Abstract
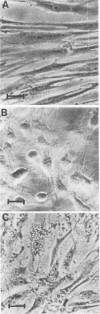
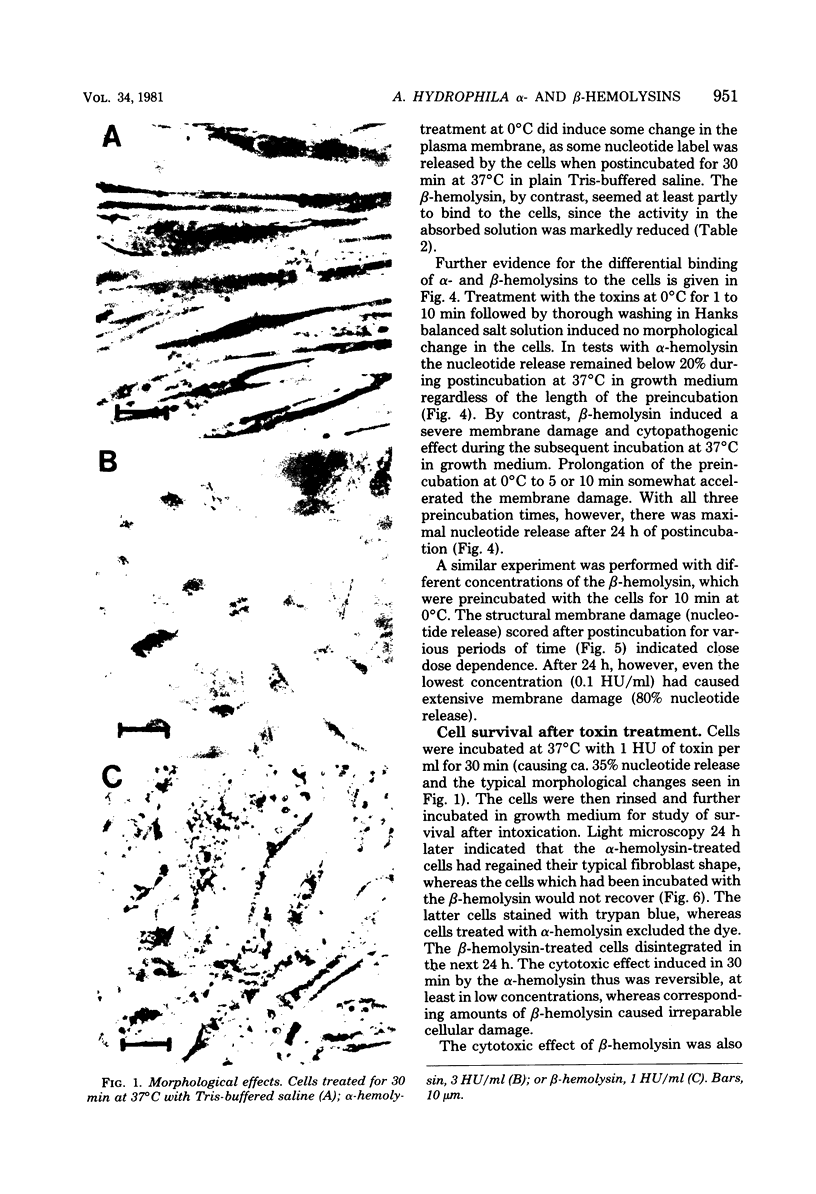
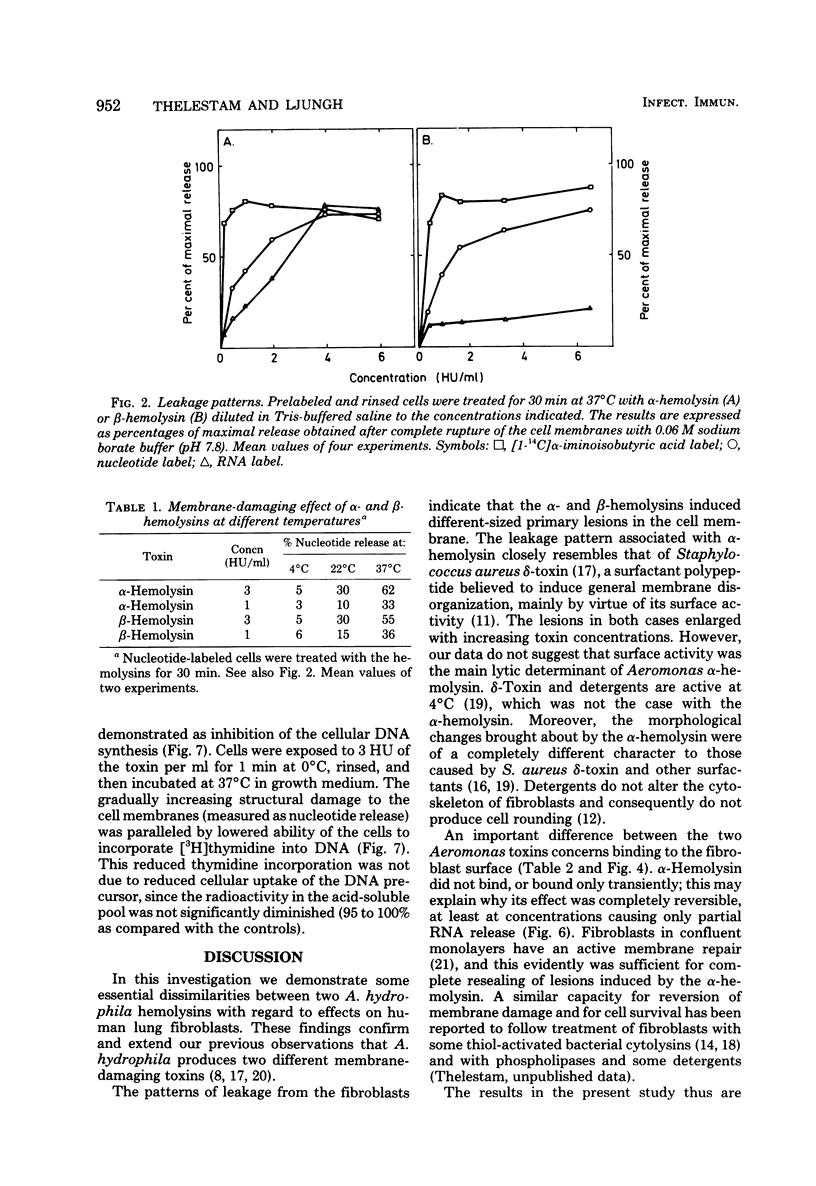
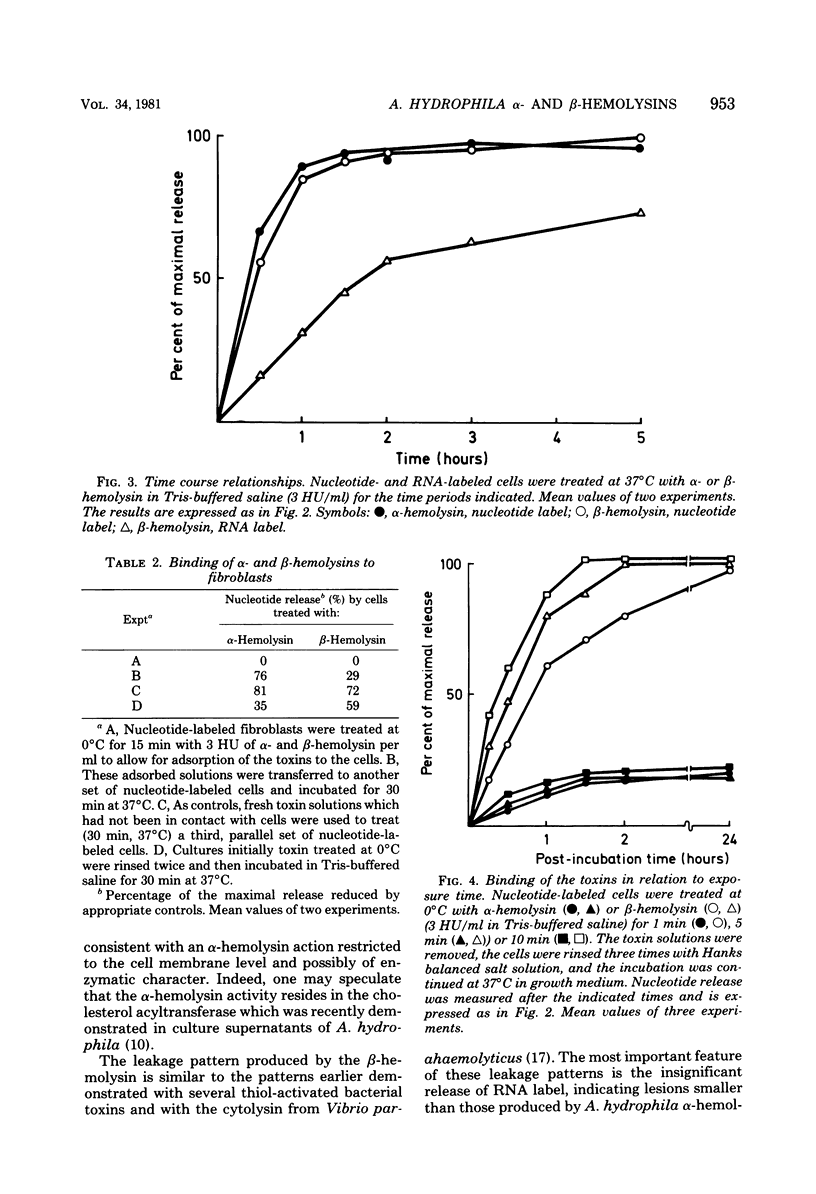
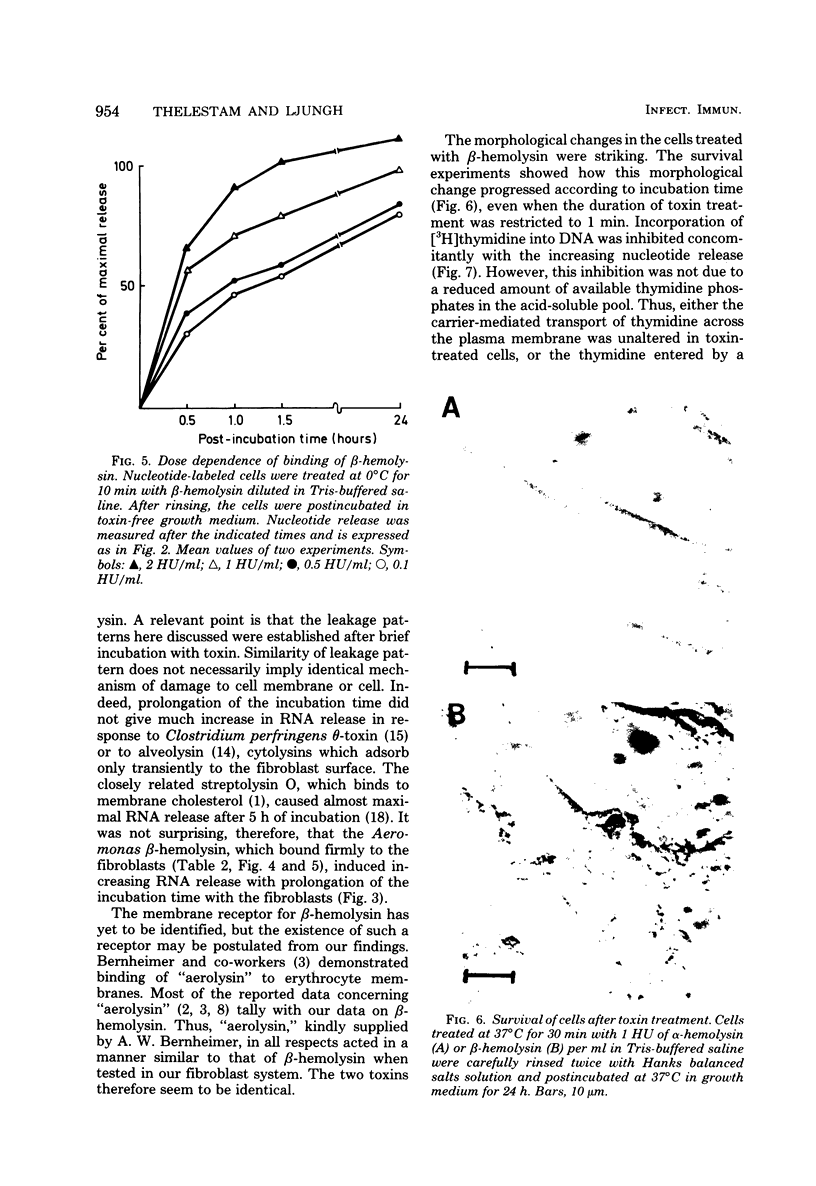
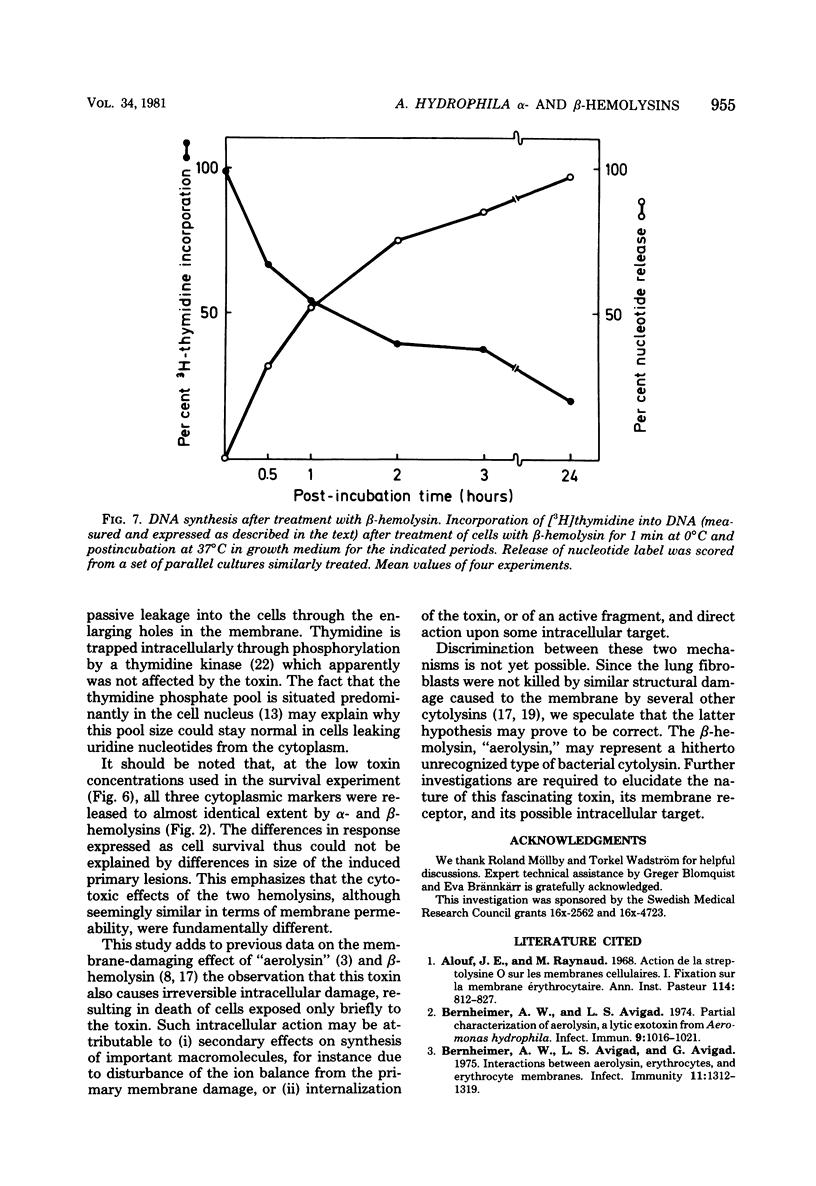
The effects of two hemolysins (alpha and beta) from Aeromonas hydrophila on human lung fibroblasts were investigated. The toxins differed distinctly in regard to the morphological changes they produced. The alpha-hemolysin caused rounding of the cells. The beta-hemolysin caused a striking vacuolization of the cytoplasm in cells which remained spread out on the growth surface. The toxins also differed as to relative size of the initial lesions they induced in the fibroblast membrane, scored by leakage of different-sized cytoplasmic markers. The alpha-hemolysin induced larger lesions than did the beta-hemolysin. It was indirectly demonstrated that the alpha-hemolysin did not bind, or bound only transiently, to the fibroblasts. By contrast, the beta-hemolysin bound rapidly and firmly. The cytopathogenic response to the alpha-hemolysin was reversible, whereas cells treated with small amounts of the beta-hemolysin for only 1 min invariably died within a few hours. Thus, the two hemolysins