Abstract
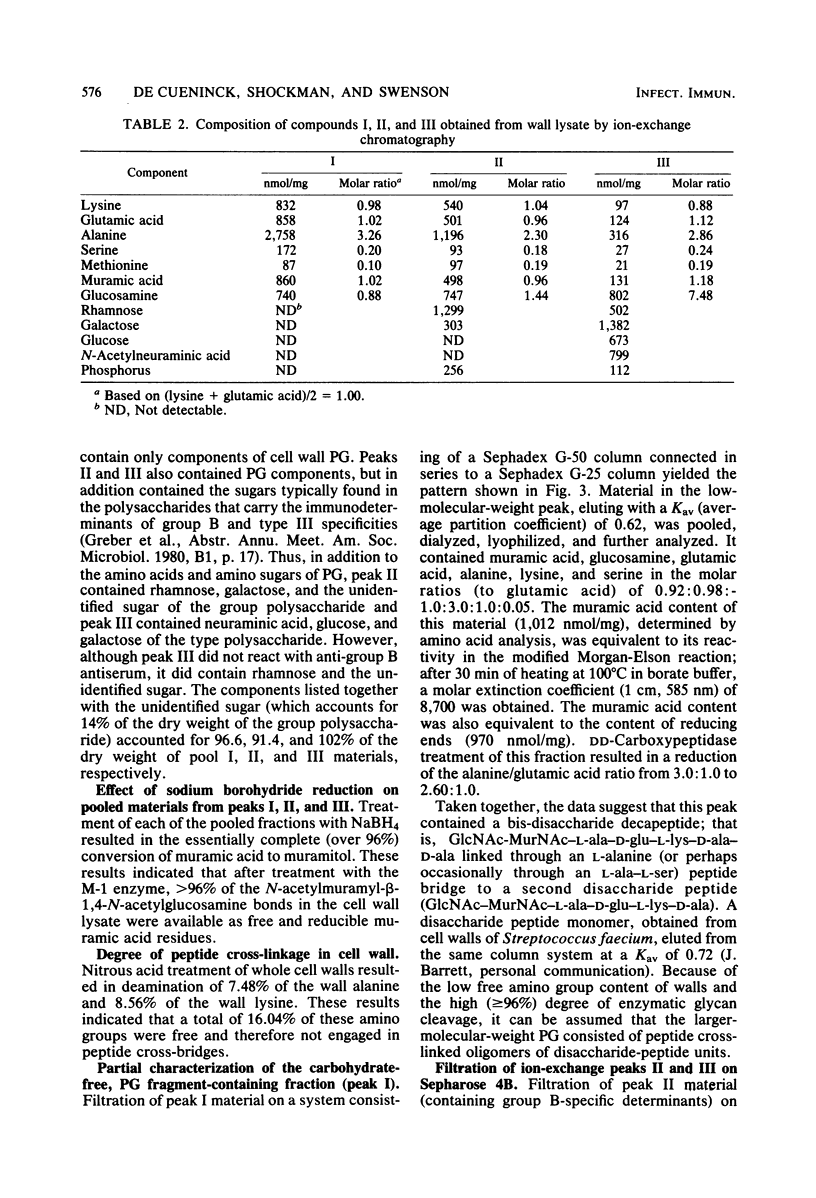
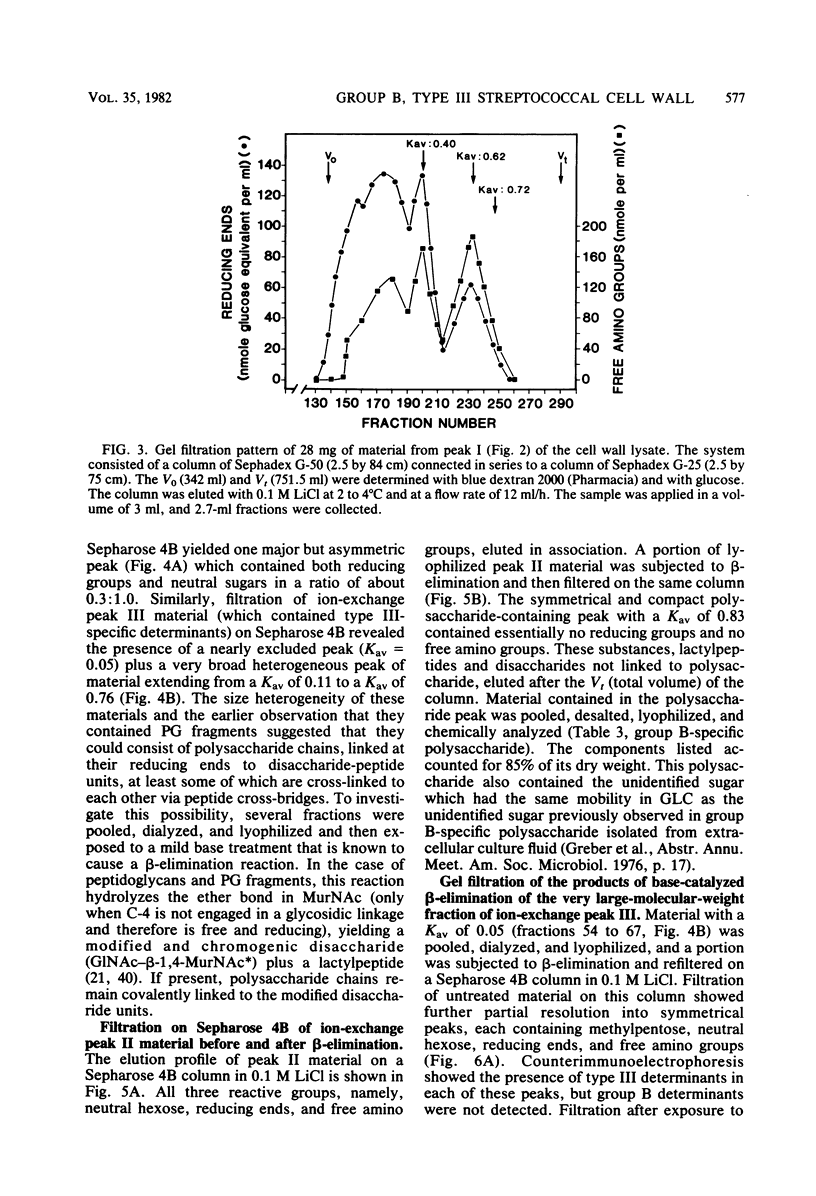
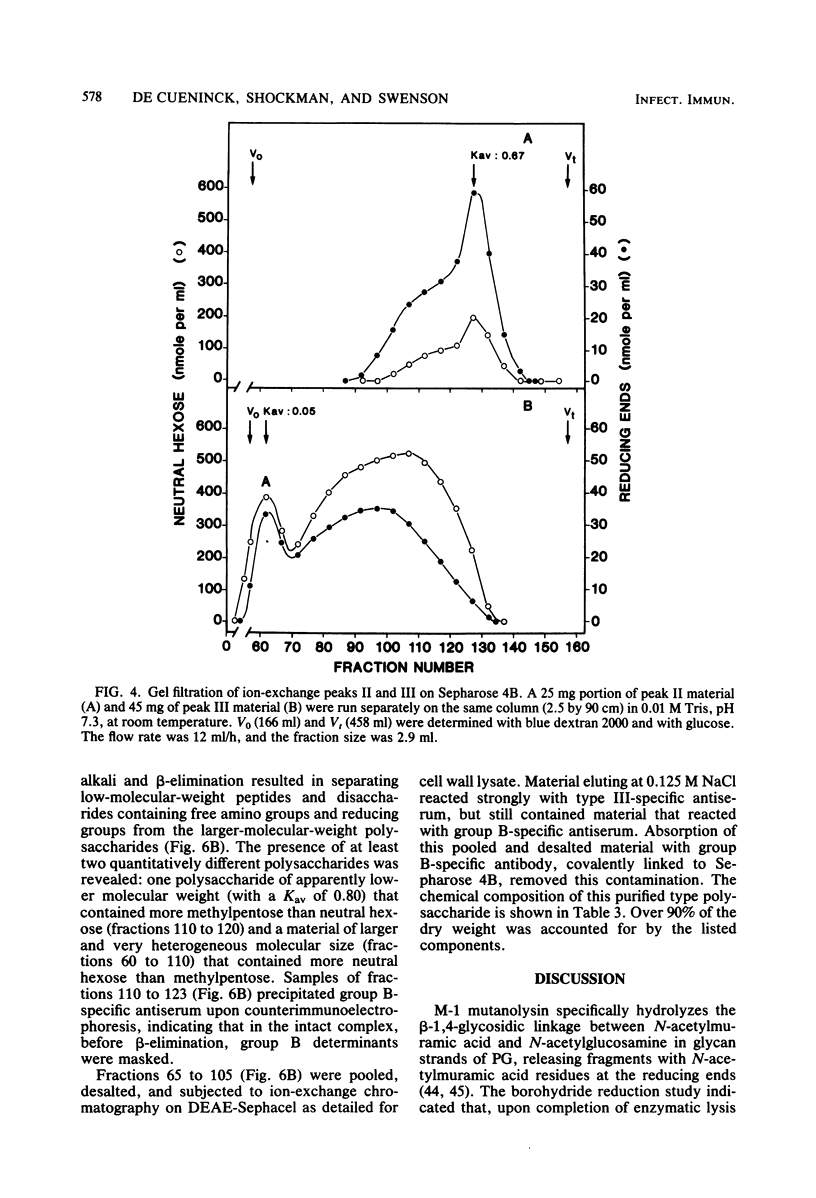
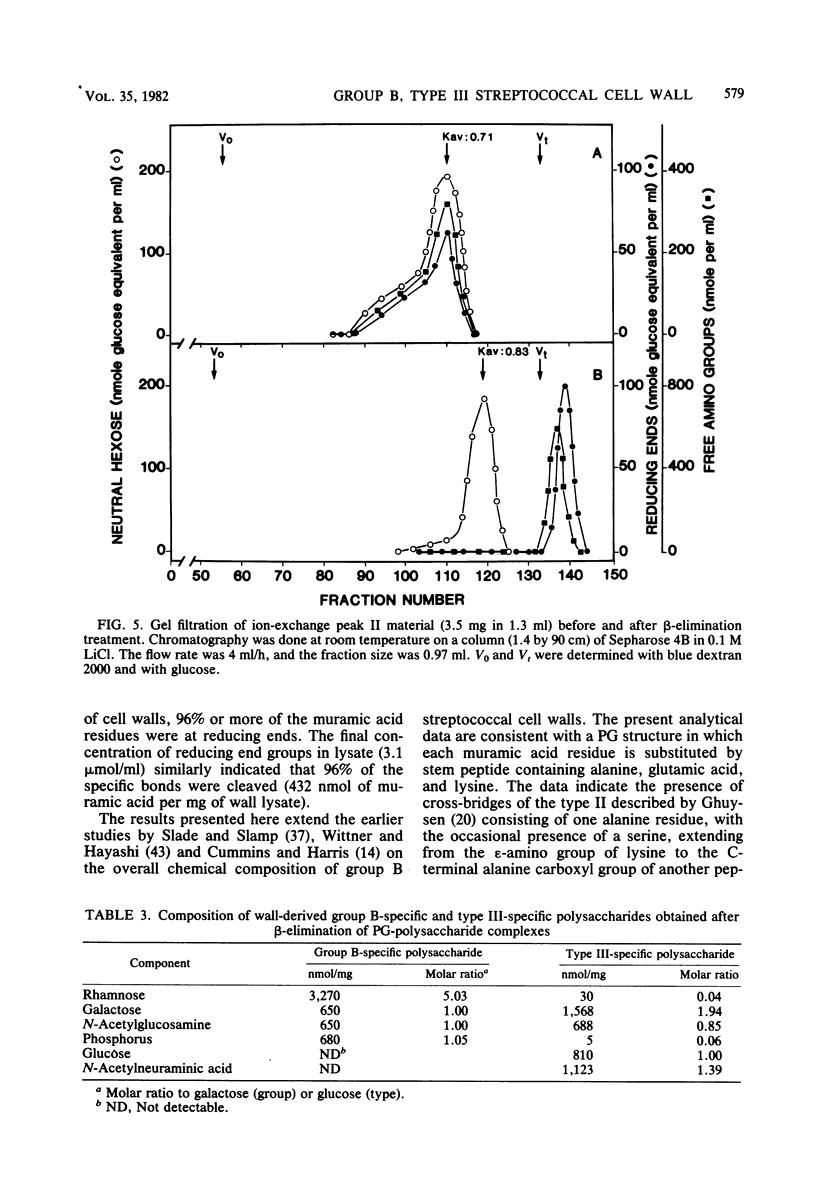
Cell walls from a group B, type III streptococcus strain were prepared, purified by extraction with sodium dodecyl sulfate, and solubilized by the M-1 fraction of mutanolysin, an endo-N-acetylmuramidase obtained from Streptomyces globisporus. The lysate was resolved into three fractions by ion-exchange chromatography: a fraction containing peptidoglycan (PG) fragments, free of neutral and acidic sugars and of phosphate; a complex of PG fragments and group B-specific polysaccharide; and a complex of PG fragments and group B-specific polysaccharide and type III-specific polysaccharide. The PG-polysaccharide complexes were large and heterogeneous in molecular size. When subjected to base-catalyzed beta-elimination, both complexes were disintegrated, and polysaccharides and low-molecular-weight PG fragments could then be separated by gel filtration. The low-molecular-weight PG fragment-containing fraction contained muramic acid, glucosamine, alanine, lysine, glutamic acid, and serine in molar ratios (to lysine) of 0.92:0.98:3.01:1.00:1.00:0.05. Wall-derived, purified group polysaccharide contained rhamnose, galactose, glucosamine, and phosphorus in molar ratios (to galactose) of 5.03:1.00:1.00:1.05. It also contained an unidentified sugar. Wall-derived, purified type III polysaccharide contained galactose, glucosamine, glucose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid in molar ratios (to glucose) of 1.94:0.85:1.00:1.39. On a dry-weight basis, the whole wall lysate contained 19.8 and 20.6% of group and type polysaccharide, respectively. Neither glycerol nor ribitol was found, and all of the cell wall phosphorus was accounted for as polysaccharide, indicating the absence of a wall teichoic acid.