Abstract
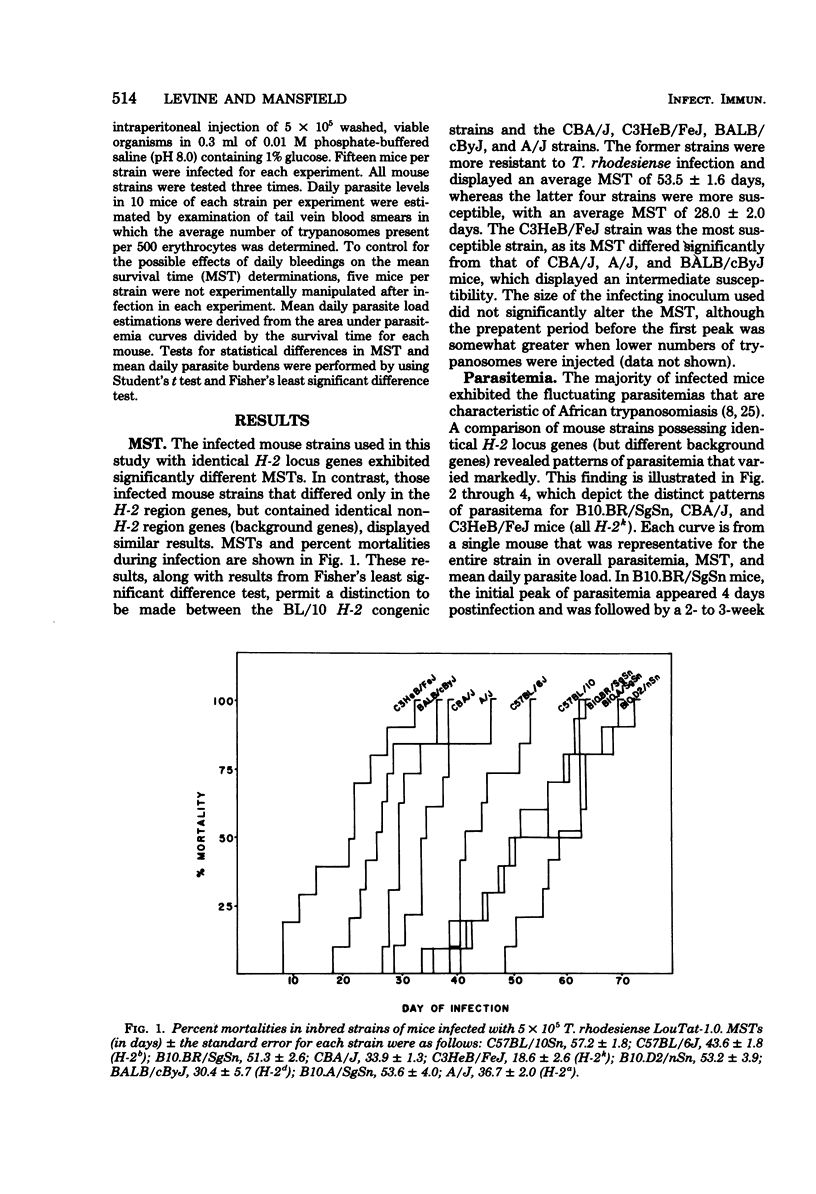
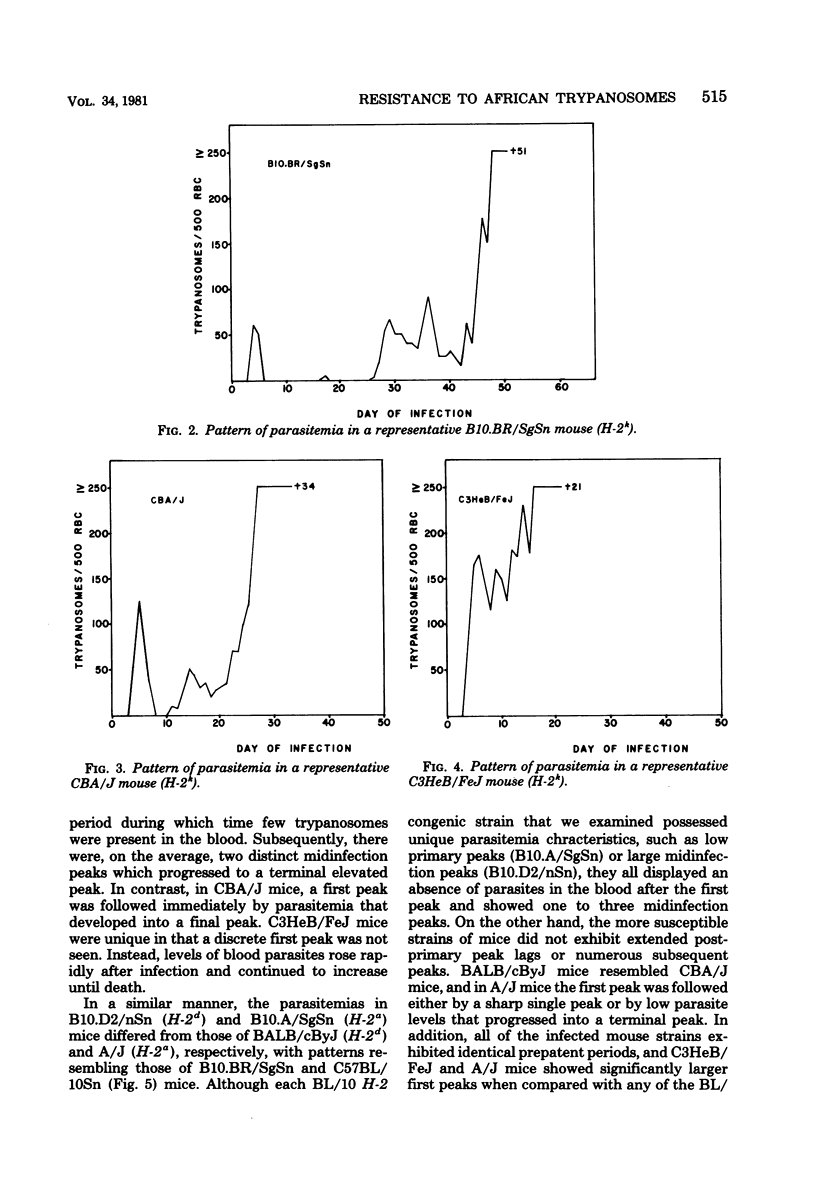
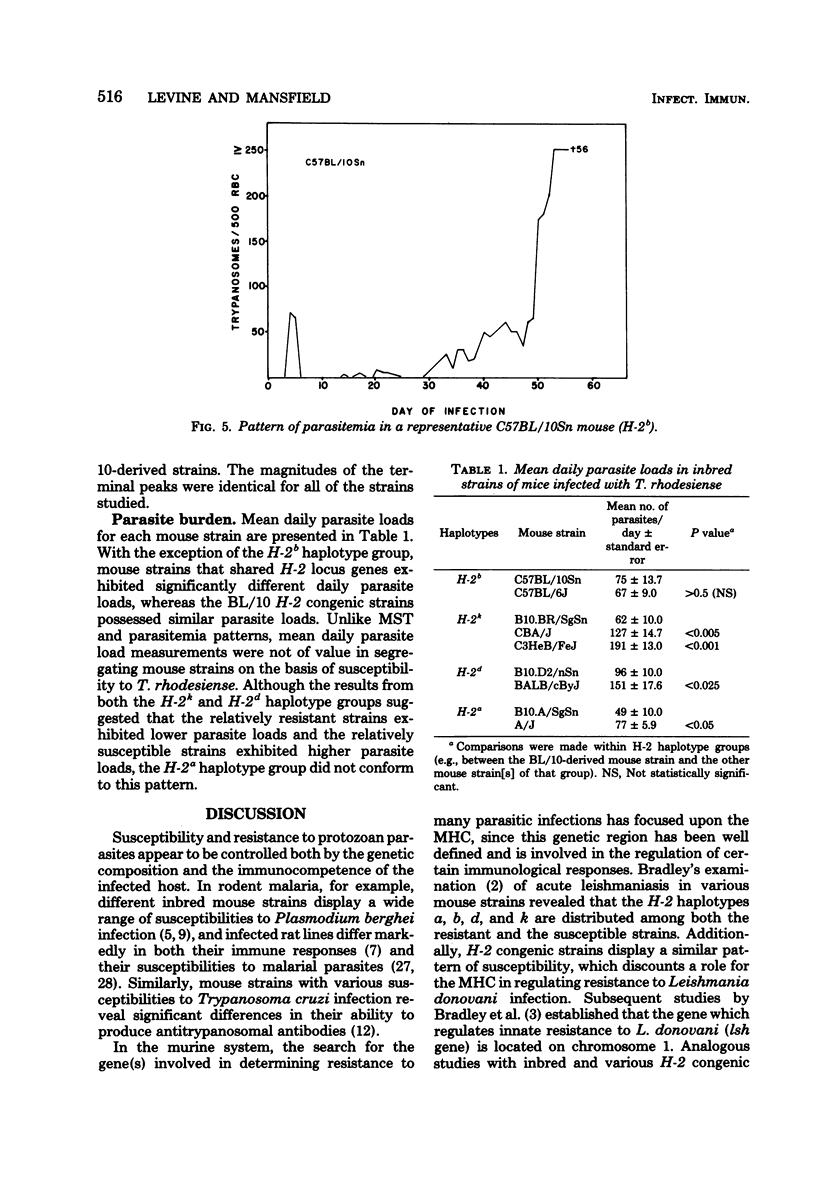
Susceptibility and resistance to Trypanosoma rhodesiense infections in inbred and H-2 congenic strains of mice were studied. Mean survival times and patterns of parasitemia were examined. C3HeB/FeJ mice were highly susceptible; CBA/J, A/J, and BALB/cByJ mice displayed an intermediate level of susceptibility; whereas C57BL/10 mice were highly resistant. H-2 congenic strains with the BL/10 background resembled the BL/10 parental type, thereby suggesting that the major histocompatibility complex does not play a major role in regulating resistance and susceptibility to infection with T. rhodesiense.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B., McDevitt H. O. Histocompatibility-linked immune response genes. Science. 1972 Jan 21;175(4019):273–279. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4019.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. II. genetic control of acute susceptibility of mice to Leishmania donovani infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Taylor B. A., Blackwell J., Evans E. P., Freeman J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. III. Mapping of the locus controlling susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):7–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E. Trypanosoma brucei: influence of host strain and parasite antigenic type on infections in mice. