Abstract
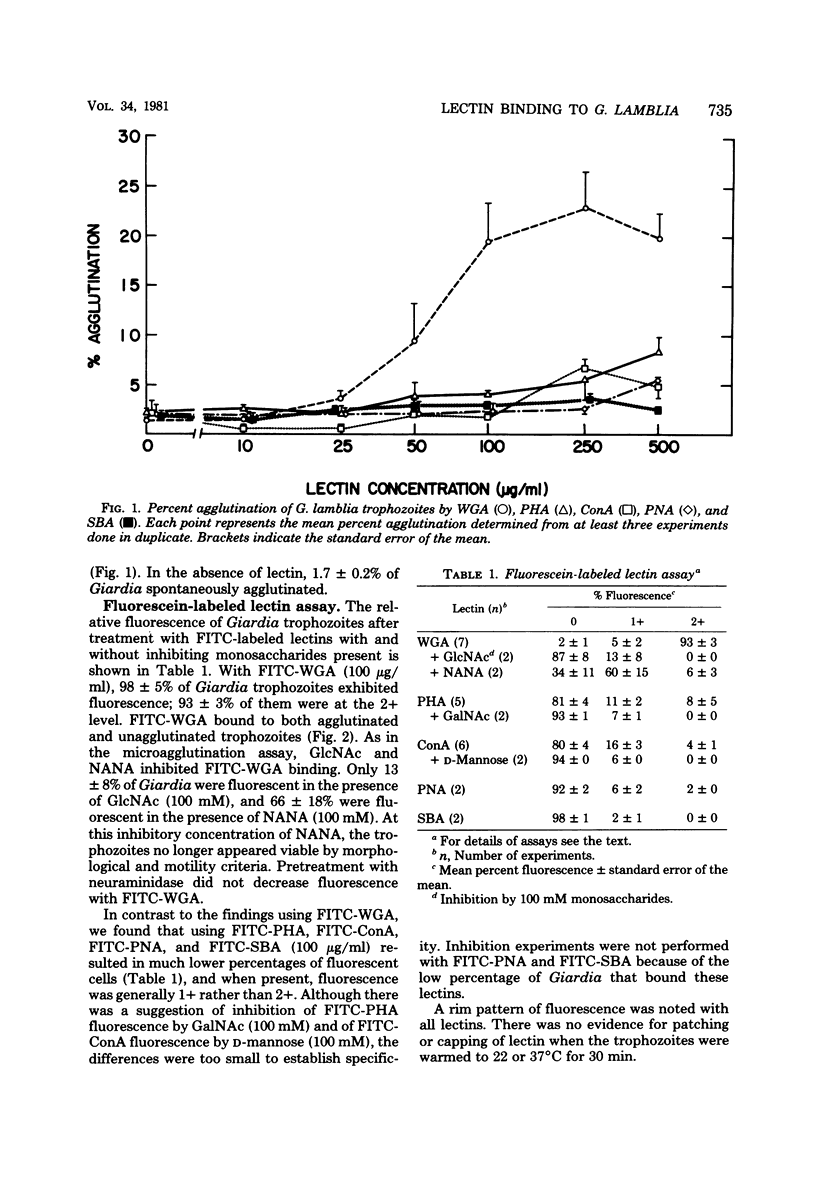
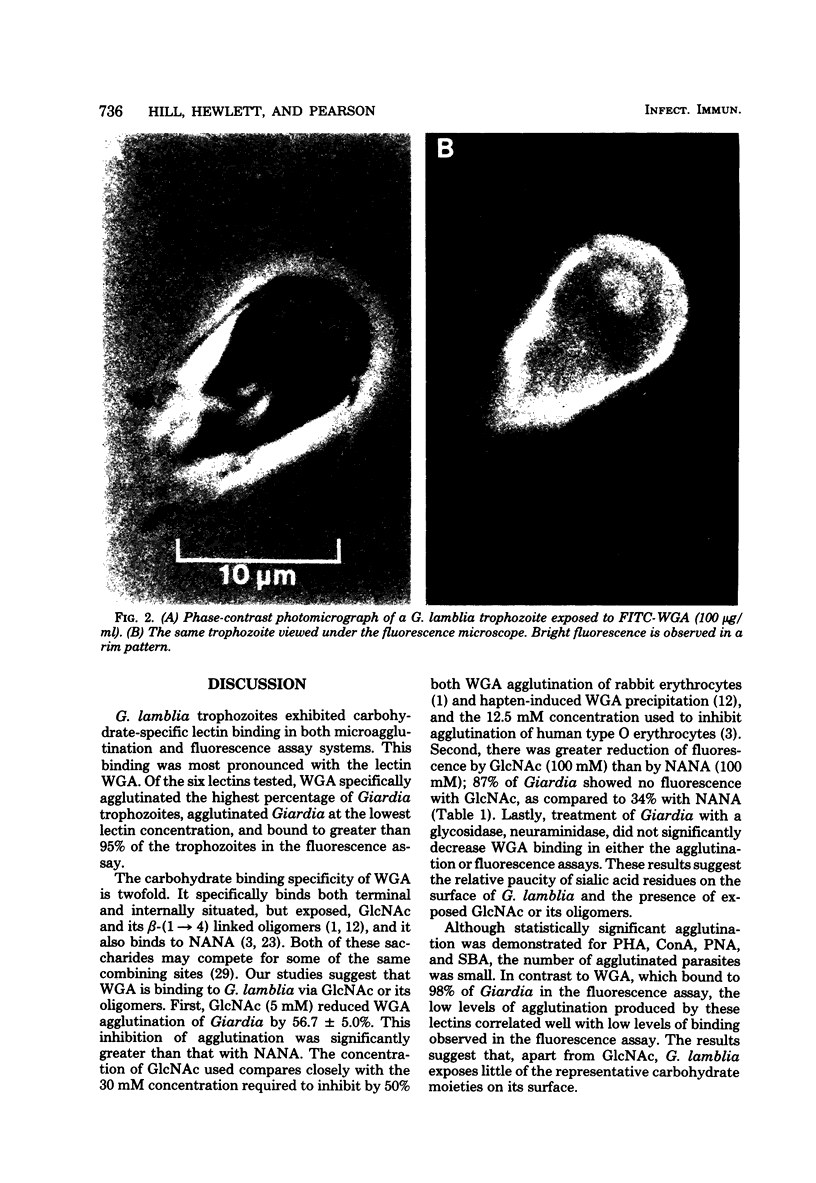
Surface carbohydrates of Giardia lamblia were examined using six plant lectins chosen because of their specificity for major carbohydrates moieties. The binding to axenically grown G. lamblia trophozoites was assessed in both a quantitative microagglutination assay and a fluorescence assay. Of the six lectins tested, wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) agglutinated the highest percentage (22.9 +/- 3.7%) of live trophozoites, and fluorescein-labeled WGA (100 micrograms/ml) bound to 98 +/- 5% of them. Since the carbohydrate specificity of WGA includes both N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) and sialic acid, inhibition experiments were performed. GlcNAc inhibited he binding of WGA to G. lamblia in both assays to a greater extent than did sialic acid. Binding of WGA was not altered by prior treatment of trophozoites with neuraminidase, suggesting that WGA was binding to GlcNAc moieties on G. lamblia and not to sialic acid. The remaining five lectins either bound nonspecifically or exhibited low percentages of binding. The apparent presence of GlcNAc but not sialic acid or other exposed surface carbohydrates may be important in the interaction of G. lamblia with its human host.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. K., Neuberger A., Sharon N. The purification, composition and specificity of wheat-germ agglutinin. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):155–162. doi: 10.1042/bj1310155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhavanandan V. P., Katlic A. W. The interaction of wheat germ agglutinin with sialoglycoproteins. The role of sialic acid. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4000–4008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R. Games parasites play: how parasites evade immune surveillance. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):21–26. doi: 10.1038/279021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Hunt R. C. Lectins. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;52:277–349. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60758-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Techniques of axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae. J Parasitol. 1968 Oct;54(5):1047–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer D. M. Cell surface saccharides of Trypanosoma lewis i. II. Lectin-mediated agglutination and fine-structure cytochemical detection of lectin-binding sites. J Cell Sci. 1976 Oct;22(1):1–19. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer D. M. Lectin binding saccharides on a parasitic protozoan. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):471–473. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykes A. C., Juranek D. D., Lorenz R. A., Sinclair S., Jakubowski W., Davies R. Municipal waterborne giardiasis: an epidemilogic investigation. Beavers implicated as a possible reservoir. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 1):165–170. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Nicholson-Weller A., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. The role of specific antibody in alternative complement pathway-mediated opsonophagocytosis of type III, group B Streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1275–1287. