Abstract
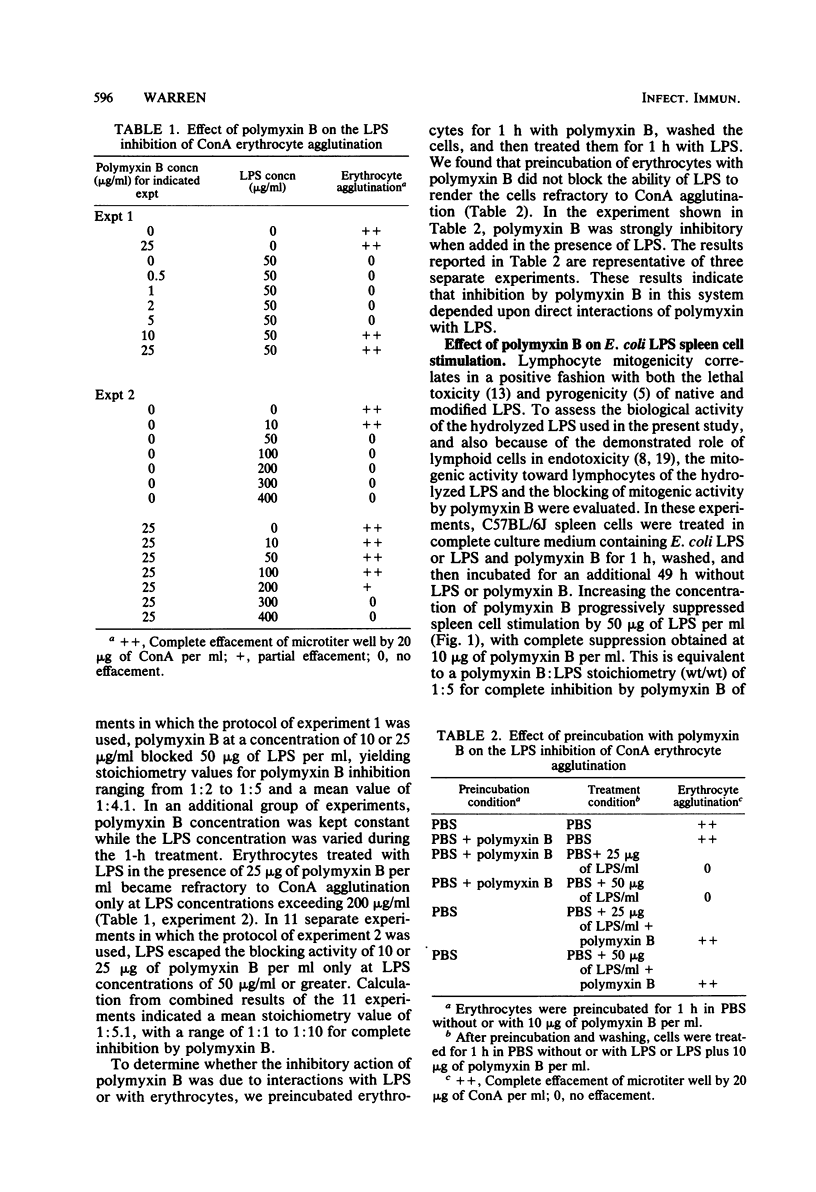
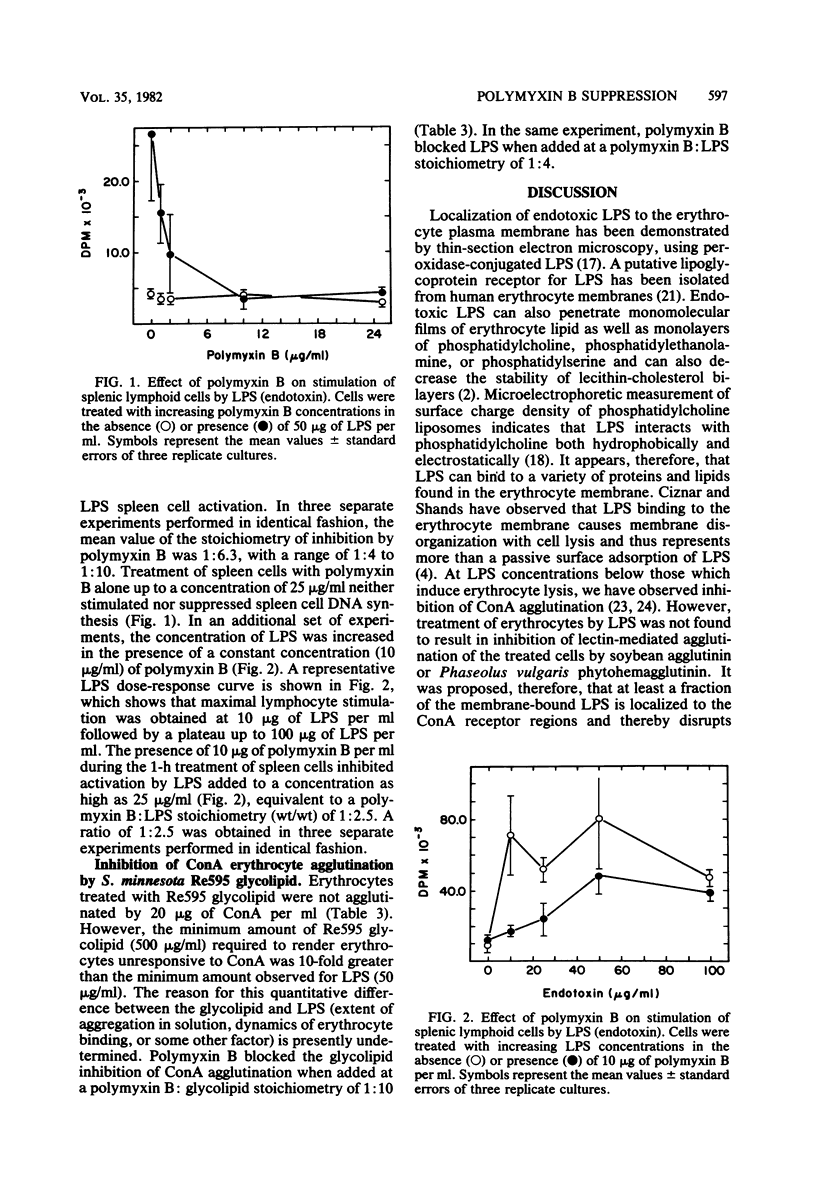
The lectin agglutinability of human erythrocytes has been utilized to examine interactions of gram-negative endotoxin with mammalian cell plasma membranes. Erythrocytes treated in buffer with Escherichia coli 0127:B8 lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or Salmonella minnesota Re595 glycolipid for 1 h became resistant to agglutination by the lectin concanavalin A (ConA) in buffer free of LPS or glycolipid. Polymyxin B, a cationic cyclic lipopeptide which specifically binds to the lipid A toxophore, was tested for possible effects on the LPS and glycolipid inhibition of Con A erythrocyte agglutination. The presence of polymyxin B during the initial 1-h treatment with LPS or glycolipid blocked the ability of the endotoxins to render erythrocytes refractory to agglutination by ConA. Inhibition by polymyxin B was stoichiometric, and in repeated experiments, LPS was completely suppressed in the hemagglutination assay at a polymyxin B:LPS weight ratio of 1:4.1 (increasing polymyxin concentration, constant LPS concentration) and 1:5.1 (constant polymyxin concentration, increasing LPS concentration). These stoichiometry values are similar to values obtained for inhibition by polymyxin B of LPS lymphoid cell activation. It was concluded, therefore, that endotoxin inhibition of ConA erythrocyte agglutination reflects interactions of erythrocyte membranes with the lipid A region of endotoxin. In addition, the stoichiometry of polymyxin B inhibition suggests a similar extent of lipid A-dependent LPS interaction with erythrocytes and lymphoid cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod B. J., Shands J. W., Jr Commitment to deoxyribonulceic acid synthesis and the cell cycle in endotoxin-stimulated murine spleen cells. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):344–349. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.344-349.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetto D. A., Shands J. W., Jr, Shah D. O. The interaction of bacterial lipopolysaccharide with phospholipid bilayers and monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Möller G. Mitogenic response of mouse spleen cells and gelation of limulus lysate by lipopolysaccharide of Yersinia pestis and evidence for neutralization of lipopolysaccharide by polymyxin B. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):400–404. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.400-404.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciznár I., Shands J. W., Jr Effect of alkali-treated lipopolysaccharide on erythrocyte membrane stability. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):362–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.362-367.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Sandberg A. L., Rosentreich D. L. Comparison of the pyrogenicity, Limulus activity mitogenicity and complement reactivity of several bacterial endotoxins and related compounds. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1238–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. B. The receptor proteins for concanavalin A and Lens culinaris phytohemagglutinin in the membrane of the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4398–4403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode L. M., Mergenhagen S. E., Rosenstreich D. L. Significant contribution of spleen cells in mediating the lethal effects of endotoxin in vivo. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):626–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.626-630.