Abstract
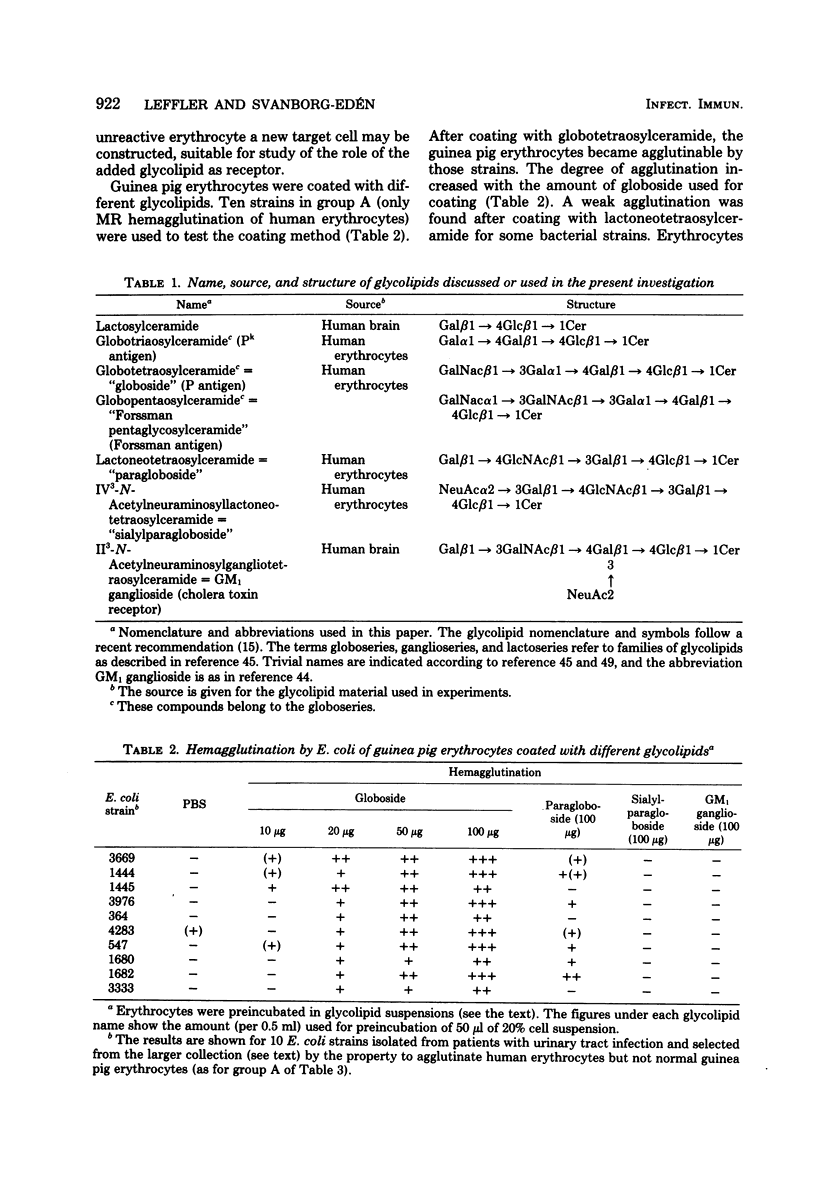
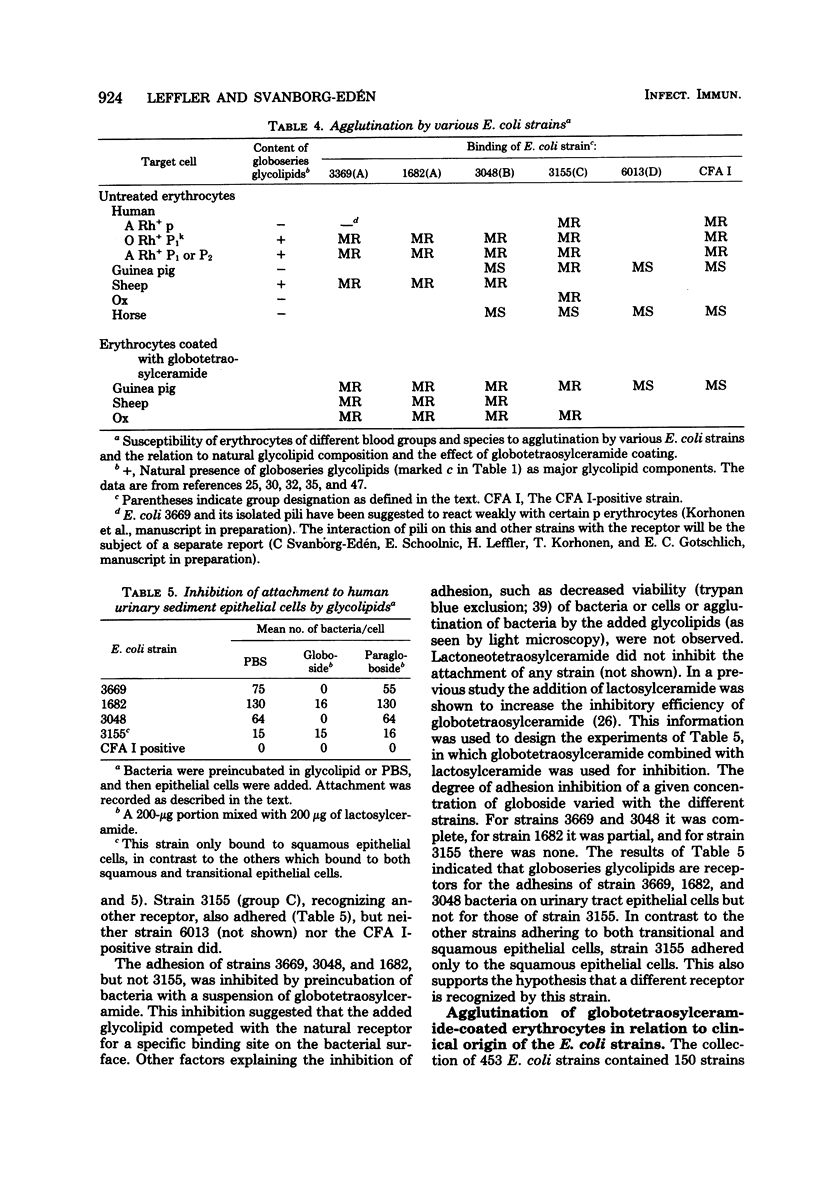
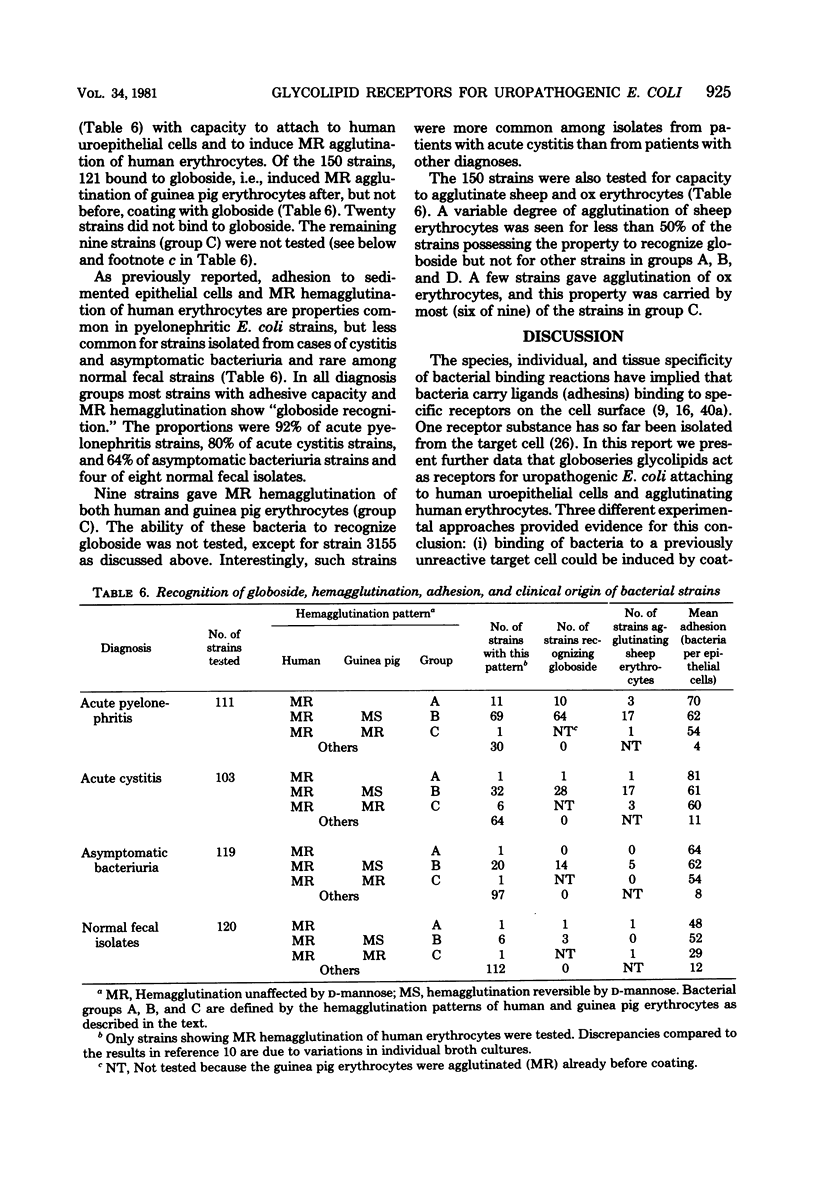
A specific family of glycolipids, the globoseries, was shown to act as receptors on human uroepithelial cells and erythrocytes for the majority of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains attaching to or hemagglutinating those cells. This was demonstrated in three different ways: (i) correlation between the natural presence of glycolipid in the target cell (erythrocytes of different species) and binding of bacteria; (ii) inhibition of attachment to human uroepithelial cells by preincubation of bacteria and glycolipid; and (iii) induction of binding to unreactive cells by coating of these cells with glycolipid. Strains reacting with the receptor agglutinated guinea pig erythrocytes in a mannose-resistant way after, but not before, coating of the cells with globotetraosylceramide. Unrelated glycolipids were not recognized. The reaction was made independent of simultaneous occurrence of mannose-sensitive adhesions on the strains by addition of D-mannose. The receptor-coated cells were used as a tool to screen for prevalence of receptor recognition in a collection of 453 E. coli strains isolated from patients with urinary tract infection or from the stools of healthy children. Of 150 strains attaching to human uroepithelial cells and agglutinating human erythrocytes, 121 bound to globotetraosylceramide (81%). Globoside recognition was especially frequent among pyelonephritis strains (74/81). The glycolipid composition of the urogenital epithelium and kidney tissue and the ability of uropathogenic E. coli to bind to these glycolipids may be a determinant in host-parasite interaction leading to urinary tract infection.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breimer M. E., Hansson G. C., Karlsson K. A., Leffler H., Pimlott W., Samuelsson B. E. Selected ion monitoring of glycospingolipid mixtures. Identification of several blood group type glycolipids in the small intestine of an individual rabbit. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1979 Jun;6(6):231–241. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200060603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Eriksson B., Hanson L. A., Jodal U., Kaijser B., Janson G. L., Lindberg U., Olling S. Adhesion to normal human uroepithelial cells of Escherichia coli from children with various forms of urinary tract infection. J Pediatr. 1978 Sep;93(3):398–403. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Hagberg L., Hanson L. A., Korhonen T., Leffler H., Olling S. Adhesion of Escherichia coli in urinary tract infection. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:161–187. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Larsson P., Lomberg H. Attachment of Proteus mirabilis to human urinary sediment epithelial cells in vitro is different from that of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):804–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.804-807.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Leffler H. Glycosphingolipids of human urinary tract epithelial cells as possible receptors for adhering Escherichia coli bacteria. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;Suppl 24:144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K. E., Karlsson K. A., Samuelsson B. E. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of anomeric structure of glycosphingolipids. Blood group ABH-active substances. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jan;192(1):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K. E., Karlsson K. A., Samuelsson B. E. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of anomeric structure of glycosphingolipids. The globo-series (one to five sugars). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jan;192(1):164–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier W., Glaser L. Surface components and cell recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:491–523. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANDA S. BLOOD GROUP ACTIVE GLYCOLIPID FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. Jpn J Exp Med. 1963 Dec;33:347–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Jodal U., Korhonen T. K., Lidin-Janson G., Lindberg U., Svanborg Edén C. Adhesion, hemagglutination, and virulence of Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.564-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Elwing H., Fredman P., Strannegård O., Svennerholm L. Gangliosides as receptors for bacterial toxins and Sendai virus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1980;125:453–470. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7844-0_40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A. Mass-spectrometric sequence studies of lipid-linked oligosaccharides: blood-group fucolipids, gangliosides and related cell-surface receptors. Prog Chem Fats Other Lipids. 1978;16:207–230. doi: 10.1016/0079-6832(78)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K. A., Samuelsson B. E., Steen G. O. The sphingolipid composition of bovine kidney cortex, medulla and papilla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 25;316(3):317–335. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kościelak J., Miller-Podraza H., Krauze R., Cedergren B. Glycolipid composition of blood group P erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 15;66(2):250–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80515-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomberg H., Jodal U., Eden C. S., Leffler H., Samuelsson B. P1 blood group and urinary tract infection. Lancet. 1981 Mar 7;1(8219):551–552. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92878-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lounatmaa K., Mäkelä P. H., Sarvas M. Effect of polymyxin on the ultrastructure of the outer membrane of wild-type and polymyxin-resistant strain of Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1400–1407. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1400-1407.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus D. M., Cass L. E. Glycosphingolipids with Lewis blood group activity: uptake by human erythrocytes. Science. 1969 May 2;164(3879):553–555. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3879.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus D. M., Naiki M., Kundu S. K. Abnormalities in the glycosphingolipid content of human Pk and p erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3263–3267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momoi M., Yamakawa T. Glucosamine-containing sphingoglycolipids from sheep erythrocytes. J Biochem. 1978 Aug;84(2):317–325. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Fishman P. H., Manganiello V. C., Vaughan M., Brady R. O. Functional incorporation of ganglioside into intact cells: induction of choleragen responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1034–1037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oashi M., Yamakawa T. Gas-liquid chromatography of oligosaccharides released from red cell glycosphingolipids by ozonolysis. J Lipid Res. 1973 Nov;14(6):698–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M., Burrows M. R., Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A. A genetic basis for resistance to enteric disease caused by E. coli. Nature. 1975 Sep 11;257(5522):135–136. doi: 10.1038/257135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Dawson G. Topographical distribution of complex carbohydrates in the erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2135–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern P. L., Bretscher M. S. Capping of exogenous Forssman glycolipid on cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):829–833. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley C. A., Crookston M. C., Brown B. L., Wherrett J. R. A and B and A1Leb substances in glycosphingolipid fractions of human serum. Vox Sang. 1975;28(1):25–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1975.tb02737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura K., Yuzawa M., Taketomi T. Characterization of major glycolipids in bovine erythrocyte membrane. J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(2):463–471. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


