Abstract
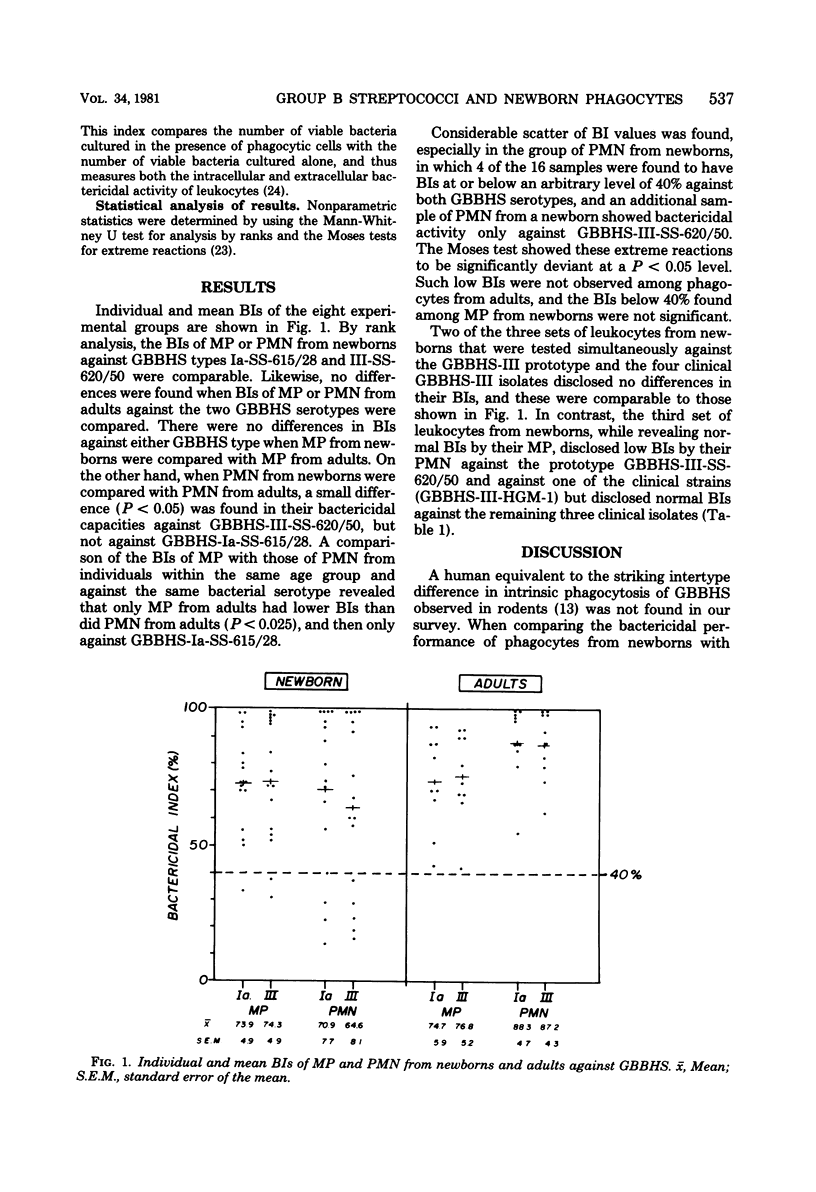
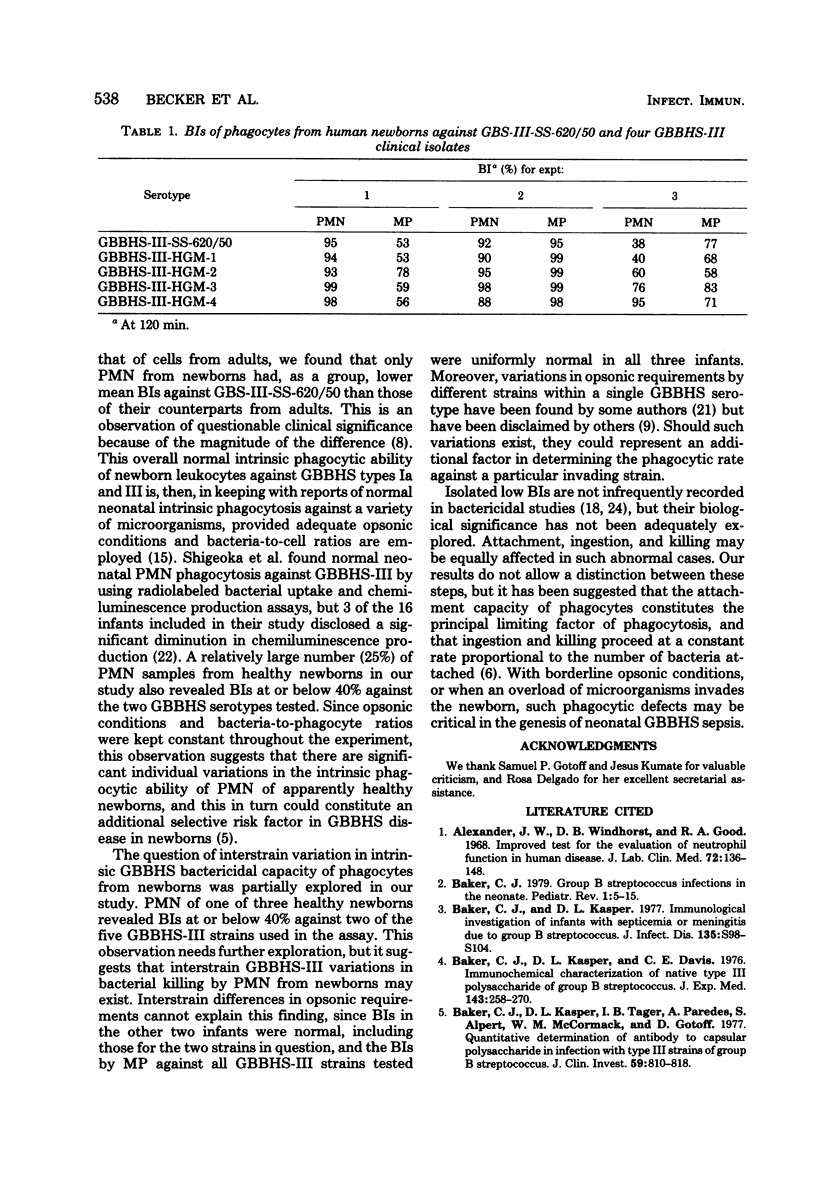
The bactericidal capacity of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear phagocytes obtained from normal newborn infants and from healthy adults was evaluated in vitro, using two group B beta-hemolytic streptococci (GBBHS) serotypes (GBBHS-Ia-SS-615/28 and GBBHS-III-SS-620/50) and uniform opsonic conditions. No intertype differences in bacteriolysis of these two serotypes were observed among leukocytes from newborns or adults. As group, only polymorphonuclear phagocytes from newborns disclosed a significantly lower mean bactericidal capacity than their adult cellular counterpart, and only with respect to GBBHS-III-SS-620/50. On the other hand, 4 or 16 polymorphonuclear samples from newborns tested revealed significantly low bactericidal capacities against both GBBHS serotypes, and an additional sample revealed a bactericidal capacity against GBBHS-III-SS-620/50 alone. Interstrain variations in the intrinsic bactericidal capacity of polymorphonuclear phagocytes from newborns against GBBHS-III may exist, as suggested by a single observation made by using four clinical isolates of GBBHS-III. Such deviant phagocytic capacities of polymorphonuclear phagocytes from newborns may constitute an additional selective risk factor in the genesis of GBBHS sepsis of the newborn.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W., Windhorst D. B., Good R. A. Improved tests for the evaluation of neutrophil function in human disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jul;72(1):136–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Davis C. E. Immunochemical characterization of the "native" type III polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1976 Feb 1;143(2):258–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.2.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Immunological investigation of infants with septicemia or meningitis due to group B Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S98–104. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Tager IRAB, Paredes A., Alpert S., McCormack W. M., Goroff D. Quantitative determination of antibody to capsular polysaccharide in infection with type III strains of group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):810–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI108703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkstén B., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Quie P. G. Limiting factors in bacterial phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Oct;85(5):345–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb03652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., Repine J. E. Quantitation of maximal bactericidal capability in human neutrophils. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Aug;88(2):316–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICKHOFF T. C., KLEIN J. O., DALY A. K., INGALL D., FINLAND M. NEONATAL SEPSIS AND OTHER INFECTIONS DUE TO GROUP B BETA-HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. N Engl J Med. 1964 Dec 10;271:1221–1228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196412102712401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Opsonic specificity of human antibody to the type III polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):1004–1008. