Abstract
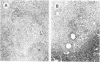
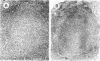
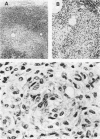
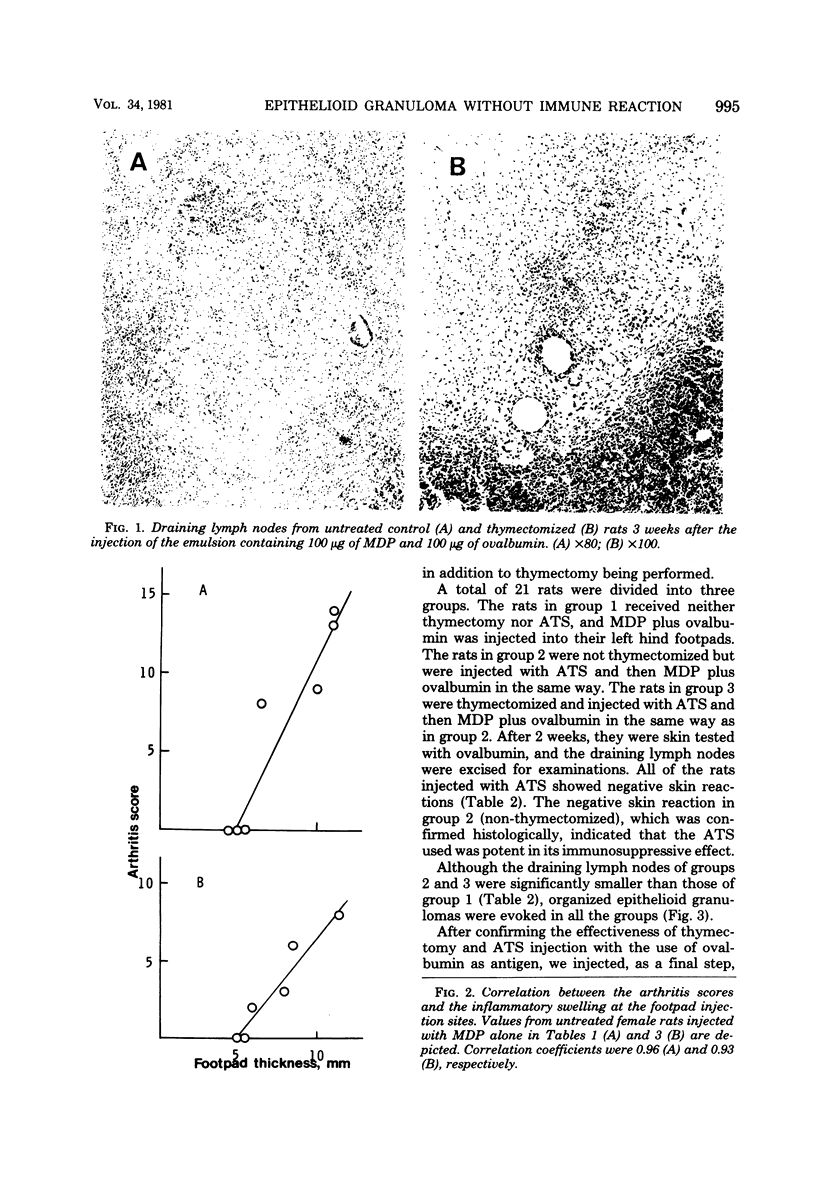
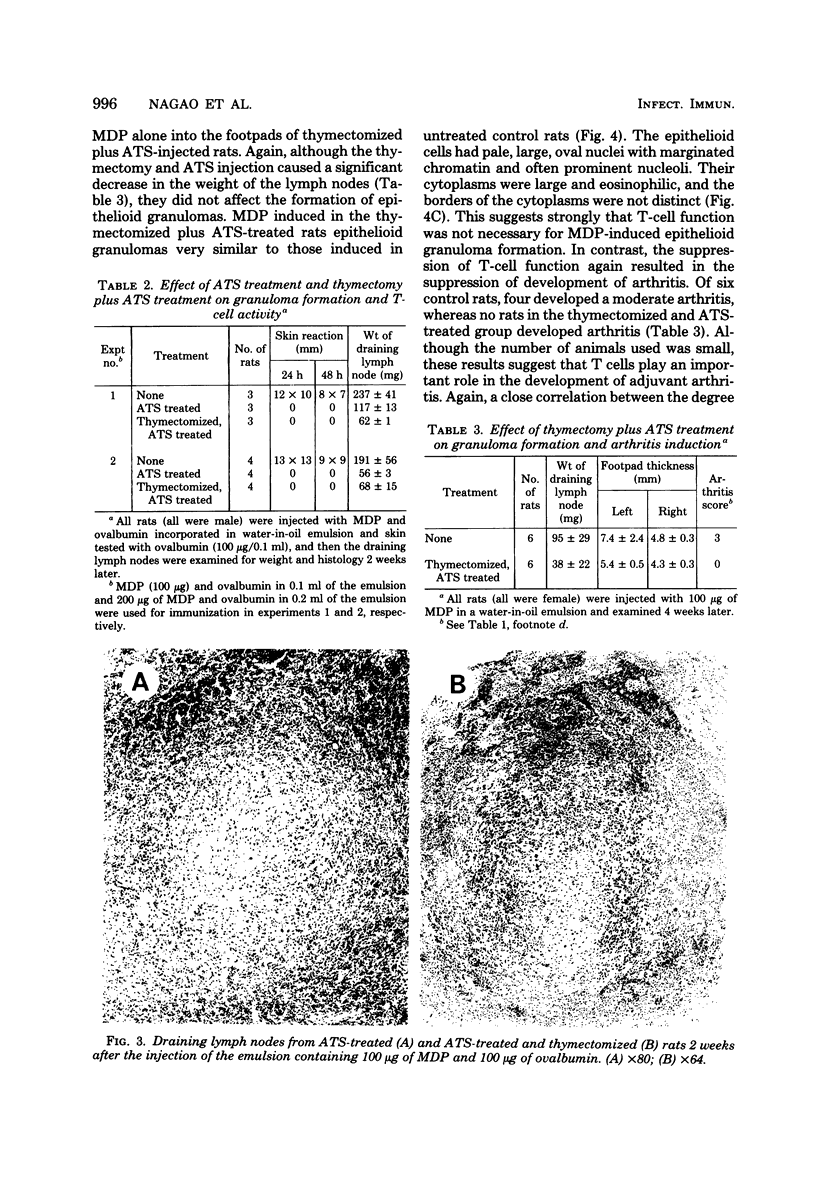
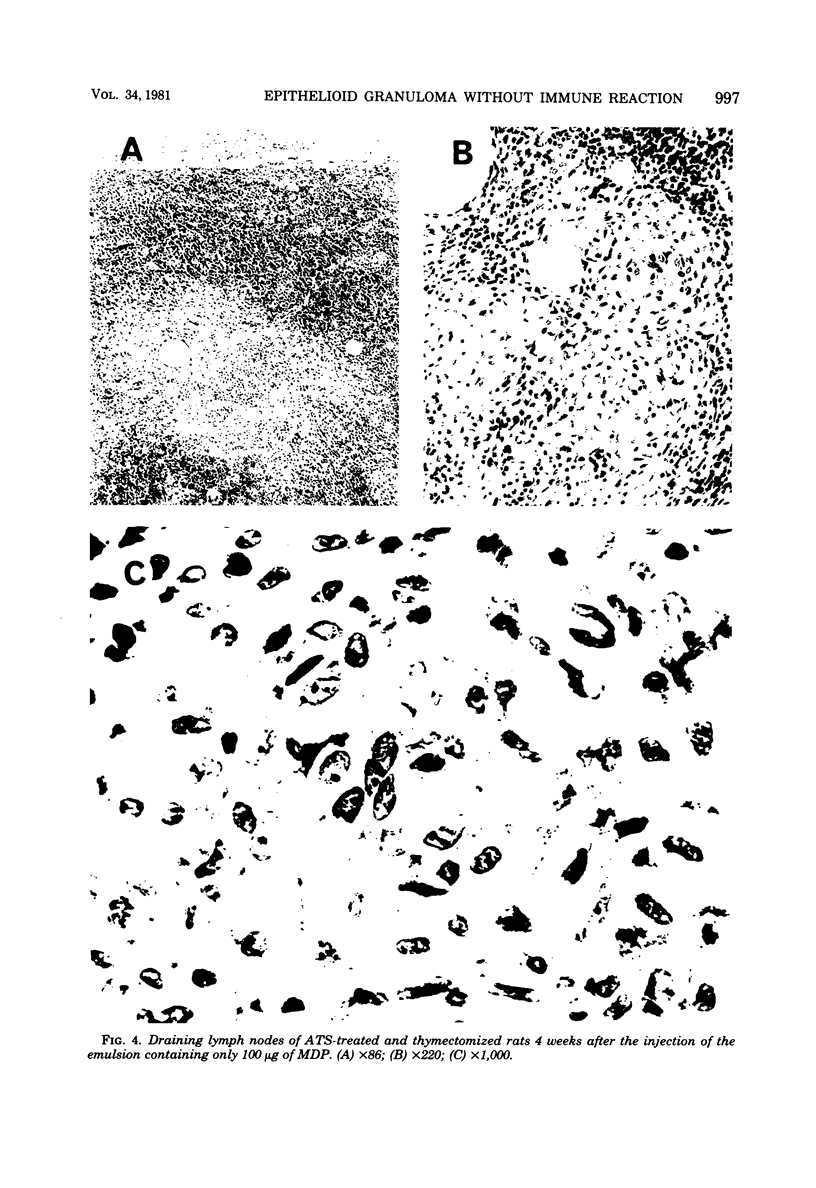
When WKA rats were either neonatally thymectomized or injected with anti-rat thymocyte sera, their T-cell functions were effectively suppressed. When neonatally thymectomized plus anti-rat thymocyte serum-treated rats were injected with non-immunogenic muramyl dipeptide in water-in-oil emulsion, they produced massive epithelioid granulomas. Essentially, no morphological difference was noticed between granulomas induced in untreated rats and in thymectomized plus anti-rat thymocyte serum-treated rats. These findings strongly suggest that muramyl dipeptide-induced epithelioid granulomas required no T cells for their formation. In contrast, the induction of adjuvant arthritis appeared to depend on the presence of T cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O. The granulomatous inflammatory response. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jul;84(1):164–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsden A. F., Boros D. L., Hood A. T. Etiology of the liver granulomatous response in Schistosoma mansoni-infected athymic nude mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.75-80.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audibert F., Heymer B., Gros C., Schleifer K. H., Seidl P. H., Chedid L. Absence of binding of MDP, a synthetic immunoadjuvant, to anti-peptidoglycan antibodies. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1219–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L. Granulomatous inflammations. Prog Allergy. 1978;24:183–267. doi: 10.1159/000401230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. Specific granulomatous hypersensitivity elicited by bentonite particles coated with soluble antigens from schistosome eggs and turcle bacilli. Nature. 