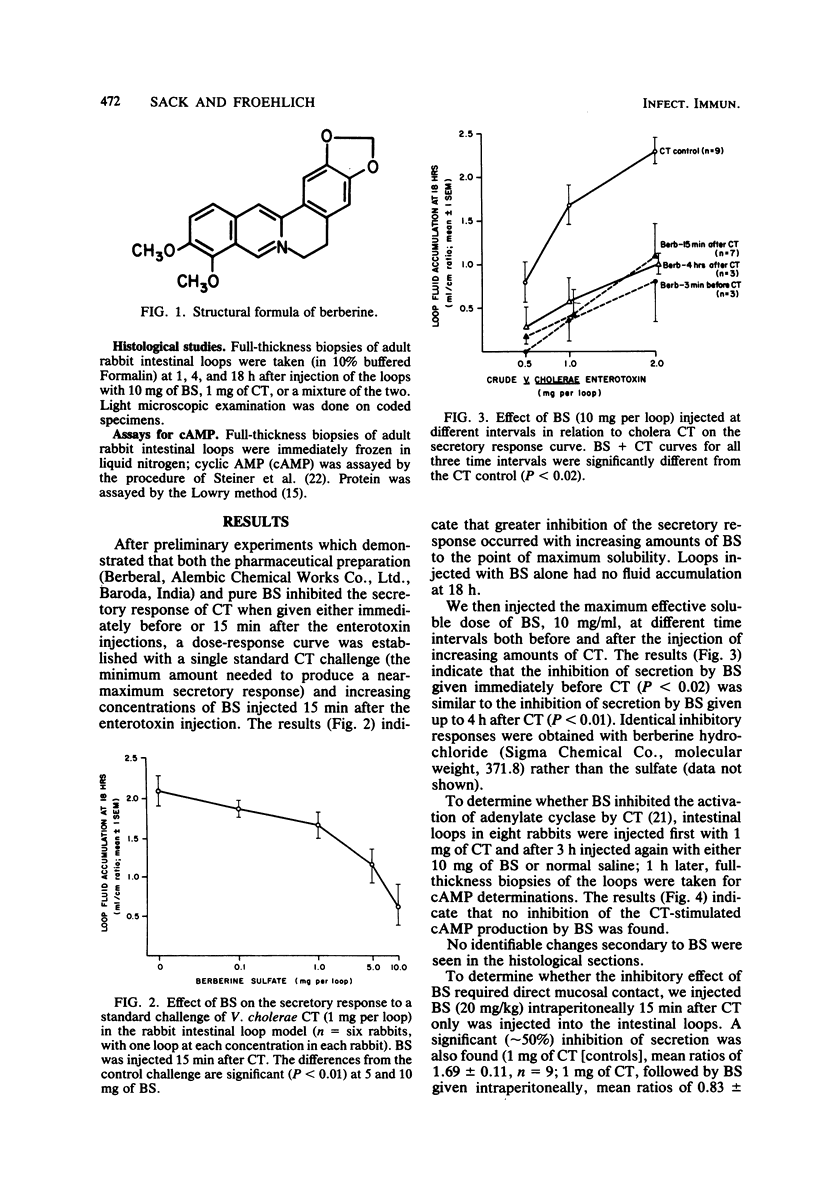
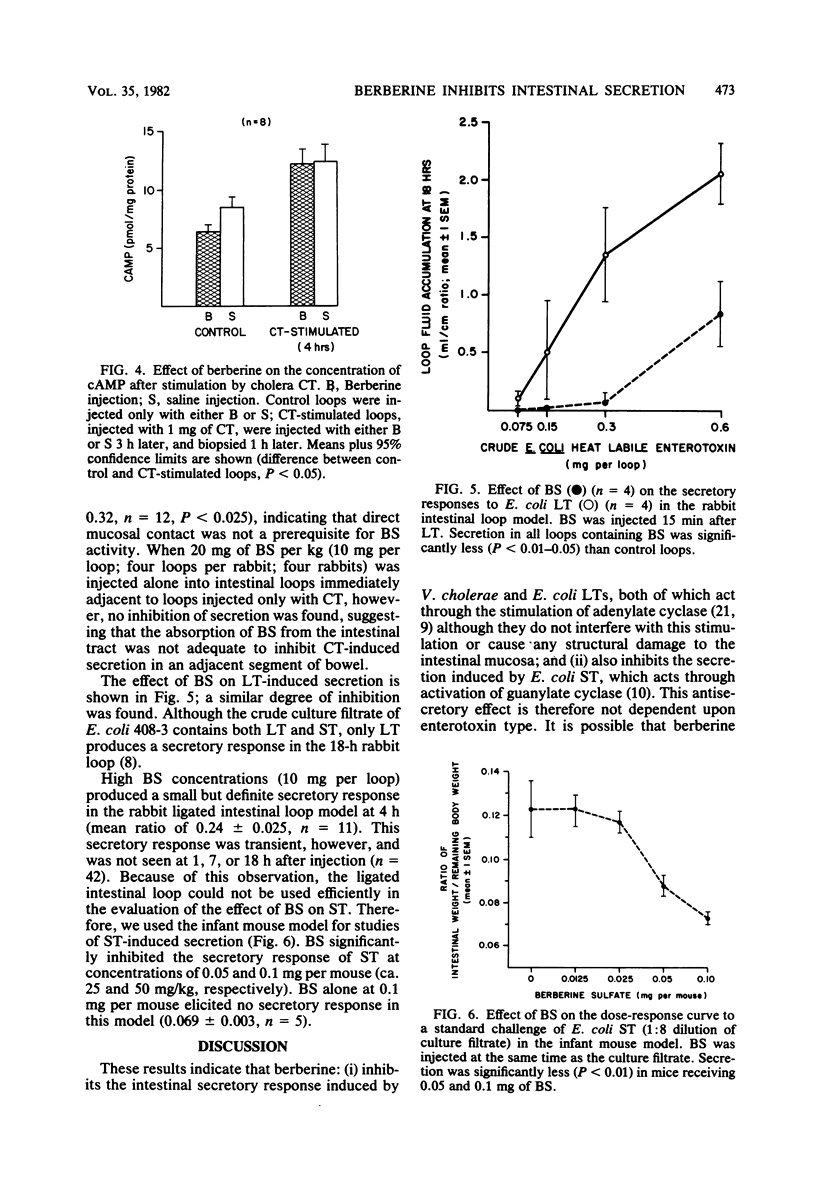
Abstract
Berberine, an alkaloid from the plant Berberis aristata, which has been known since ancient times as an antidiarrheal medication in India and China, inhibited by approximately 70% the secretory responses of the heat-labile enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in the rabbit ligated intestinal loop model. The drug was effective when given either before or after enterotoxin binding and when given either intraluminally or parenterally; it did not inhibit the stimulation of adenylate cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and caused no histological damage to intestinal mucosa. Berberine also markedly inhibited the secretory response of E. coli heat-stable enterotoxin in the infant mouse model. Although the mechanism of action of the drug is not yet known, these data provide a rationale for its apparent clinical usefulness in treating acute diarrheal disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbey D. M., Knoop F. C. Effect of chlorpromazine on the secretory activity of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1000–1003. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1000-1003.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhter M. H., Sabir M., Bhide N. K. Anti-inflammatory effect of berberine in rats injected locally with cholera toxin. Indian J Med Res. 1977 Jan;65(1):133–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhter M. H., Sabir M., Bhide N. K. Possible mechanism of antidiarrhoeal effect of berberine. Indian J Med Res. 1979 Aug;70:233–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin A. H., Subbaiah T. V., Abbasi K. M. Berberine sulfate: antimicrobial activity, bioassay, and mode of action. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Sep;15(9):1067–1076. doi: 10.1139/m69-190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupte S. Use of berberine in treatment of giardiasis. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jul;129(7):866–866. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120440082020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix T. R., Paulk H. T. Intestinal secretion. Int Rev Physiol. 