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Nicholson-Weller A., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. The role of specific antibody in alternative complement pathway-mediated opsonophagocytosis of type III, group B Streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1275–1287. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer R. R., Gotoff S. P. Immunological aspects of group B streptococcal infections. Infection. 1978;6(4):146–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01641901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer R., Vogel L. C., Kelly P., Padnos D., Goldman M., Adueh W. M., Gotoff S. P. Murine resistance to type III group B streptococci. Infection. 1980;8(2):54–57. doi: 10.1007/BF01639146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Baker C. J., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Association of elevated levels of extracellular neuraminidase with clinical isolates of type III group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):738–746. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.738-746.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills E. L., Thompson T., Björkstén B., Filipovich D., Quie P. G. The chemiluminescence response and bactericidal activity of polymorphonuclear neutrophils from newborns and their mothers. Pediatrics. 1979 Mar;63(3):429–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J. P., Sieger L., Anthony B. F. Bactericidal capacity of monocytes of newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1976 Nov;89(5):797–801. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80810-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass M. A., Gray B. M., Khare S., Dillon H. C., Jr Prospective studies of group B streptococcal infections in infants. J Pediatr. 1979 Sep;95(3):437–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., White J. G., Holmes B., Good R. A. In vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):668–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI105568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeoka A. O., Hall R. T., Hill H. R. Strain specificity of opsonins for group B streptococci types II and III. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):438–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.438-445.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeoka A. O., Santos J. I., Hill H. R. Functional analysis of neutrophil granulocytes from healthy, infected, and stressed neonates. J Pediatr. 1979 Sep;95(3):454–460. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80535-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steigbigel R. T., Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. Phagocytic and bacterial properties of normal human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):131–142. doi: 10.1172/JCI107531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennerstrom D. E., Schutt R. W. Adult mice as a model for early onset group B streptococcal disease. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):741–744. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.741-744.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


