Abstract
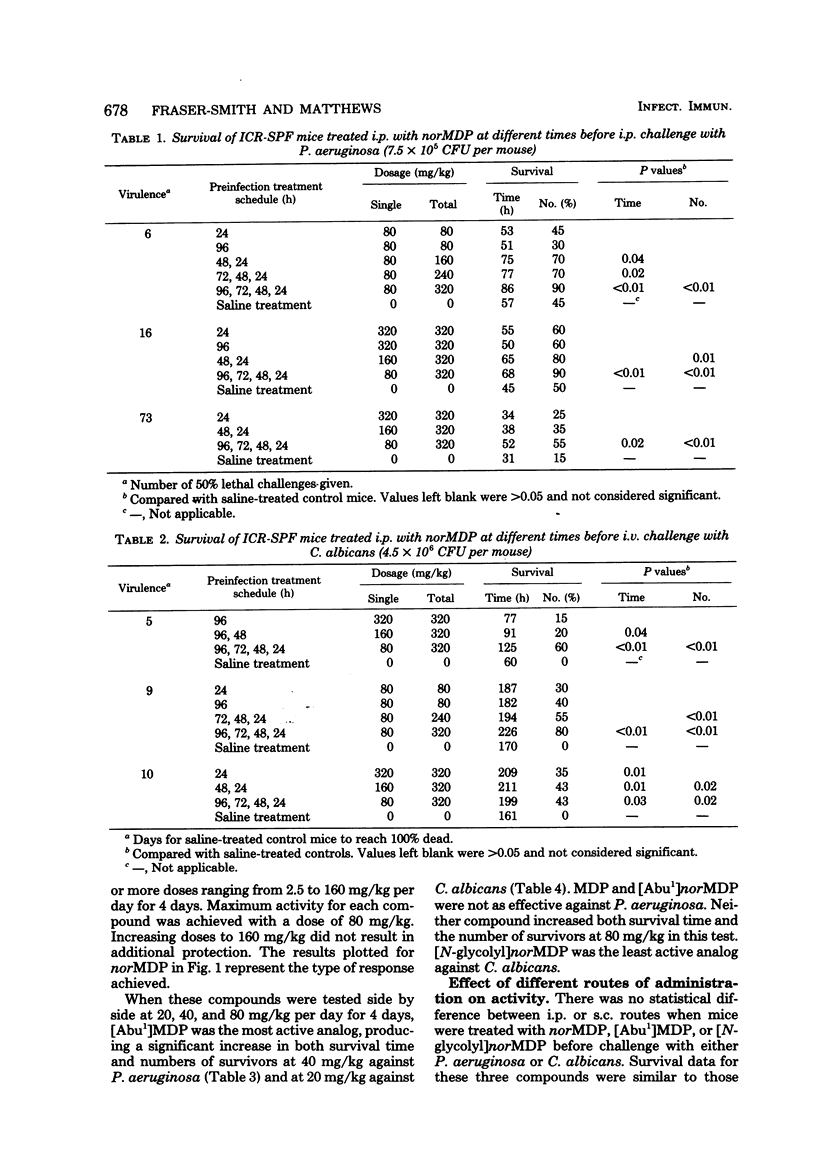
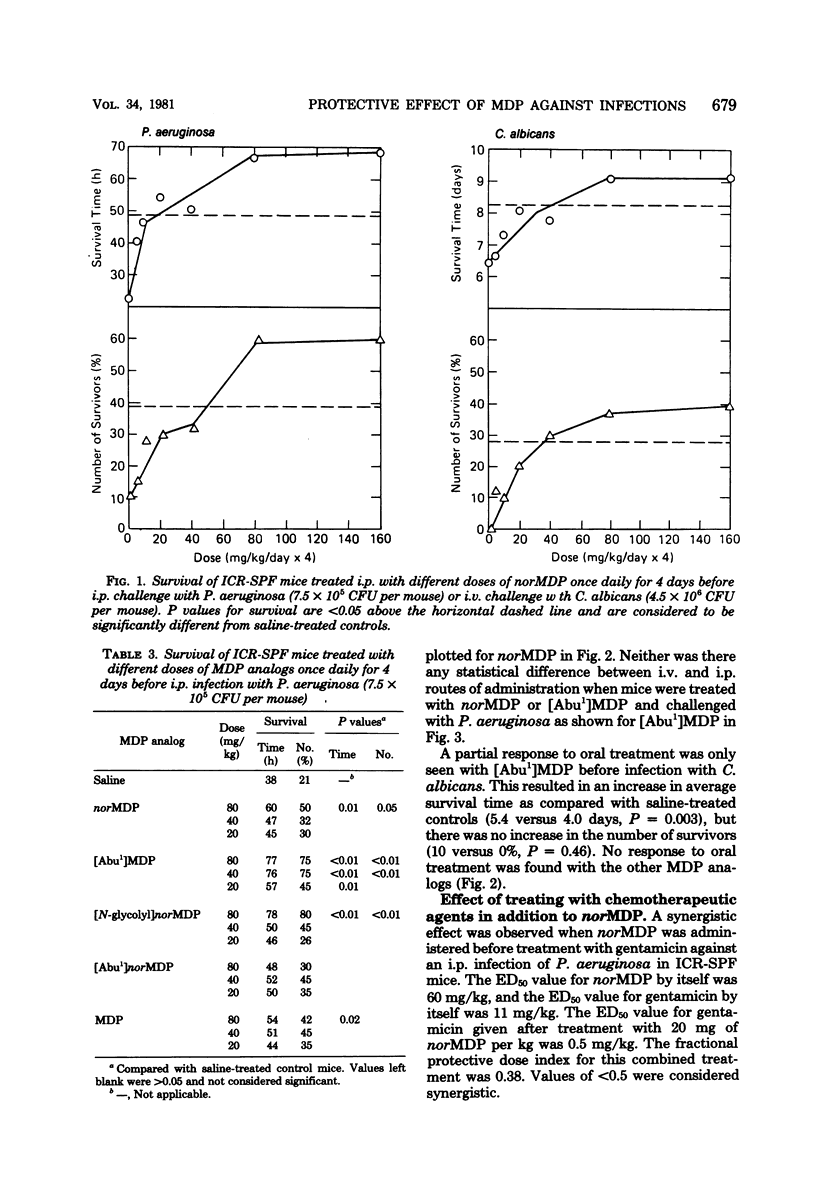
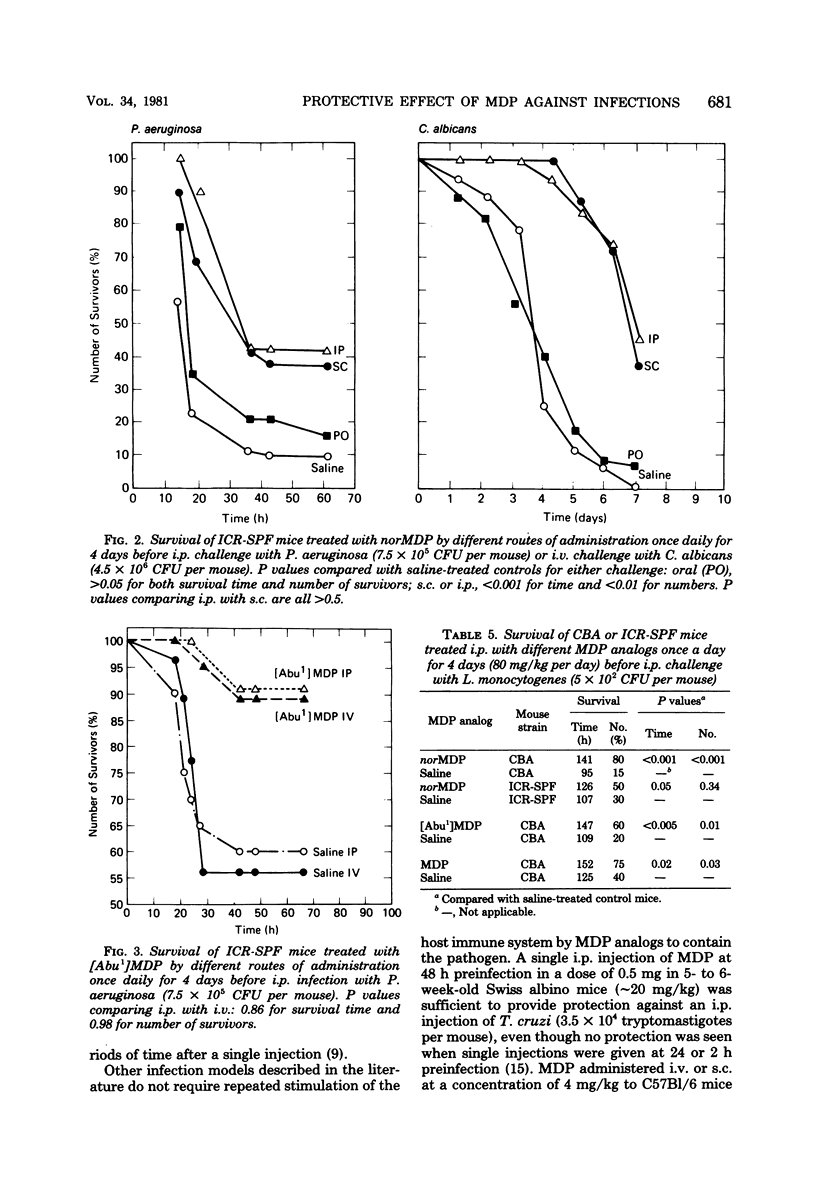
Two analogs of N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine (muramyl dipeptide) were found to give better protection than muramyl dipeptide against intraperitoneal Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection or intravenous Candida albicans infection in mice. The analogs tested were N-acetyl-nor-muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine and N-acetylmuramyl-L-alpha-amino-butyryl-D-isoglutamine. The optimum treatment was 80 mg/kg per day given once daily for 4 consecutive days before infection by the intraperitoneal, intravenous, or subcutaneous route. Dose response was limited. The compounds were not orally active. Synergism was seen between N-acetyl-nor-muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine and gentamicin. No postinfection protection was observed. A nonspecific stimulation of macrophage cells by muramyl dipeptide analogs may contribute to the protection because antiinfective activity against Listeria monocytogenes given intraperitoneally was achieved with CBA mice.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Audibert F., Chédid L., Lefrancier P., Choay J. Distinctive adjuvanticity of synthetic analogs of mycobacterial water-soluble components. Cell Immunol. 1976 Feb;21(2):243–249. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P. Infections in cancer patients. Cancer Treat Rev. 1975 Jun;2(2):89–128. doi: 10.1016/s0305-7372(75)80005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Audibert F., Lefrancier P., Choay J., Lederer E. Modulation of the immune response by a synthetic adjuvant and analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2472–2475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Audibert F., Lefrancier F., Choay J., Sela M. Enhancement of certain biological activities of muramyl dipeptide derivatives after conjugation to a multi-poly(DL-alanine)--poly(L-lysine) carrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6557–6561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Lefrancher P., Choay J., Lederer E. Enhancement of nonspecific immunity to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection by a synthetic immunoadjuvant (N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine) and several analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2089–2093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellouz F., Adam A., Ciorbaru R., Lederer E. Minimal structural requirements for adjuvant activity of bacterial peptidoglycan derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 19;59(4):1317–1325. