Abstract
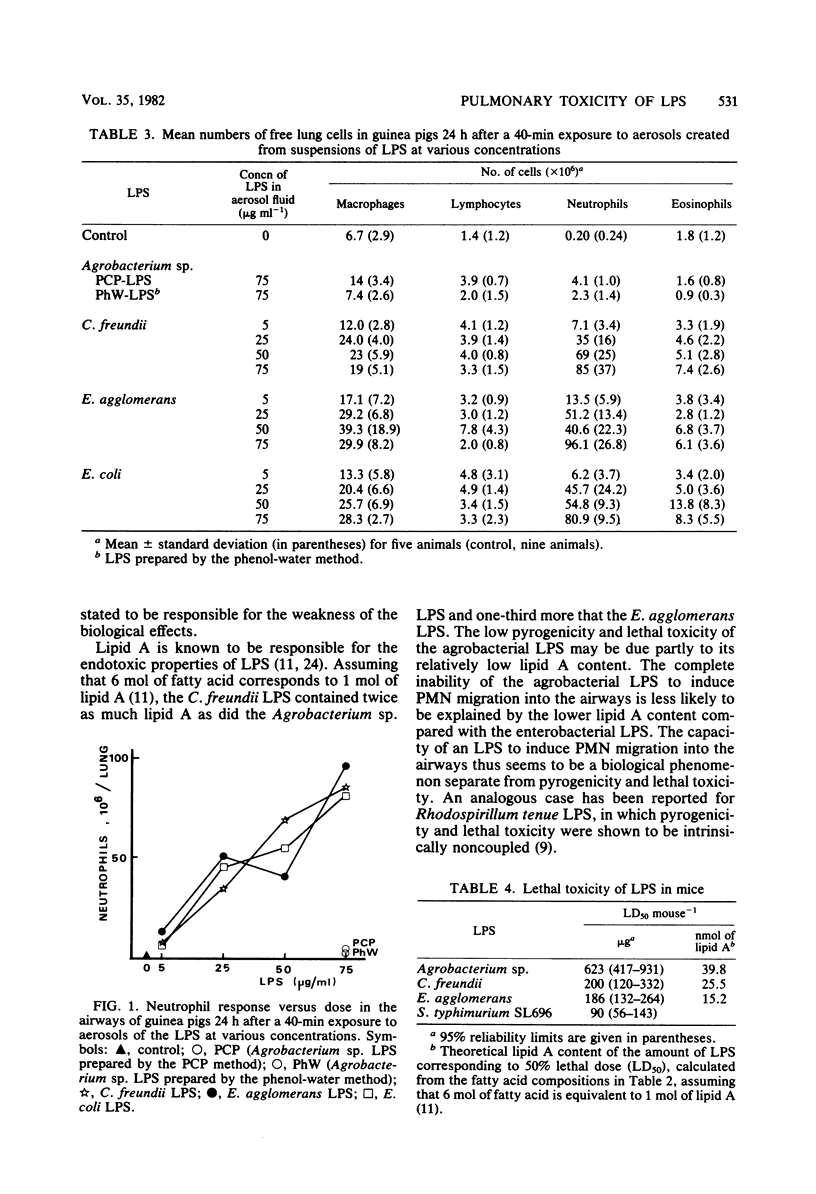
Lipopolysaccharides from three gram-negative bacteria isolated from bale cotton and piggery air were analyzed for their chemical composition, and their pulmonary toxicity for guinea pigs, lethal toxicity for mice, and pyrogenicity for rabbits were measured. Lipopolysaccharides from Enterobacter agglomerans and Citrobacter freundii had closely related chemical compositions; both were pyrogenic for rabbits and caused a dose-dependent influx of polymorphonuclear leukocytes into the airways of guinea pigs. The lethal toxicities of these lipopolysaccharides in mice were comparable to that of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharide, which was used as a reference. Lipopolysaccharide from Agrobacterium sp. was chemically different from those of E. agglomerans and C. freundii, did not induce any influx of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and was only weakly toxic or pyrogenic. The low biological activity of the agrobacterial lipopolysaccharide may be due to its different chemical composition.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinkotai F. F., Whitaker C. J. Airborne bacteria and the prevalence of byssinotic symptoms in 21 cotton spinning mills in Lancashire. Ann Occup Hyg. 1978 Dec;21(3):239–250. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/21.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. Qualitative and quantitative colorimetric determination of heptoses. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):983–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donham K. J., Rubino M., Thedell T. D., Kammermeyer J. Potential health hazards to agricultural workers in swine confinement buildings. J Occup Med. 1977 Jun;19(6):383–387. doi: 10.1097/00043764-197706000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C. Physical state and biological activity of lipopolysaccharides. Toxicity and immunogenicity of the lipid A component. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):214–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Roppel J., Weckesser J., Rietschel E. T., Mayer H. Biological activities of lipopolysaccharides and lipid A from Rhodospirillaceae. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):407–412. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.407-412.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helander I., Salkinoja-Salonen M., Rylander R. Chemical structure and inhalation toxicity of lipopolysaccharides from bacteria on cotton. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):859–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.859-862.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Lehmann V., Mayer H., Rietschel E. T., Weckesser J. Chemical structure and biological activities of lipid A's from various bacterial families. Naturwissenschaften. 1978 Nov;65(11):578–585. doi: 10.1007/BF00364907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muittari A., Rylander R., Salkinoja-Salonen M. Endotoxin and bath-water fever. Lancet. 1980 Jul 12;2(8185):89–89. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92965-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Haglind P., Lundholm M., Mattsby I., Stenqvist K. Humidifier fever and endotoxin exposure. Clin Allergy. 1978 Sep;8(5):511–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1978.tb01504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Lundholm M. Bacterial contamination of cotton and cotton dust and effects on the lung. Br J Ind Med. 1978 Aug;35(3):204–207. doi: 10.1136/oem.35.3.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Snella M. C. Acute inhalation toxicity of cotton plant dusts. Br J Ind Med. 1976 Aug;33(3):175–180. doi: 10.1136/oem.33.3.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thedell T. D., Mull J. C., Olenchock S. A. A brief report of gram-negative bacterial endotoxin levels in airborne and settled dusts in animal confinement buildings. Am J Ind Med. 1980;1(1):3–7. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildfeuer A., Heymer B., Schleifer K. H., Haferkamp O. Investigations on the specificity of the Limulus test for the detection of endotoxin. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):867–871. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.867-871.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