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. C., Edwards M. S., Baker C. J. Luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence for evaluation of type III group B streptococcal opsonins in human sera. J Infect Dis. 1980 Mar;141(3):370–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.3.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony B. F. Immunity to the group B streptococci: interaction of serum and macrophages with types Ia, Ib, and Ic. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1186–1198. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLEIWEIS A. S., KARAKAWA W. W., KRAUSE R. M. IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR THE PREPARATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1198–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1198-1200.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Barrett F. F. Transmission of group B streptococci among parturient women and their neonates. J Pediatr. 1973 Dec;83(6):919–925. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80524-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Edwards M. S., Kasper D. L. Immunogenicity of polysaccharides from type III, group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1107–1110. doi: 10.1172/JCI109011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Correlation of maternal antibody deficiency with susceptibility to neonatal group B streptococcal infection. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):753–756. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Davis C. E. Immunochemical characterization of the "native" type III polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1976 Feb 1;143(2):258–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.2.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Identification of sialic acid in polysaccharide antigens in group B Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):284–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.284-288.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Tager IRAB, Paredes A., Alpert S., McCormack W. M., Goroff D. Quantitative determination of antibody to capsular polysaccharide in infection with type III strains of group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):810–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI108703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. The chemical composition of the cell wall in some gram-positive bacteria and its possible value as a taxonomic character. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):583–600. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. B., Eisenstein T. K., Shockman G. D., Greber T. F., Swenson R. M. Soluble group- and type-specific antigens from type III group B Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):195–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.195-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R., Bhatti T., Chambers R. E. The determination of carbohydrate in biological materials by gas-liquid chromatography. Methods Biochem Anal. 1971;19:229–344. doi: 10.1002/9780470110386.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Opsonic specificity of human antibody to the type III polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):1004–1008. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciosi R. A., Knostman J. D., Zimmerman R. A. Group B streptococcal neonatal and infant infections. J Pediatr. 1973 Apr;82(4):707–718. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80604-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freimer E. H. Type-specific polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococci. II. The chemical basis for serological specificity of the type II HCl antigen. J Exp Med. 1967 Mar 1;125(3):381–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M., Bricas E., Leyh-Bouille M., Lache M., Shockman G. D. The peptide N alpha-(L-alanyl-D-isoglutaminyl)-N epsilon-(D-isoasparaginyl)-L-lysyl-D-alanine and the disaccharide N-acetylglucosaminyl-beta-1,4-N-acetylmuramic acid in cell wall peptidoglycan of Streptococcus faecalis strain ATCC 9790. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2607–2619. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemming V. G., Hall R. T., Rhodes P. G., Shigeoka A. O., Hill H. R. Assessment of group B streptococcal opsonins in human and rabbit serum by neutrophil chemiluminescence. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1379–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI108593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holton J. B., Schwab J. H. Adjuvant properties of bacterial cell wall mucopeptides. J Immunol. 1966 Jan;96(1):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KABAT E. A., BEZER A. E. The effect of variation in molecular weight on the antigenicity of dextran in man. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Dec;78(2):306–318. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90354-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. A., Karakawa W. W. Existence of multiple immunodeterminants in the type-specific capsular substance of group B type Ia streptococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):983–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.983-991.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. A., Karakawa W. W. Multiple polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococcus, type Ia: emphasis on a sialic acid type-specific polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2155–2160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Baltimore R. S., Crabb J. H., Schiffman G., Jennings H. J. Immunodeterminant specificity of human immunity to type III group B streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):327–339. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., Freimer E. H. Type-specific polysaccharide antigens of group B streptococci. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Jun;64(2):191–203. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz E., Ghuysen J. M., Heymann H. Cell walls of Streptococcus pyogenes, type 14. C polysaccharide-peptidoglycan and G polysaccharide-peptidoglycan complexes. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3659–3670. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell H., Norcross N. L. The isolation and some physiochemical and biologic properties of the type 3 antigen of group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):90–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., SLAMP W. C. Cell-wall composition and the grouping antigens of Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:345–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.345-351.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai J. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Lancefield R. C. Isolation of type-specific polysaccharide antigen from group B type Ib streptococci. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):58–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITTNER M. K., HAYASHI J. A. STUDIES OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. VII. CARBOHYDRATE COMPOSITION OF GROUP B CELL WALLS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:398–402. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.398-402.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W. Immunochemistry of purified polysaccharide type antigens of group B streptococcal types Ia, Ib, and Ic. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):845–852. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.845-852.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokogawa K., Kawata S., Nishimura S., Ikeda Y., Yoshimura Y. Mutanolysin, bacteriolytic agent for cariogenic Streptococci: partial purification and properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):156–165. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



