Abstract
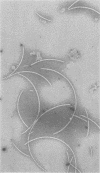
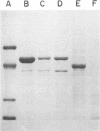
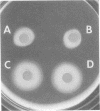
Flagella from various strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were isolated by shearing the flagella followed by differential centrifugation to obtain typical filaments as viewed through an electron microscope. Electrophoretic analysis showed a major protein band corresponding to a flagellin with molecular weight of 53,000. Among the strains tested, flagellar antigen (FAg) preparations isolated from strains 1244 and 1210 routinely gave the highest percentage of flagellin, with the least amount of protein impurities, when grown on succinate-mineral salts medium. All FAg preparations contained 3 to 10 micrograms of 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate-positive material per mg of protein. Strain PA-103 lacked flagella and exhibited no flagellin band, and preparations from PA-103 had a relatively higher content of 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate. The isolation of highly purified, single-banded flagellin could be accomplished by elution of the 53,000-molecular weight gel band. Amino acid analysis showed 16 amino acids, but no proline. Antisera to FAg preparations were used to demonstrate inhibition of motility of strains RM-46 and M-2. Heated RM-46 FAg antisera and PA-103 antisera did not inhibit motility.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorg R., Schmitt W. Immunologische und elektrophoretische Charakterisierung der Flagelline unterschiedlicher H-Typen von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1980;168(3):217–226. doi: 10.1007/BF02122856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven R. C., Montie T. C. Motility and chemotaxis of three strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa used for virulence studies. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Apr;27(4):458–460. doi: 10.1139/m81-070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H., Sokol P. A. Evidence for the role of toxin A in the pathogenesis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in humans. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):538–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Haidaris C. G. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: extracellular protease and elastase as in vivo virulence factors. Can J Microbiol. 1979 May;25(5):593–599. doi: 10.1139/m79-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Jr, Higuchi J. H., Chaudhuri T. R., Woods D. E. Bacterial adherence to epithelial cells in bacillary colonization of the respiratory tract. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jan;121(1):55–63. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y. Pathogenesis of the mouse keratitis produced with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Dec;45(6):515–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulton R. C., Montie T. C. Chemotaxis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):274–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.274-280.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Sastry P. A., Frost L. S., Carpenter M., Armstrong G. D., Watts T. H. Biochemical studies on pili isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Oct;25(10):1175–1181. doi: 10.1139/m79-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penke B., Ferenczi R., Kovács K. A new acid hydrolysis method for determining tryptophan in peptides and proteins. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick I. G., Ford C. W., Shackleford G. M., Berry L. J. Improved protection against cholera in adult rabbits with a combined flagellar-toxoid vaccine. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):375–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.375-380.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saelinger C. B., Snell K., Holder I. A. Experimental studies on the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: direct evidence for toxin production during Pseudomonas infection of burned skin tissues. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):555–561. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:397–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell K., Holder I. A., Leppla S. A., Saelinger C. B. Role of exotoxin and protease as possible virulence factors in experimental infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):839–845. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.839-845.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Bass J. A., Johanson W. G., Jr, Straus D. C. Role of adherence in the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):694–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.694-699.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. The role of exotoxins in the pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):626–630. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]