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Hammarström S., Sundblad G. Precipitation and carbohydrate-binding specificity studies on wheat germ agglutinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 9;405(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Hayes C. E. The lectins: carbohydrate-binding proteins of plants and animals. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1978;35:127–340. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Skutelsky E., Danon D., Sharon N. The purification, composition, and specificity of the anti-T lectin from peanut (Arachis hypogaea). J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8518–8523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López C. E., Dykes A. C., Juranek D. D., Sinclair S. P., Conn J. M., Christie R. W., Lippy E. C., Schultz M. G., Mires M. H. Waterborne giardiasis: a communitywide outbreak of disease and a high rate of asymptomatic infection. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Oct;112(4):495–507. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Palomo A., Gonzalez-Robles A., De la Torre M. Selective agglutination of pathogenic strains of Entamoeba histolytica induced con A. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 10;245(145):186–187. doi: 10.1038/newbio245186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E. A. Giardia lamblia: isolation and axenic cultivation. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Feb;39(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. The interactions of lectins with animal cell surfaces. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;39:89–190. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60939-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterholm M. T., Forfang J. C., Ristinen T. L., Dean A. G., Washburn J. W., Godes J. R., Rude R. A., McCullough J. G. An outbreak of foodborne giardiasis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 1;304(1):24–28. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101013040106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Loures M. A., Villalta F., Andrade A. F. Lectin receptors as markers for Trypanosoma cruzi. Developmental stages and a study of the interaction of wheat germ agglutinin with sialic acid residues on epimastigote cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1375–1392. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters B. P., Ebisu S., Goldstein I. J., Flashner M. Interaction of wheat germ agglutinin with sialic acid. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5505–5511. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Rahman A., Pelster B., Brandis H. Search for the presence of lectin-binding sites on Toxoplasma gondii. J Parasitol. 1977 Dec;63(6):1076–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S. Axenic growth of Giardia lamblia in Diamond's TPS-1 medium. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(2):213–215. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. S. Crystallographic elucidation of the saccharide binding mode in wheat germ agglutinin and its biological significance. J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 15;141(3):267–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