from A. hydrophila, despite many biochemical similarities, show essential dissimilarities in their interactions with cultured cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E., Raynaud M. Action de la streptolysine O sur les membranes cellulaires. I. Fixation sur la membrane érythrocytaire. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Jun;114(6):812–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S., Avigad G. Interactions between aerolysin, erythrocytes, and erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1312–1319. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1312-1319.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S. Partial characterization of aerolysin, a lytic exotoxin from Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1016–1021. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1016-1021.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger Y., Lallier R., Cousineau G. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1161–1164. doi: 10.1139/m77-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahle H. K. The purification and some properties of two Aeromonas proteinases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(6):726–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin J., Thelestam M. The lysis of human diploid fibroblasts with borate buffer. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(1):115–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre S., Buckley J. T. Presence of glycerophospholipid: cholesterol acyltransferase and phospholipase in culture supernatant of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):402–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.402-407.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. The detertent-resistant cytoskeleton of tissue culture cells includes the nucleus and the microfilament bundles. Exp Cell Res. 1977 May;106(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoog L., Bjursell G. Nuclear and cytoplasmic pools of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6434–6438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Alouf J. E., Geoffroy C., Möllby R. Membrane-damaging action of alveolysin from Bacillus alvei. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1187–1192. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1187-1192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Classification of microbial, plant and animal cytolysins based on their membrane-damaging effects of human fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):156–169. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Cytotoxic effects on the plasma membrane of human diploid fibroblasts--a comparative study of leakage tests. Med Biol. 1976 Feb;54(1):39–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Determination of toxin-induced leakage of different-size nucleotides through the plasma membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):640–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.640-648.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Interaction of streptolysin O from Streptococcus pyogenes and theta-toxin from Clostridium perfringens with human fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.863-872.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R., Wadström T. Effects of staphylococcal alpha-, beta-, delta-, and gamma-hemolysins on human diploid fibroblasts and HeLa cells: evaluation of a new quantitative as say for measuring cell damage. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):938–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.938-946.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Ljungh A., Wretlind B. Enterotoxin, haemolysin and cytotoxic protein in Aeromonas hydrophila from human infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Apr;84(2):112–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren L., Glick M. C. Membranes of animal cells. II. The metabolism and turnover of the surface membrane. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jun;37(3):729–746. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlhueter R. M., Marz R., Plagemann P. G. Thymidine transport in cultured mammalian cells. Kinetic analysis, temperature dependence and specificity of the transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 17;553(2):262–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90231-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Hedén L., Wadström T. Formation of extracellular haemolysin by Aeromonas hydrophila in relation to protease and staphylolytic enzyme. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Sep;78(1):57–65. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Möllby R., Wadström T. Separation of two hemolysins from Aeromonas hydrophila by isoelectric focusing. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):503–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.503-505.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]