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Apr;44(2):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eling W., van Zon A., Jerusalem C. The course of a Plasmodium berghei infection in six different mouse strains. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Dec 13;54(1):29–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00380634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG J., KENDRICK L. P. Parasitemia and survival in inbred strains of mice infected with Plasmodium berghei. J Parasitol. 1957 Aug;43(4):413–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser D. L., Silvers W. K. Genetic determinants of immunological responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:1–66. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenser J., Spira D. T., Zuckerman A. Neutralizing antibody in Rodent Malaria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1975;69(2):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(75)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: genetics of natural resistance to infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):583–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.583-588.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F., Howard J. G. Mechanisms of resistance against experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infection: the importance of antibodies and antibody-forming capacity in the Biozzi high and low responder mice. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1208–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanham S. M., Godfrey D. G. Isolation of salivarian trypanosomes from man and other mammals using DEAE-cellulose. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Dec;28(3):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly F. The role of genetics in Gross virus leukemogenesis. Bibl Haematol. 1970;(36):213–220. doi: 10.1159/000391710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield J. M. Immunobiology of African trypanosomiasis. Cell Immunol. 1978 Aug;39(1):204–210. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison W. I., Murray M. Trypanosoma congolense: inheritance of susceptibility to infection in inbred strains of mice. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Dec;48(3):364–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison W. I., Roelants G. E., Mayor-Withey K. S., Murray M. Susceptibility of inbred strains of mice to Trypanosoma congolense: correlation with changes in spleen lymphocyte populations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Apr;32(1):25–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trischmann T., Tanowitz H., Wittner M., Bloom B. Trypanosoma cruzi: role of the immune response in the natural resistance of inbred strains of mice. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Aug;45(2):160–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. Antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):613–617. doi: 10.1038/273613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


