Abstract
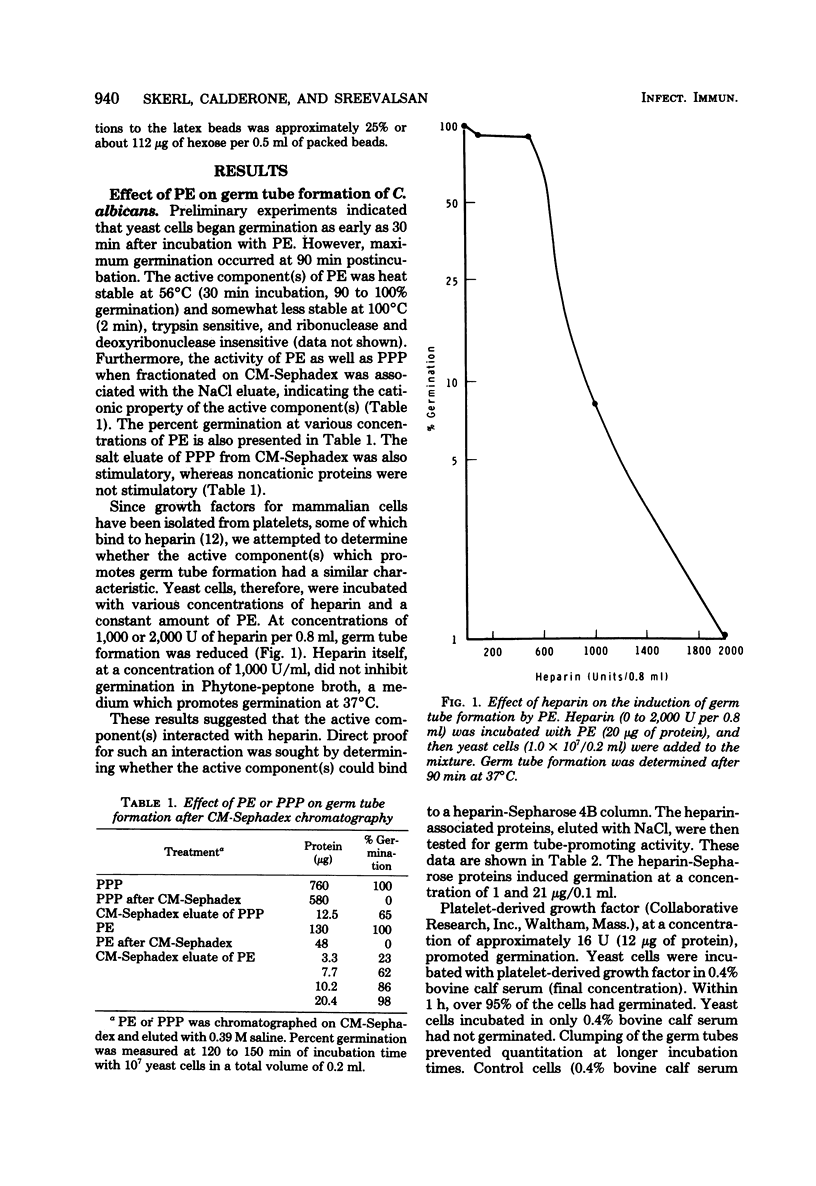
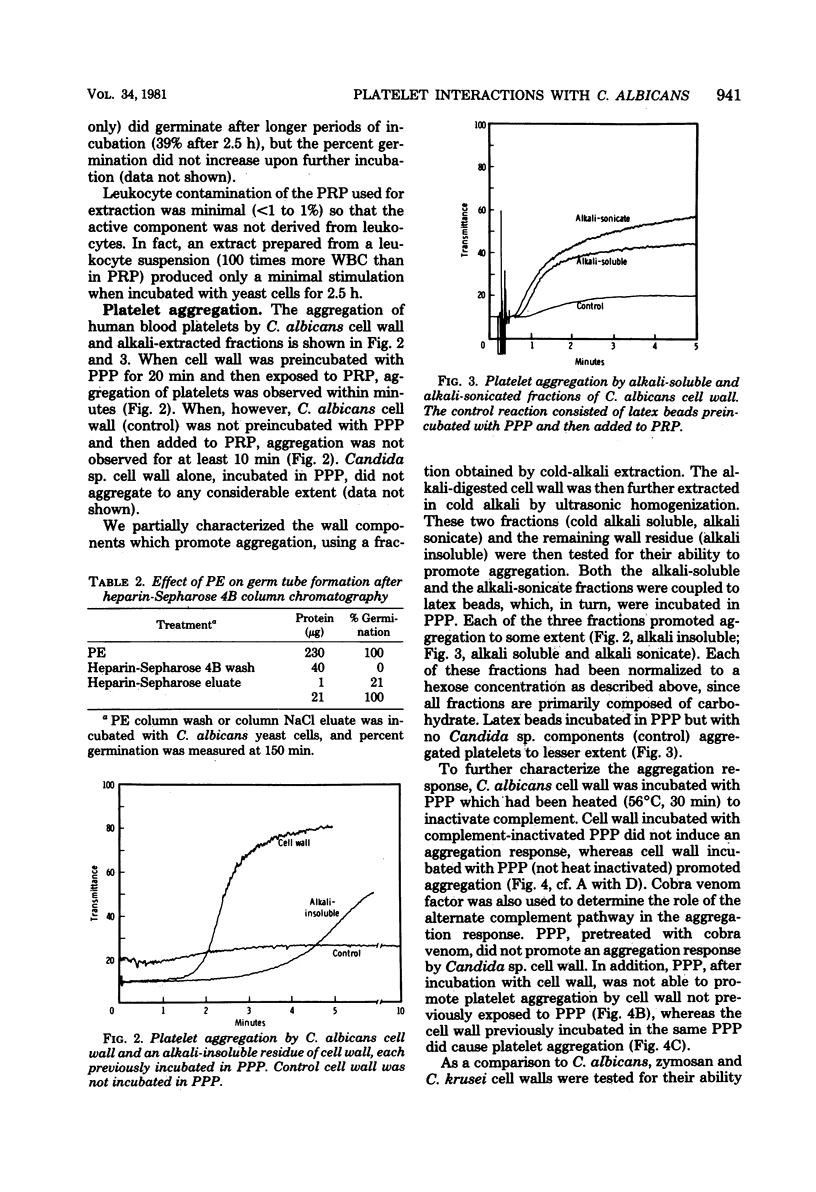
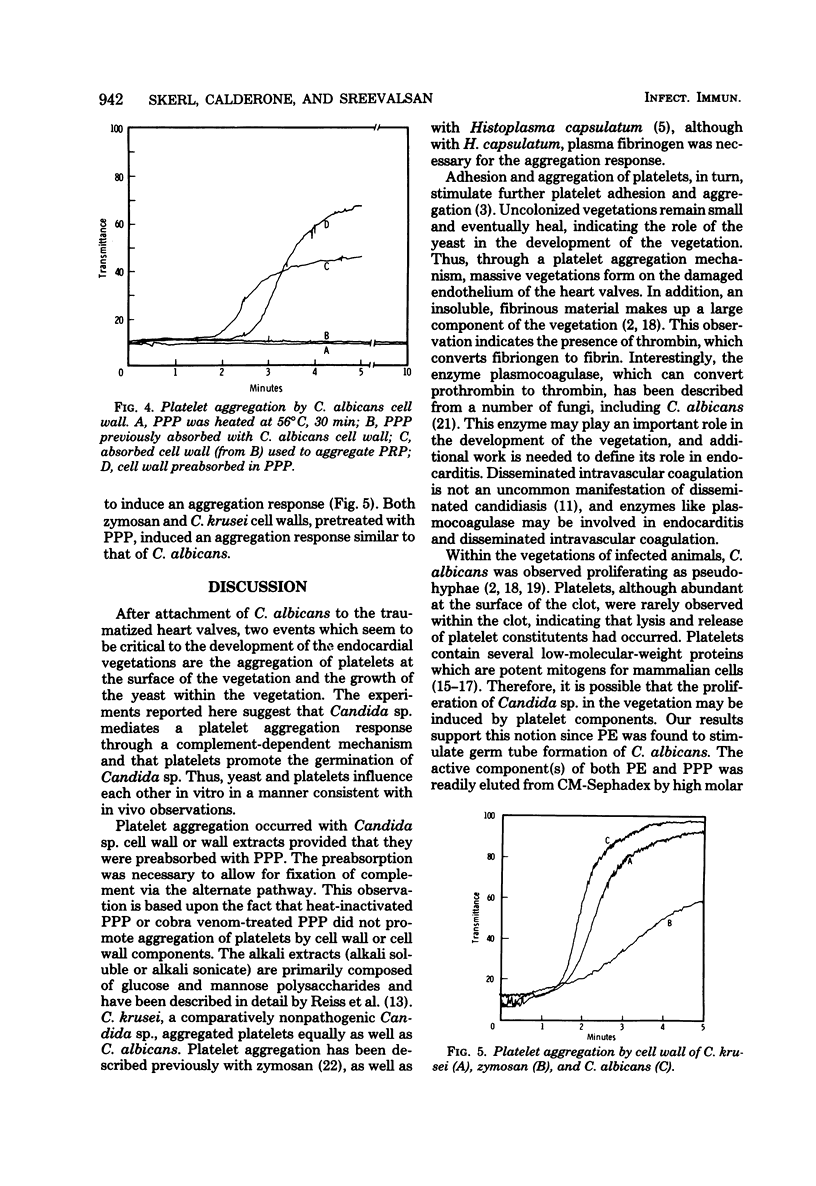
The interaction of human platelets and Candida albicans was studied. Platelet-rich plasma was obtained from freshly drawn blood or outdated platelet concentrates. From the platelet-rich plasma, a platelet extract was derived which stimulated germ tube formation by C. albicans when incubated with yeast cells at 37 degrees C. The active component(s) was heat stable, trypsin sensitive, and ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease insensitive, and possessed cationic properties since it readily attached to carboxymethyl-Sephadex. The active component(s) seemed to bind to heparin also, since germ tube-promoting activity was eluted from a heparin-cyanogen bromide-activated Sepharose 4B column. In addition, platelet-derived growth factor (Collaborative Research, Inc.) stimulated germination when incubated with low amounts (0.4% final concentration) of bovine calf serum. The aggregation of platelets, prepared as platelet-rich plasma by C. albicans cell wall or alkali-extracted cell wall fractions, was also studied. Aggregation of platelets was observed when cell wall or cell wall fractions were incubated with platelet-poor plasma at 37 degrees C for 20 min and then added to platelet-rich plasma. The component of platelet-poor plasma which promoted aggregation of platelets by C. albicans cell wall or alkali-extracted fractions was inactivated at 56 degrees C (30 min) and by cobra venom factor, indicating a role for the alternate complement pathway in the aggregation response.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow A. J., Aldersley T., Chattaway F. W. Factors present in serum and seminal plasma which promote germ-tube formation and mycelial growth of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):261–272. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Rotondo M. F., Sande M. A. Candida albicans endocarditis: ultrastructural studies of vegetation formation. