Abstract
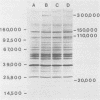
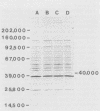
The humoral immune responses to Trypanosoma brucei infection were examined in N'dama and in Zebu, two breeds of cattle recognized for their differing susceptibility to trypanosomiasis. Regardless of the clinical course, animals of both breeds produced antibodies to nonsurface trypanosome antigen(s) detectable by both immunodiffusion and immune fluorescence. As a new approach to assessment of the humoral response to trypanosome infection, protein antigens responded to were isolated by immune precipitation, and their molecular weights were determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. This allowed the detection of differences in the immune response which correlated with the clinical course of the disease. All cattle of both breeds which exhibited a capacity to control the disease recognized at least one of three specific antigens: protein of 110,000, 150,000, and 300,000 daltons. The N'dama, which proved less susceptible to the disease, generally responded to more of the three identified trypanosome protein antigens than did the Zebu. Animals which died of trypanosomiasis failed to produce detectable antibodies to any of the three specific proteins, although they sometimes exhibited antibodies to another trypanosome antigen.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHCROFT M. T., BURTT E., FAIRBAIRN H. The experimental infection of some African wild animals with Trypanosoma rhodesiense, T. brucei and T. congolense. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1959 Jun;53:147–161. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1959.11685912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbet A. F., McGuire T. C. Crossreacting determinants in variant-specific surface antigens of African trypanosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1989–1993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz G. An evaluation of the capillary and latex agglutination and heterophile antibody tests for the detection of Trypanosoma rhodesiense infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;47(6):773–778. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Conjugates of immunoglobulin G with different fluorochromes. I. Characterization by anionic-exchange chromatography. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(3):273–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK H. F., SHEPARD C. C. A DIALYSIS TECHNIQUE FOR PREPARING FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:642–644. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Sacks D. L., Ogilvie B. M., Askonas B. A. Membrane fractions of trypanosomes mimic the immunosuppressive and mitogenic effects of living parasites on the host. Parasite Immunol. 1979 Autumn;1(3):241–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1979.tb00709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Identification, purification and properties of clone-specific glycoprotein antigens constituting the surface coat of Trypanosoma brucei. Parasitology. 1975 Dec;71(3):393–417. doi: 10.1017/s003118200004717x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DESOWITZ R. S. Studies on Trypanosoma vivax. X. The activity of some blood fractions in facilitating infection in the white rat. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1954 Jun;48(2):142–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington J. C., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Pert J. H. Polymer-induced precipitation of antigen-antibody complexes: "precipiplex" reactions. Immunochemistry. 1971 May;8(5):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90504-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaaya G. P., Tizard I. R., Maxie M. G., Valli V. E. Inhibition of leukopoiesis by sera from Trypanosoma congolense infected calves: partial characterization of the inhibitory factor. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1980 Jun;31(2):232–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. [125I]protein A: a tracer for general use in immunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1978;24(3-4):269–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanham S. M., Godfrey D. G. Isolation of salivarian trypanosomes from man and other mammals using DEAE-cellulose. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Dec;28(3):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M., Murray P. K., McIntyre W. I. An improved parasitological technique for the diagnosis of African trypanosomiasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1977;71(4):325–326. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(77)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOENAERS F., NEUJEAN G., EVENS F. Valeur pratique de la réaction de fixation du complément dans la maladie du sommeil à T. gambiense. I. Le diagnostic de la maladie. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop (1920) 1953 Apr;33(2):140–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. Z., Young J. R. An immunochemical method for mRNA purification. Application to messenger RNA encoding trypanosome variable surface antigen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1495–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY R. J. Antibody against Trypanosoma vivax present in normal cotton rat serum. Exp Parasitol. 1957 Jul;6(4):404–411. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(57)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I., Nielsen K. H., Seed J. R., Hall J. E. Biologically active products from African Trypanosomes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Dec;42(4):664–681. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.4.664-681.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meirvenne N., Janssens P. G., Magnus E. Antigenic variation in syringe passaged populations of Trypanosoma (Trypanozoon) brucei. 1. Rationalization of the experimental approach. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1975;55(1):1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. Antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):613–617. doi: 10.1038/273613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]