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90458-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Sone S., Fogler W. E., Barnes Z. L. Eradication of spontaneous metastases and activation of alveolar macrophages by intravenous injection of liposomes containing muramyl dipeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1680–1684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Wirsing von König C. H. Failure of synthetic muramyl dipeptide to increase antibacterial resistance. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):288–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.288-291.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD J. G., BIOZZI G., HALPERN B. N., STIFFEL C., MOUTON D. The effect of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (BCG) infection on the resistance of mice to bacterial endotoxin and Salmonella enteritidis infection. Br J Exp Pathol. 1959 Jun;40(3):281–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphres R. C., Henika P. R., Ferraresi R. W., Krahenbuhl J. L. Effects of treatment with muramyl dipeptide and certain of its analogs on resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):462–466. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.462-466.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kireszenbaum F., Ferraresi R. W. Enhancement of host resistance against Trypanosoma cruzi infection by the immunoregulatory agent muramyl dipeptide. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):273–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.273-278.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Sharma S. D., Ferraresi R. W., Remington J. S. Effects of muramyl dipeptide treatment on resistance to infection with Toxoplasma gondii in mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):716–722. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.716-722.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson C. L., Ushijima R. N., Karim R., Baker M. B., Baker R. E. Herpesvirus hominis type 2 infections in rabbits: effect of prior immunization with attenuated Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) cells. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):465–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.465-468.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular kinetics associated with the development of acquired cellular resistance. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):299–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parant M., Parant F., Chedid L. Enhancement of the neonate's nonspecific immunity to Klebsiella infection by muramyl dipeptide, a synthetic immunoadjuvant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3395–3399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parant M., Parant F., Chedid L., Yapo A., Petit J. F., Lederer E. Fate of the synthetic immunoadjuvant, muramyl dipeptide (14C-labelled) in the mouse. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1979;1(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(79)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Warren C. Activity of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim against Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):736–740. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senterfitt V. C., Shands J. W. Salmonellosis in Mice Infected with Mycobacterium bovis BCG II. Resistance to Infection. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):583–586. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.583-586.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher N. A., Chaparas S. D., Greenberg L. E., Bernard S. Effects of BCG, Corynebacterium parvum, and methanol-extration residue in the reduction of mortality from Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans infections in immunosuppressed mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1325–1330. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1325-1330.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Nagao S., Nagao R., Kotani S., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Stimulation of the reticuloendothelial system of mice by muramyl dipeptide. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.302-307.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS D. W. Enhanced resistance of mice to infection with Pasteurella pestis following vaccination with fractions of phenol-killed tubercle bacilli. Nature. 1960 Jun 25;186:1060–1061. doi: 10.1038/1861060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters R. V., Ferraresi R. W. Muramyl dipeptide stimulation of particle clearance in several animal species. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Nov;28(5):457–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. W. Nonspecific stimulation and modulation of the immune response and of states of resistance by the methanol-extraction residue fraction of tubercle bacilli. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1972 Dec;35:157–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


