Abstract
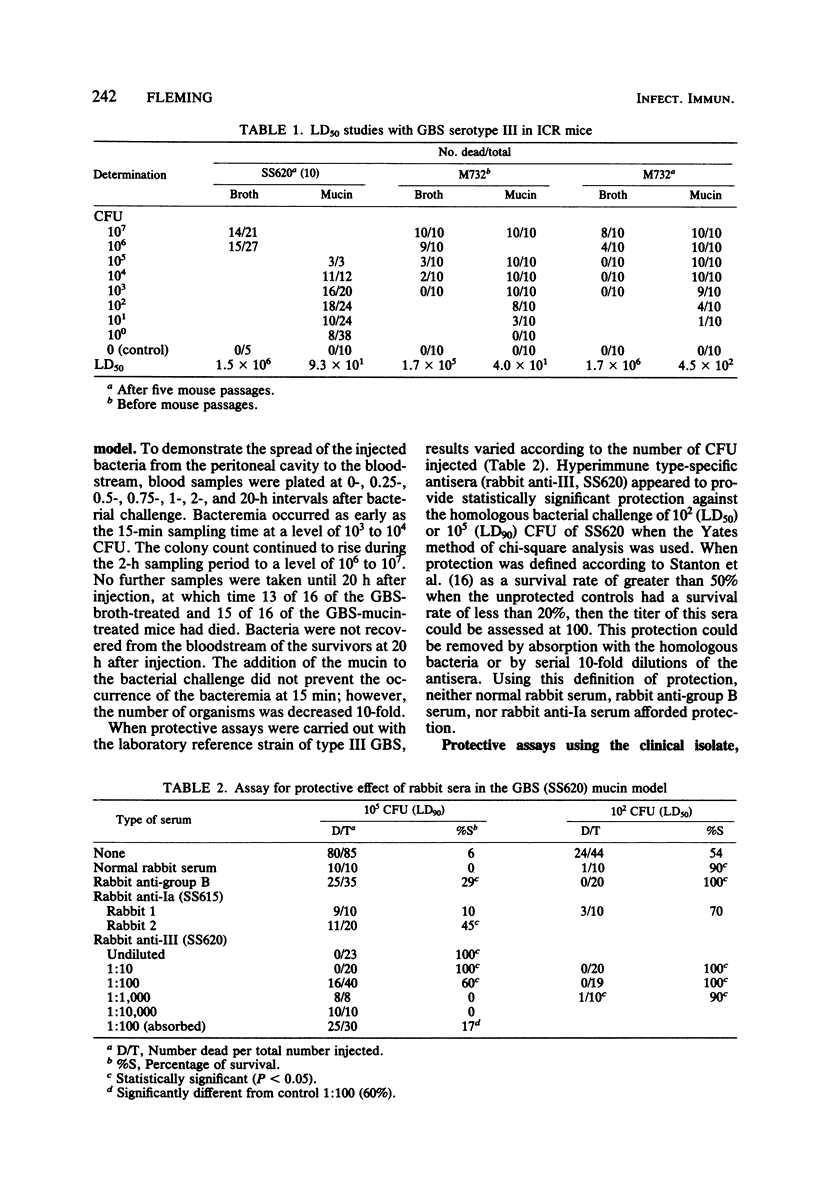
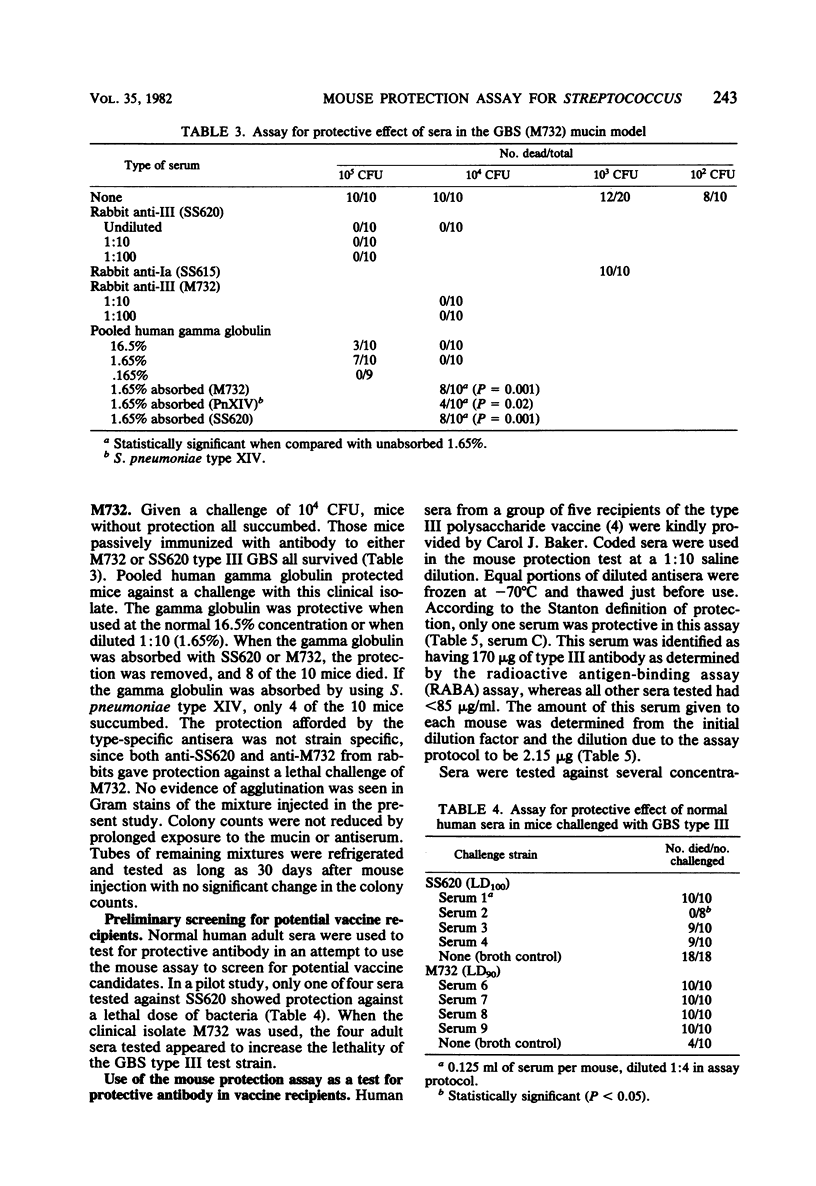
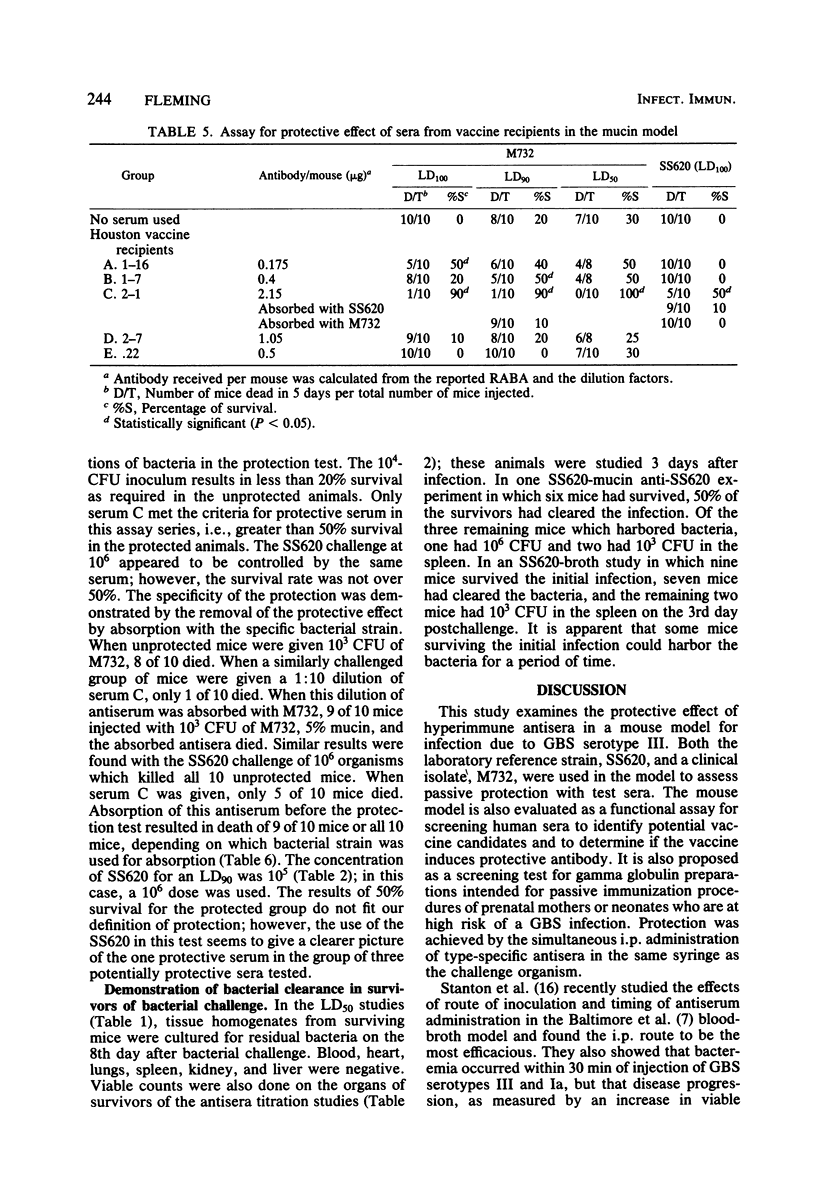
The mucin model for group B Streptococcus (GBS) type III was used to assay the protective effect of sera against a type III challenge in mice. Hyperimmune rabbit sera, prepared by the Lancefield method against the laboratory reference strain (SS620) and a clinical isolate (M732), protected against a lethal challenge with either strain of GBS type III. Absorption of the sera with either of these type III strains removed the protective effect. Neither normal rabbit sera nor heterologous antisera (anti-Ia, SS615) provided protection; however, protection was obtained with pooled human gamma globulin. Sera from adult volunteers were tested to assay protective levels in the mouse model. Human sera enhanced the mouse lethality of the clinical isolate, M732, but not the laboratory reference strain, SS620. Sera from adults vaccinated with type III polysaccharide of GBS were also tested. The murine-mucin-GBS model may be developed as a screening test to measure protective antibody levels in the pre- and postvaccine treatment period. The model may also be used to measure protective antibody in pooled human gamma globulin for use in the passive immunization of high-risk individuals.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. J., Goroff D. K., Alpert S. L., Hayes C., McCormack W. M. Comparison of bacteriological methods for the isolation of group of B Streptococcus from vaginal cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):46–48. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.46-48.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J. Group B streptococcal infections. Adv Intern Med. 1980;25:475–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Edwards M. S., Schiffman G. Influence of preimmunization antibody levels on the specificity of the immune response to related polysaccharide antigens. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 24;303(4):173–178. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007243030401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Microcapsule of type III strains of group B Streptococcus: production and morphology. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):189–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.189-194.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Webb B. J., Kasper D. L., Yow M. D., Beachler C. W. The natural history of group B streptococcal colonization in the pregnant woman and her offspring. II. Determination of serum antibody to capsular polysaccharide from type III, group B Streptococcus. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 May 1;137(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Antibody to group B Streptococcus type III in human sera measured by a mouse protection test. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):56–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.56-61.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Kasper D. L., Vecchitto J. Mouse protection test for group B Streptococcus type III. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):81–88. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Chow A. W., Anthony B. F., Guze L. B. Serious infections in adults due to group B streptococci. Clinical and serotypic characterization. Am J Med. 1976 Oct;61(4):498–503. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleat P. H., Ross J., Needham J. R. Antibody levels in mothers colonised with group B streptococci during pregnancy and in their newborn infants, as measured by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1980 Feb;168(1):49–53. doi: 10.1007/BF02121651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. O. Mucin model for group B type III streptococcal infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):449–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.449-454.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Rosell K. G., Kasper D. L. Structural determination and serology of the native polysaccharide antigen of type-III group B Streptococcus. Can J Biochem. 1980 Feb;58(2):112–120. doi: 10.1139/o80-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner P. I., Gopalakrishna K. V., Wolinsky E., McHenry M. C., Tan J. S., Rosenthal M. Group B streptococcus (S. agalactiae) bacteremia in adults: analysis of 32 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Nov;56(6):457–473. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197711000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas J. M. Serious group B beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections in adults: report of two cases and review of the literature. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1978 Feb;142(2):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. F., Baltimore R. S., Shedd D. G. Effects of route and time of administration of antiserum on protection of mice from lethal infection due to group B Streptococcus type III. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):391–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.391-395.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel L. C., Boyer K. M., Gotoff S. P., Kasper D. L., Baker C. J. Comparison of assays for antibody to group B Streptococcus, type III. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):530–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin J., Forsgren A. Group B streptococci in venereal disease clinic patients. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Dec;51(6):401–404. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.6.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennerstrom D. E., Schutt R. W. Adult mice as a model for early onset group B streptococcal disease. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):741–744. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.741-744.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W. Detection of group B streptococcal antibodies in human sera by radioimmunoassay: concentrations of type-specific antibodies in sera of adults and infants infected with group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):194–201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.194-201.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