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. A., Staehelin L. A., Kuettner C. A. Lectin-mediated agglutination of erythrocyte ghost membranes following depletion of membrane protein and intramembrane particles. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Dec;110(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Chemically-induced cation permeability in red cell membrane vesicles. The sidedness of the response and the proteins involved. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 4;508(2):236–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90327-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs D. M., Morrison D. C. Inhibition of the mitogenic response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in mouse spleen cells by polymyxin B. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):21–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S., Rosenstreich D. L. Binding of bacterial endotoxin to murine spleen lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):156–164. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.156-164.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Hargie M. P., Schenck J. R., Finley R. A., Sievert H. W., Rietschel E. T., Rosenstreich D. L. Biologic properties of nontoxic derivatives of a lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli K235. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):674–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Betz S. J., Jacobs D. M. Isolation of a lipid A bound polypeptide responsible for "LPS-initiated" mitogenesis of C3H/HeJ spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):840–846. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. The interactions of lectins with animal cell surfaces. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;39:89–190. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60939-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygren H., Dahlen G. Ultrastructural localisation of lipopolysaccharide-binding sites with peroxidase-conjugated lipopolysaccharides. J Immunol Methods. 1979;25(4):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onji T., Liu M. S. Changes in surface charge density on liposomes induced by Escherichia coli endotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 12;558(3):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F., Adye J. C., Bezkorovainy A., Jirgensons B. Properties and activity of the lipopolysaccharide-receptor from human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 26;13(7):1379–1389. doi: 10.1021/bi00704a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F., Adye J. C. Endotoxin-binding substances from human leukocytes and platelets. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):978–986. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.978-986.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallas C. H., Warren J. R., Kowalski M. M. Energy metabolism and Na+,K+ redistribution in human erythrocytes treated with lipopolysaccharide endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Jul;161(3):255–259. doi: 10.3181/00379727-161-40531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. R., Kowalski M. M. Inhibition of ConA erythroagglutination by alkali-treated lipopolysaccharide. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jul;107(2):462–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90374-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. R., Kowalski M. M., Wallas C. H. Effect of alkali-treated lipopolysaccharide on the intracellular cations of human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):389–394. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.389-394.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



