Abstract
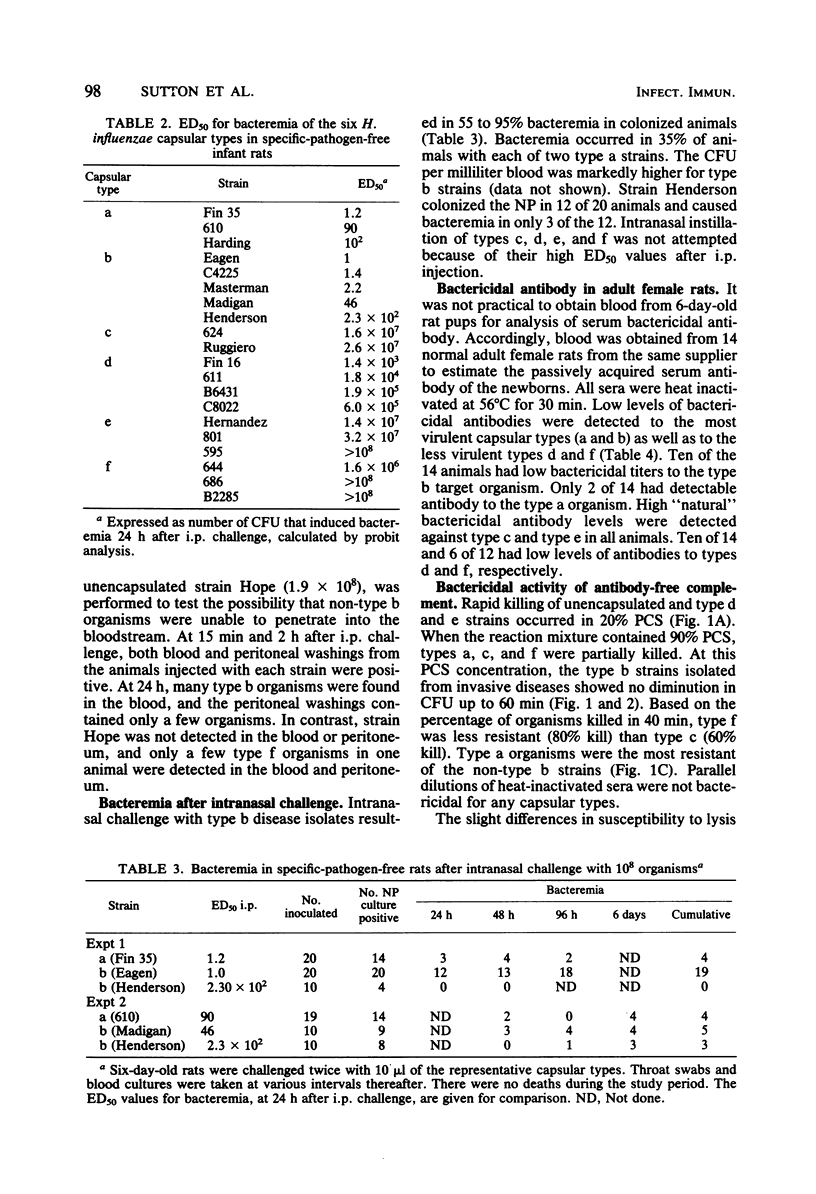
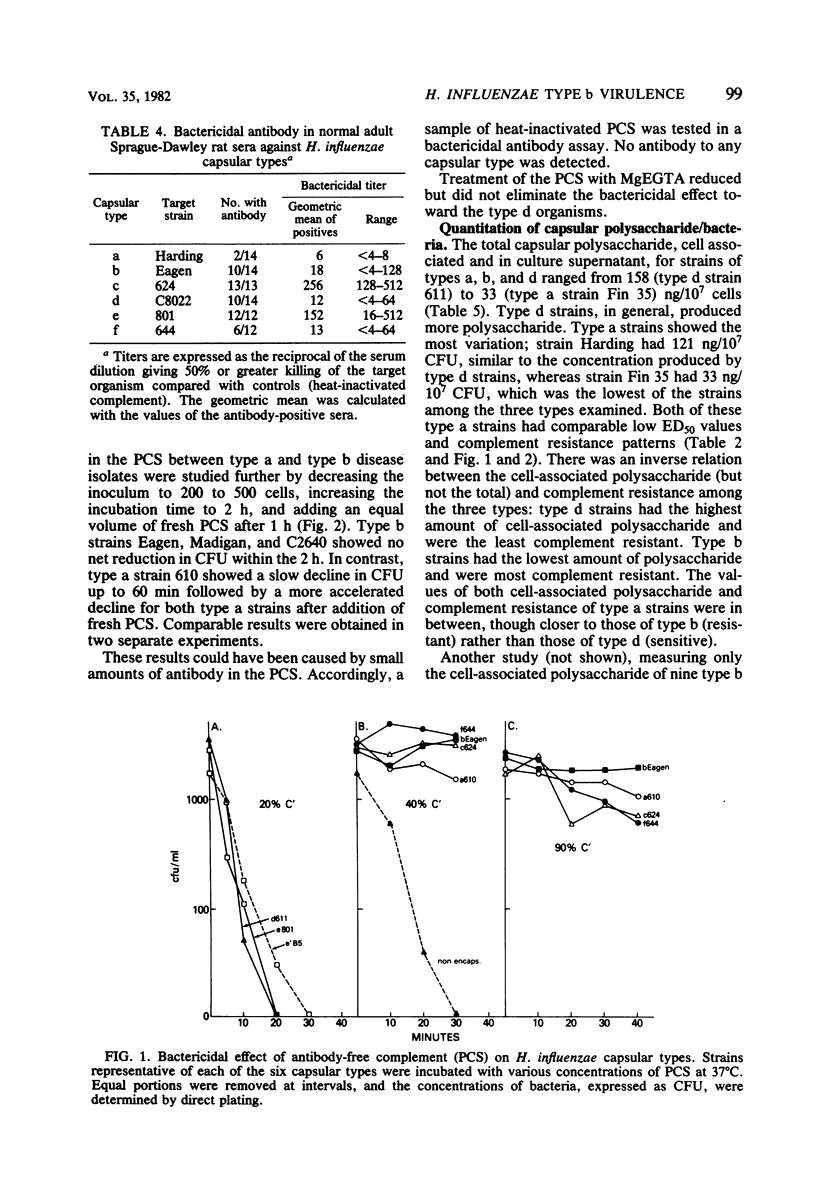
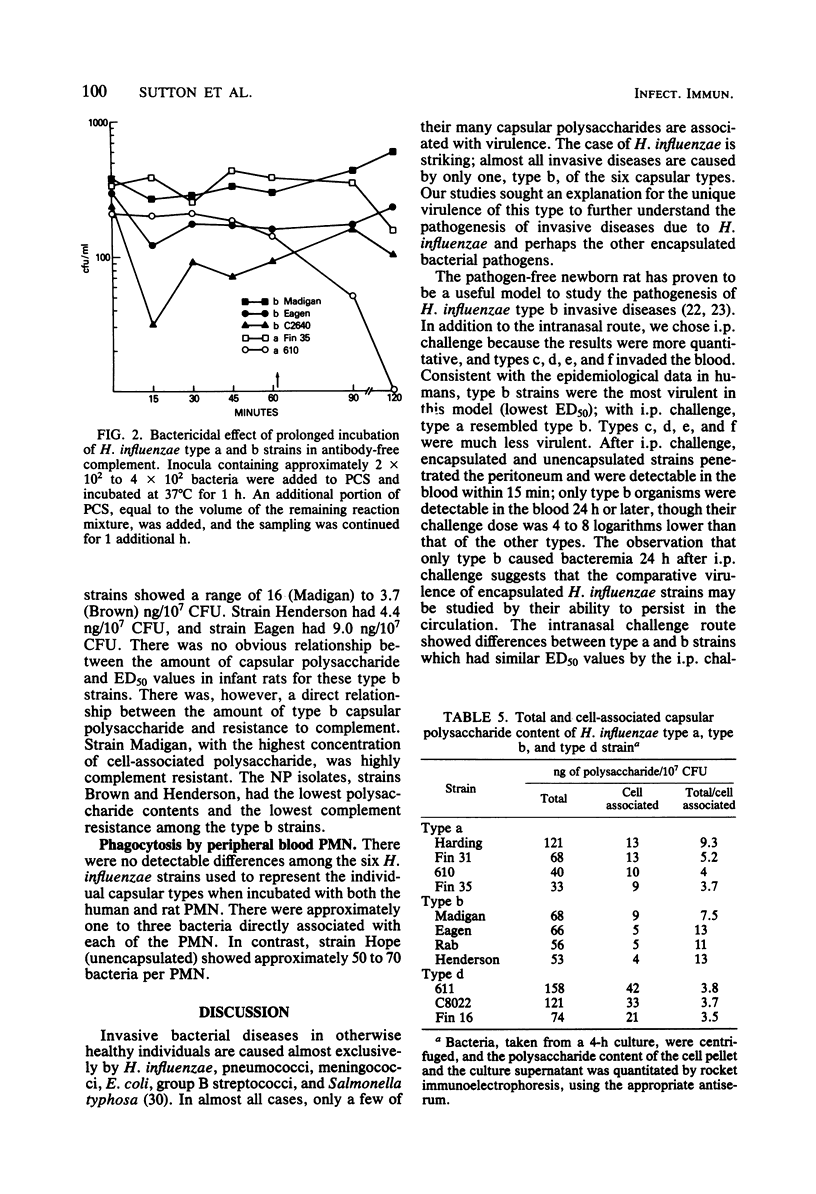
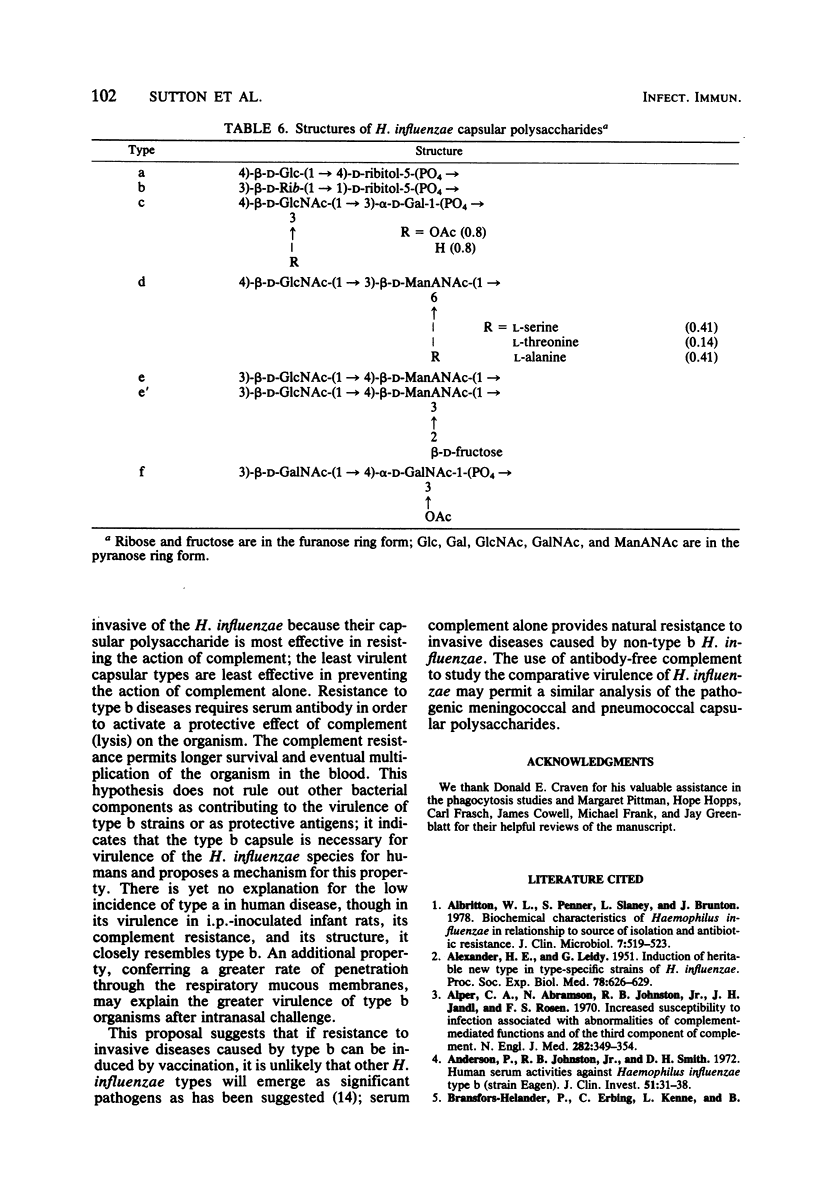
Studies were undertaken to gain insight into the virulence of type b in contrast to the other Haemophilus influenzae capsular types. A relationship was found between the comparative virulence of H. influenzae types in humans and their resistance to the bactericidal effect of antibody-free complement. Type b was most resistant to the bactericidal effect of complement. The other types could be divided into three groups based upon their susceptibility to complement; this grouping was also related to their structural similarities. No association between virulence and either the biotype, source of isolate, in vitro association with peripheral polymorphonuclear leukocytes, or the total amount of capsular polysaccharide was found. However, among the type b strains, higher levels of cell-associated polysaccharide were associated with increased resistance to complement. The relative virulence of the six H. influenzae types in the infant rat model was generally similar to that in humans. After intraperitoneal challenge, type b and type a strains had the lowest 50% effective doses for bacteremia, removed by several logs from the values of the other types. By intranasal challenge, type b strains produced higher rates and levels of bacteremia than did type a strains. High levels of natural bactericidal antibodies to types c and e were found in adult female rats; this finding alone could not account for the differences in virulence among the H. influenzae types in the infant rat model. We propose that the virulence of type b strains is due to their greater resistance to the bactericidal activity of serum complement alone. Resistance to type b disease requires serum antibody to induce the complement-mediated reaction.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER H. E., LEIDY G. Induction of heritable new type in type specific strains of H. influenzae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Nov;78(2):625–626. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albritton W. L., Penner S., Slaney L., Brunton J. Biochemical characteristics of Haemophilus influenzae in relationship to source of isolation and antibiotic resistance. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):519–523. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.519-523.