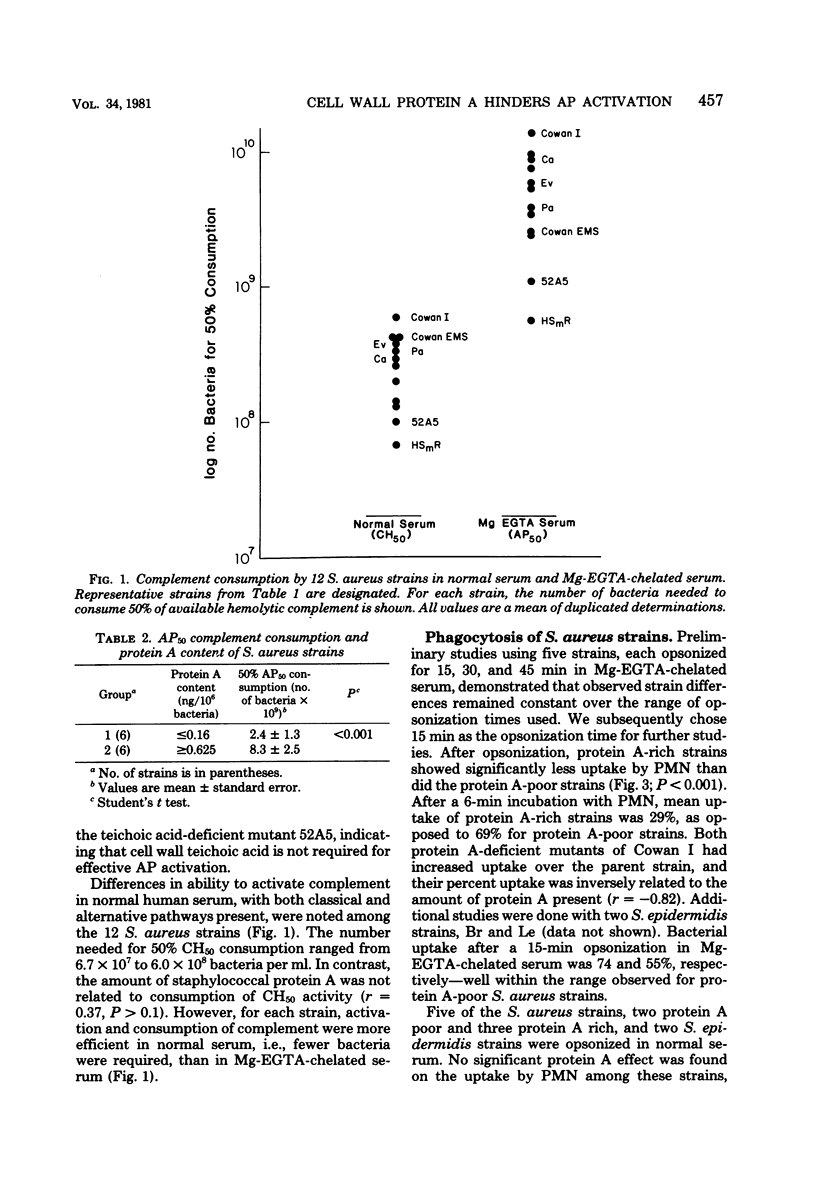
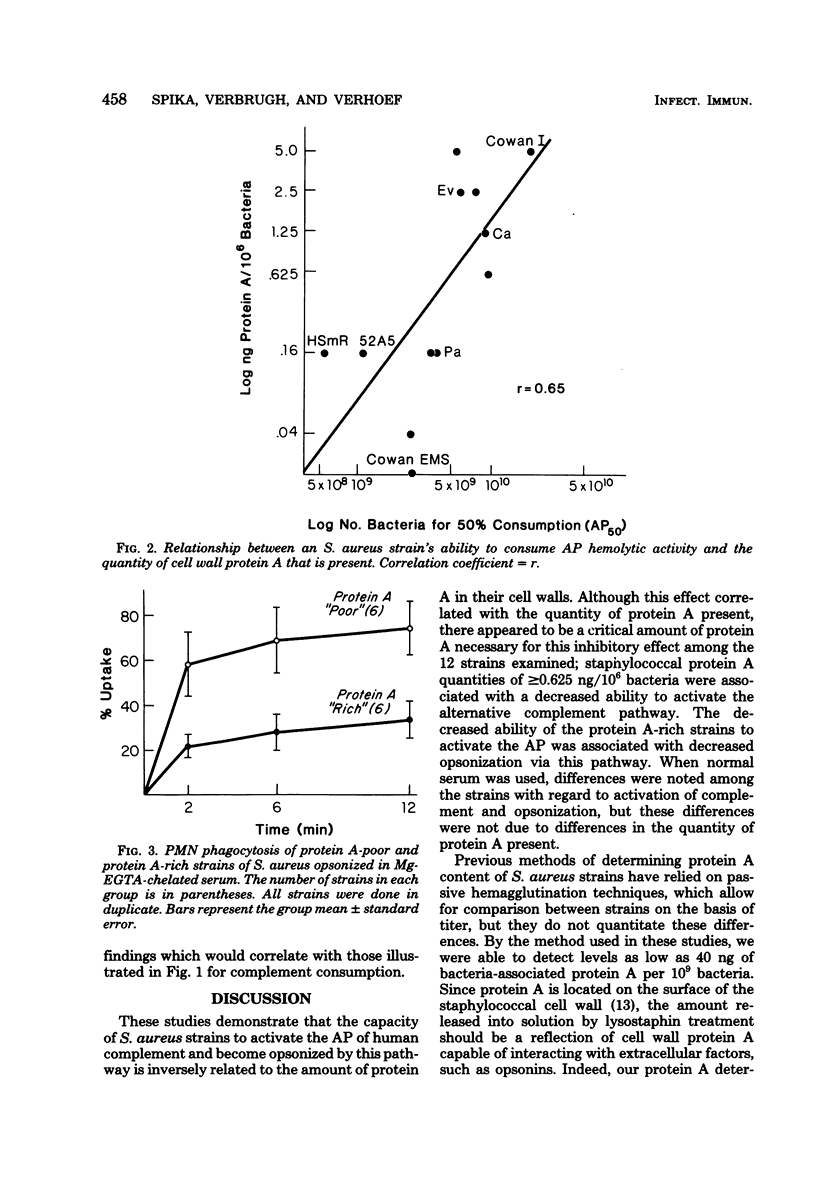
Twelve Staphylococcus aureus strains with known amounts of protein A were compared with regard to alternative pathway complement activation and opsonization in human serum. "Protein A-poor" strains (less than or equal to 0.16 ng/10(6) bacteria) were, on the average, 3. 4-fold more efficient in alternative pathway complement activation than "protein A-rich" strains (greater than or equal to 0.625 ng/10(6) bacteria) (P less than 0.001). Protein A-poor strains were significantly better phagocytized by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes after opsonization in magnesium-ethylene glycol-bis (beta-amino-ethyl ether)-N, N-tetraacetic acid-chelated serum than were the protein A-rich strains (P less than 0.001). No significant differences between protein A-poor and -rich strains were found in complement activation and opsonization in normal serum. Cell wall-bound protein A appeared to hinder alternative pathway complement activation by S. aureus, which resulted in decreased opsonization of these bacteria in the absence of an intact classical pathway. These studies suggest that protein A may cover alternative pathway complement-activating sites within the peptidoglycan matrix of the staphylococcal cell wall.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forsgren A., Nordström K., Philipson L., Sjöquist J. Protein A mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):245–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.245-250.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Influence of the alternate complement pathway in opsonization of several bacterial species. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):402–404. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.402-404.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Nelson R. A., Jr Complement dependent immune phagocytosis. I. Requirements for C'1, C'4, C'2, C'3. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jul;51(1):45–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys D. W., Wheat L. J., White A. Staphylococcal heat-stable opsonins. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jul;84(1):122–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Gewurz H. Activation and inhibition of IgG mediated complement fixation by staphylococcal protein A. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):211–220. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch H., Kümel G., Hammer H. J. Large-scale purification of IgM from human sera. Comparison of three optimized procedures utilizing protein A chromatography. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1980;177(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF01851630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Effect of protein A on staphylococcal opsonization. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.760-764.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Douglas S. D., Quie P. G., Verhoef J. The key role of peptidoglycan in the opsonization of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):597–609. doi: 10.1172/JCI108971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Field R. J., Gitlin J. D., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. The opsonic fragment of the third component of human complement (C3). J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1329–1347. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålenheim G., Götze O., Cooper N. R., Sjöquist J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Consumption of human complement components by complexes of IgG with protein A of Staphylococcus aureus. Immunochemistry. 1973 Aug;10(8):501–507. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peterson P. K., Smith D. E., Nguyen B. Y., Hoidal J. R., Wilkinson B. J., Verhoef J., Furcht L. T. Human fibronectin binding to staphylococcal surface protein and its relative inefficiency in promoting phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.811-819.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Van Dijk W. C., Peters R., Van Der Tol M. E., Verhoef J. The role of Staphylococcus aureus cell-wall peptidoglycan, teichoic acid and protein A in the processes of complement activation and opsonization. Immunology. 1979 Jul;37(3):615–621. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P., Kim Y., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Opsonic requirements for staphylococcal phagocytosis. Heterogeneity among strains. Immunology. 1977 Aug;33(2):191–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G., Michael A. F. Activation of complement by cell surface components of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):388–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.388-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