1977;12:257–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lange S., Lönnroth I. Reversal of cyclic AMP-mediated intestinal secretion in mice by chlorpromazine. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1103–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri S. C., Dutta N. K. Berberine and chloramphenicol in the treatment of cholera and severe diarrhoea. J Indian Med Assoc. 1967 Jan 1;48(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Merson M. H., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Martin W. T., Dewitt W. E., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Bessudo D. M. Laboratory investigation of diarrhea in travelers to Mexico: evaluation of methods for detecting enterotoxigenic Echerichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):486–495. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.486-495.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munshi C. P., Vaidya P. M., Buranpuri J. J., Gulati O. D. Kala-azar in Gujarat. J Indian Med Assoc. 1972 Oct 1;59(7):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani G. H., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Holmgren J., Lönnroth I. Chlorpromazine reduces fluid-loss in cholera. Lancet. 1979 Feb 24;1(8113):410–412. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90885-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabir M., Akhter M. H., Bhide N. K. Antagonism of cholera toxin by berberine in the gastrointestinal tract of adult rats. Indian J Med Res. 1977 Mar;65(3):305–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Johnson J., Pierce N. F., Keren D. F., Yardley J. H. Challenge of dogs with live enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and effects of repeated challenges on fluid secretion in jejunal Thiry-Vella loops. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):15–24. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah T. V., Amin A. H. Effect of berberine sulphate on Entamoeba histolytica. Nature. 1967 Jul 29;215(5100):527–528. doi: 10.1038/215527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turjman N., Gotterer G. S., Hendrix T. R. Prevention and reversal of cholera enterotoxin effects in rabbit jejunum by nicotinic acid. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1155–1160. doi: 10.1172/JCI109030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