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Abramson N., Johnston R. B., Jr, Jandl J. H., Rosen F. S. Increased susceptibility to infection associated with abnormalities of complement-mediated functions and of the third component of complement (C3). N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 12;282(7):350–354. doi: 10.1056/nejm197002122820701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Johnston R. B., Jr, Smith D. H. Human serum activities against Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI106793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Loos M. Antibody-independent binding of the first component of complement (C1) and its subcomponent C1q to the S and R forms of Salmonella minnesota. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1138–1144. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1138-1144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosson F. J., Jr, Winkelstein J. A., Moxon E. R. Participation of complement in the nonimmune host defense against experimental Haemophilus influenzae type b septicemia and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):882–887. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.882-887.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan W., Tsui F. P., Schneerson R. Structural studies of the Haemophilus influenzae type f capsular polysaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1980 Mar;79(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83839-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung J. C., Wicher K. Minimum number of bacteria needed for antigen detection by counterimmunoelectrophoresis: in vivo and in vitro studies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):681–687. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.681-687.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Howard C. J. The sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli related to their K antigens. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):331–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodes D. S., Leidy G. Meningitis caused by Hemophilus influenzae type e. J Pediatr. 1977 Nov;91(5):844–845. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E., Wentworth B. B., Beasley R. P., Foy H. M. Correlation of circulating capsular polysaccharide with bacteremia in pneumococcal pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):431–437. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.431-437.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Sørensen I., Frederiksen W. Biochemical characteristics of 130 recent isolates from Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):409–412. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.409-412.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIDY G., HAHN E., ZAMENHOF S., ALEXANDER H. E. Biochemical aspects of virulence of Hemophilus influenzae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1195–1202. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman S. J., Kucera J. C., Brunken J. M. Nasopharyngeal carriage of antibiotic-resistant Haemophilus influenzae in healthy children. Pediatrics. 1979 Sep;64(3):287–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Wellek B., Thesen R., Opferkuch W. Antibody-independent interaction of the first component of complement with Gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):5–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.5-9.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Stonebraker F. E., Robbins J. B. Use of antiserum agar for detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b in the pharynx. Pediatr Res. 1975 May;9(5):513–516. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197505000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Murphy P. A. Haemophilus influenzae bacteremia and meningitis resulting from survival of a single organism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1534–1536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Vaughn K. A. The type b capsular polysaccharide as a virulence determinant of Haemophilus influenzae: studies using clinical isolates and laboratory transformants. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):517–524. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor P. F., Little T. W. A simple method for isolating leucocytes from bovine blood and their separation into lymphocyte and granulocyte fractions. Res Vet Sci. 1975 May;18(3):336–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A., Lepow I. H. Host defense against Neisseria meningitidis requires a complement-dependent bactericidal activity. Science. 1979 Jul 20;205(4403):298–299. doi: 10.1126/science.451601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. H., Crosson F. J., Jr, Winkelstein J. A., Moxon E. R. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by Haemophilus influenzae type B. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):400–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.400-402.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Stull T. L., Smith A. L. Comparative virulence of Haemophilus influenzae with a type b or type d capsule. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):518–524. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.518-524.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Ellman L., Frank M. M. Bactericidal and opsonic properties of C4-deficient guinea pig serum. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):477–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERZL J., KOSTKA J., LANC A. Development of bactericidal properties against gram-negative organisms in the serum of young animals. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1962 May;7:162–174. doi: 10.1007/BF02928237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERZL J., PESAK V., KOSTKA J., JILEK M. THE RELATION BETWEEN THE BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY OF COMPLEMENT AND THE CHARACTER OF THE BACTERIAL SURFACES. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1964 Sep;89:284–298. doi: 10.1007/BF02873307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santosham M., Moxon E. R. Detection and quantitation of bacteremia in childhood. J Pediatr. 1977 Nov;91(5):719–721. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Bradshaw M., Whisnant J. K., Myerowitz R. L., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. An Escherichia coli antigen cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b: occurrence among known serotypes, and immunochemical and biologic properties of E. coli antisera toward H. influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1551–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Age-related susceptibility to Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.397-401.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Morrison D. C., Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Bactericidal activity of the alternative complement pathway generated from 11 isolated plasma proteins. J Exp Med. 1979 Apr 1;149(4):870–882. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.4.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith D. H., Averill D. R., Jr, Marino J., Moxon E. R. Production of Haemophilus influenzae b meningitis in infant rats by intraperitoneal inoculation. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):278–290. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.278-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Huang S. N., Welch W. D., Young L. S. Restricted complement activation by Escherichia coli with the K-1 capsular serotype: a possible role in pathogenicity. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2174–2180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TACHIBANA D. K. CHARACTERIZATION OF THE BACTERICIDAL ACTION OF PRECOLOSTRAL PIGLET AND CALF SERA AGAINST GRAM NEGATIVE ENTERIC BACTERIA IN ROUGH PHASE. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1965 May;10:145–155. doi: 10.1007/BF02881005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Simpson D. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Homozygous deficiency of the second component of complement presenting with recurrent bacterial meningitis. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Jun;55(6):471–473. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.6.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui F. P., Schneerson R., Egan W. Structural studies of the Haemophilus influenzae type e capsular polysaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1981 Jan 15;88(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84603-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., van Dijk W. C., van Erne M. E., Peters R., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Quantitation of the third component of human complement attached to the surface of opsonized bacteria: opsonin-deficient sera and phagocytosis-resistant strains. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):808–814. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.808-814.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Tomasz A. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by pneumococcal cell wall teichoic acid. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):174–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Barrera O., Sutton A., May J., Hochstein D. H., Robbins J. D., Robbins J. B., Parkman P. D., Seligmann E. B., Jr Standardization and control of meningococcal vaccines, group A and group C polysaccharides. J Biol Stand. 1977;5(3):197–215. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(77)80005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