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):279–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.279-289.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. Platelet structure and function role of prostaglandins. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1980 May-Jun;10(3):187–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowa N., Taxer S. S., Howard D. H. Germination of Candida albicans induced by proline. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):830–835. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.830-835.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Prez R. M., Steckley S., Stroud R. M., Hawiger J. Interaction of Histoplasma capsulatum with human platelets. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):32–39. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T. Experimental bacterial endocarditis. IV. Structure and evolution of very early lesions. J Pathol. 1975 Feb;115(2):81–89. doi: 10.1002/path.1711150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H. Coupling of glycosaminoglycans to agarose beads (sepharose 4B). Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):677–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1240677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON S. A. Candida (Monilia) albicans: effect of amino acids, glucose, pH, chlortetracycline (aureomycin), dibasic sodium and calcium phosphates, and anaerobic and aerobic conditions on its growth. AMA Arch Derm Syphilol. 1954 Jul;70(1):49–60. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1954.01540190051003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch P. A., Calderone R. A. Adherence of Candida albicans to a fibrin-platelet matrix formed in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):650–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.650-656.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L. Ultrastructural observations in disseminated candidiasis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Oct;102(10):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D., Niewiarowski S., Varma K. G., Rucker S. Inhibition of mitogenic activity of a platelet growth factor (platelet basic protein) in 3T3 cells by heparin. Thromb Res. 1980 Jun 15;18(6):883–888. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss E., Stone S. H., Hasenclever H. F. Serological and cellular immune activity of peptidoglucomannan fractions of Candida albicans cell walls. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):881–890. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.881-890.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Nist C., Kariya B., Rivest M. J., Raines E., Callis J. Physiological quiescence in plasma-derived serum: influence of platelet-derived growth factor on cell growth in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Dec;97(3 Pt 2 Suppl 1):497–508. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Vogel A. The platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Bowman C. R., Calderone R. A. Experimental Candida albicans endocarditis: characterization of the disease and response to therapy. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):140–147. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.140-147.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig M. S., Speth C. P., Kozinn P. J., Toni E. F., Taschdjian C. L. Candida endocarditis after cardiac surgery. Clues to earlier detection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1973 Apr;65(4):583–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaikina N. A., Elinov N. P. Fungal plasmocoagulase. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1968 Jun 28;35(1):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02053273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Grant R. A. Aggregation and release reaction induced in human blood platelets by zymosan. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1219–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