1971 Jan 15;229(5281):200–201. doi: 10.1038/229200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byram J. E., Sher A., DiPietro J., von Lichtenberg F. Potentiation of schistosome granuloma formation. By lentinan--a T-cell adjuvant. Am J Pathol. 1979 Feb;94(2):201–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damais C., Parant M., Chedid L. Nonspecific activation of murine spleen cells in vitro by a synthetic immunoadjuvant (N-acetyl-muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine). Cell Immunol. 1977 Nov;34(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori K., Tanaka A. Granuloma formation by synthetic bacterial cell wall fragment: muramyl dipeptide. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):613–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.613-620.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. L. Granulomatous hypersensitivity. Prog Allergy. 1967;11:36–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eugui E. M., Houssay R. H. Passive transfer of unresponsiveness by lymph node cells. Studies on adjuvant disease. Immunology. 1975 Apr;28(4):703–710. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymer B., Hobik H. P., Schäfer H., Bültmann B., Spanel R., Haferkamp O. Animal experimental studies on chronic granulomatous inflammation and T-lymphocyte-system. Beitr Pathol. 1975 Nov;156(2):128–144. doi: 10.1016/s0005-8165(75)80146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAKOVIC K., WAKSMAN B. H. EFFECT OF SENSITIZATION TO BSA ON ADJUVANT DISEASE IN NORMAL AND NEONATALLY THYMECTOMIZED RATS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jul;119:676–678. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasdon E. J., Schlossman S. F. An experimental model of pulmonary arterial granulomatous inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jun;71(3):365–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayashima K., Koga T., Onoue K. Role of T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. II. Different subpopulations of T lymphocytes functioning in the development of the disease. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1127–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Tanaka A., Kotani S., Shiba T., Kusumoto S., Yokogawa K., Kawata S., Ozawa A. Arthritis-inducing ability of a synthetic adjuvant, N-acetylmuramyl peptides, and bacterial disaccharide peptides related to different oil vehicles and their composition. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.70-75.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee M. P., Myrvik Q. N., Leake E. S. Organization of allergic granulomas and dependence on insoluble antigen. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Sep;24(3):253–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtar N. M., Spector W. G. Facsimile epithelioid cells obtained from stimulated peritoneal macrophages and their secretory activity in vitro. J Pathol. 1979 Jul;128(3):117–126. doi: 10.1002/path.1711280302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Miki T., Tanaka A. Macrophage activation by muramyl dipeptide (MDP) without lymphocyte participation. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(1):41–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Tanaka A. Muramyl dipeptide-induced adjuvant arthritis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):624–626. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.624-626.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Tanaka A., Yamamoto Y., Koga T., Onoue K., Shiba T., Kusumoto K., Kotani S. Inhibition of macrophage migration by muramyl peptides. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):308–312. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.308-312.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota F., Parker D., Turk J. L. Further evidence for non-T-cell regulation of delayed hypersensitivity in the guinea pig. Cell Immunol. 1979 Mar 15;43(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou J. M., Spector W. G. The origin, properties and fate of epithelioid cells. J Pathol. 1971 Nov;105(3):187–203. doi: 10.1002/path.1711050305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Bendtzen K., Greineder D. Mediators of immunity: lymphokines and monokines. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:55–136. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell T. L., Spector W. G. The effect of neonatal and adult thymectomy on the inflammatory response. J Pathol. 1972 Sep;108(1):15–21. doi: 10.1002/path.1711080103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton J. S., Weiss L. Transformation of monocytes in tissue culture into macrophages, epithelioid cells, and multinucleated giant cells. An electron microscope study. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):303–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Emori K. Epithelioid granuloma formation by a synthetic bacterial cell wall component, muramyl dipeptide (MDP). Am J Pathol. 1980 Mar;98(3):733–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Benacerraf B. Immunologic events in experimental hypersensitivity granulomas. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jun;71(3):349–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. G., Kreeftenberg J. G., Kruijt B. C., Kruizinga W., Steerenberg P. The athymic nude rat. II. Immunological characteristics. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Feb;15(2):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood F. D., Pearson C. M., Tanaka A. Capacity of mycobacterial wax D and its subfractions to induce adjuvant arthritis in rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;35(5):456–467. doi: 10.1159/000230198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]