Abstract
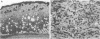
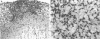
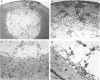
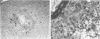
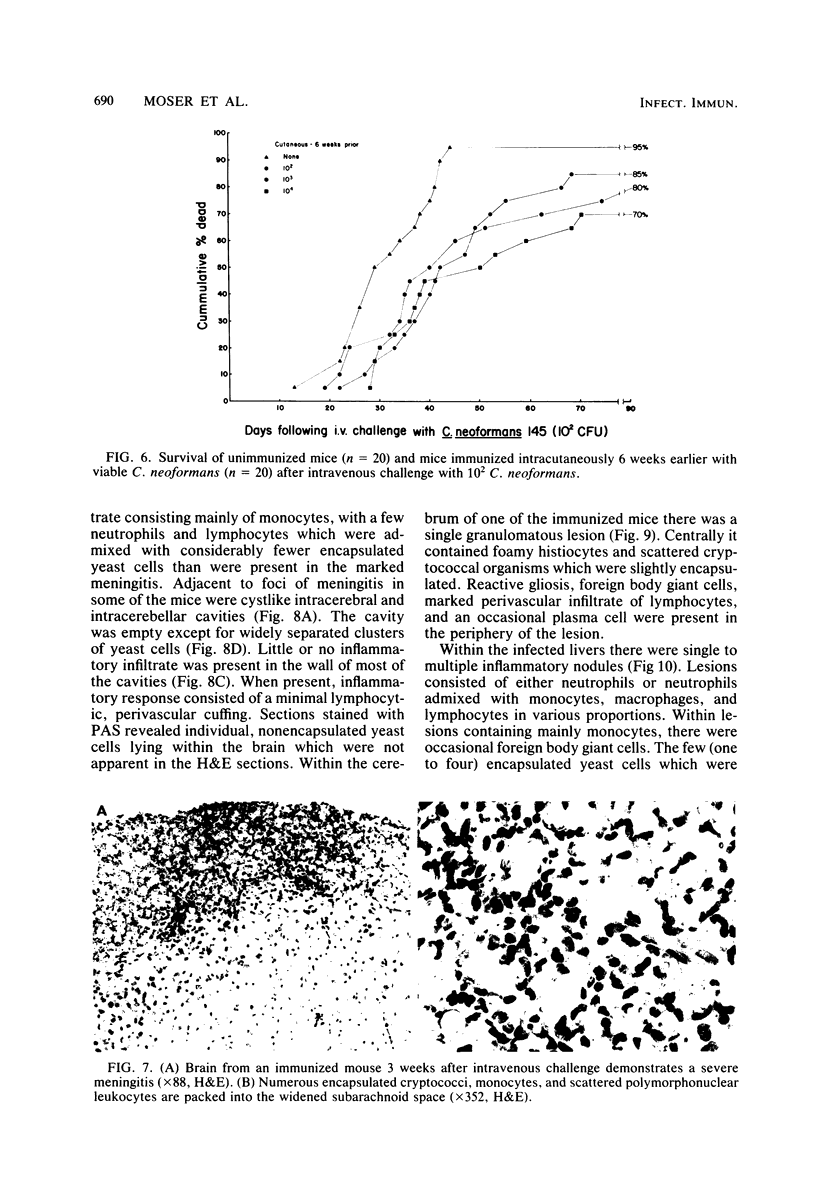
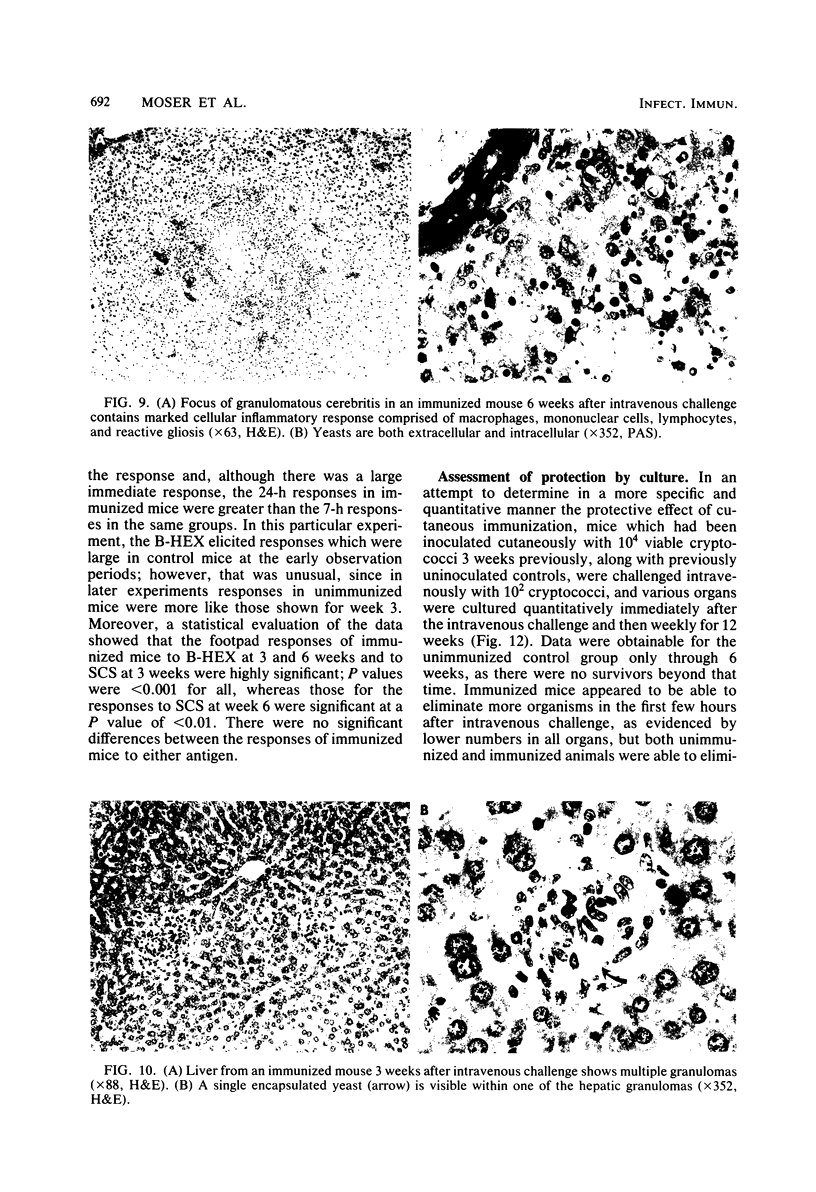
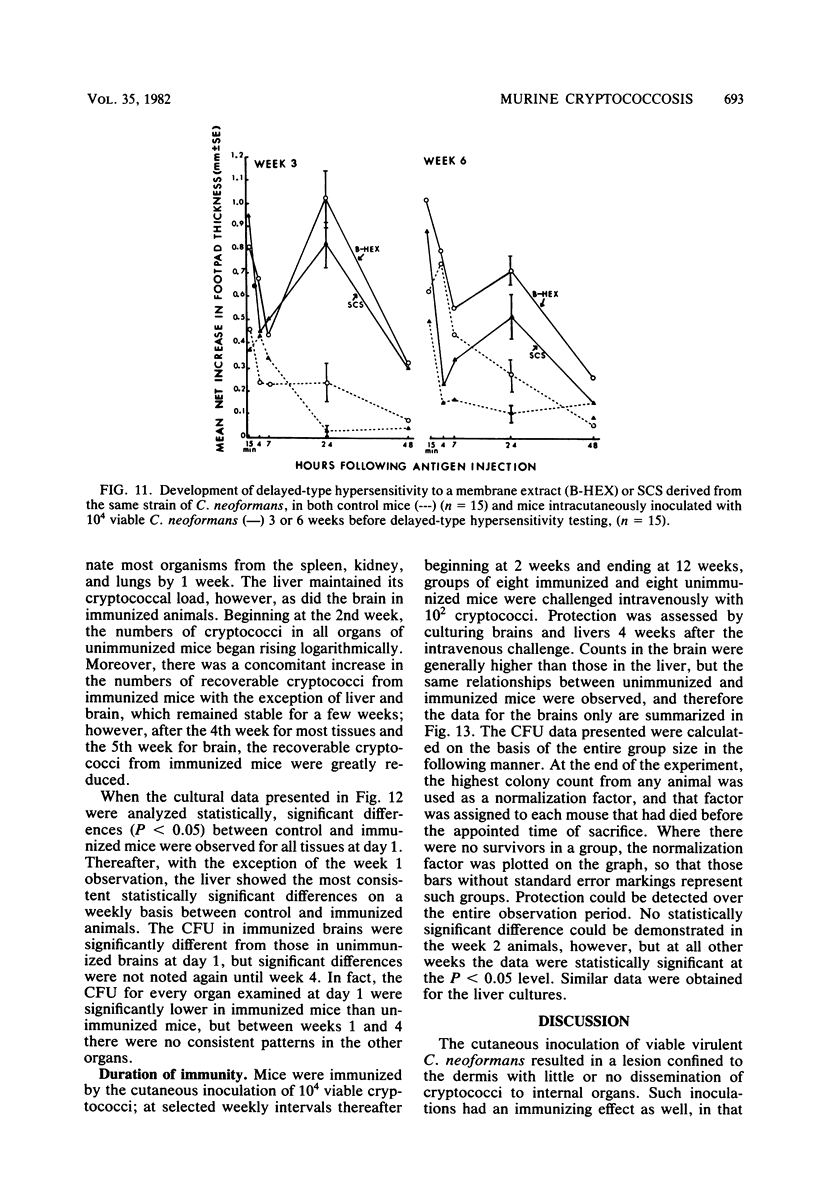
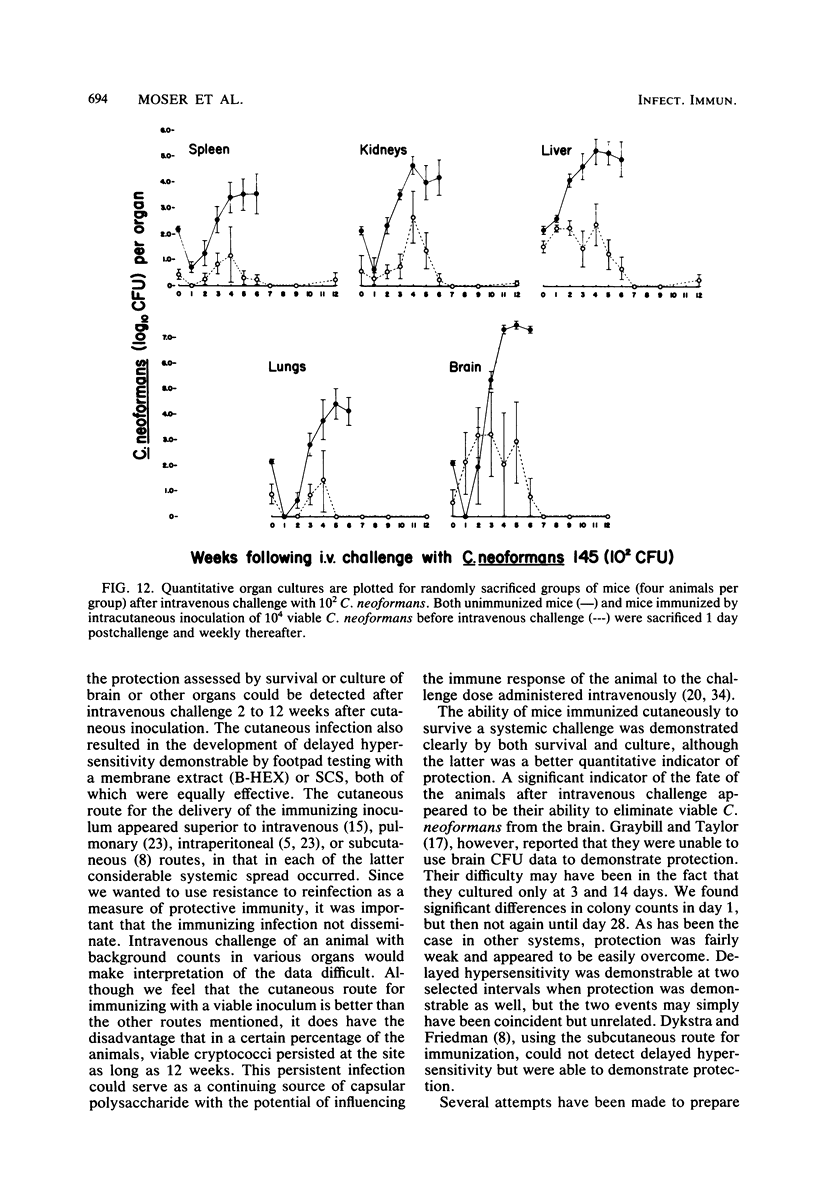
Immune responses, including protection and delayed hypersensitivity, were evaluated in experimental murine cryptococcosis. Mice were immunized by the intracutaneous inoculation of viable virulent Cryptococcus neoformans yeasts. Response to the cutaneous infection was evaluated histologically and by cultural assays of the internal organs, as well as by intravenous challenge with the same strain. Protection was assessed by survival, histopathology, and quantitative organ culture. The intracutaneous inoculation of cryptococci resulted in a local inflammatory response that effectively limited dissemination of the organisms systemically and induced the development of delayed hypersensitivity demonstrable with a membrane extract of C. neoformans and with soluble cytoplasmic substances. A protective response was induced by the cutaneous inoculation of cryptococci as well, in that immunized animals survived longer, with about 25% of the challenged group ridding themselves completely of the cryptococci. Protection could be demonstrated by cultural analyses, but all animals, whether control or immunized, allowed considerable multiplication of the inoculum during the first 4 weeks after intravenous challenge. It would appear, therefore, that the protective mechanism(s) required additional antigenic stimulation before it could eventually function to eliminate all cryptococci from tissues. Histologically, there were no differences in pathology of the internal organs between immunized and unimmunized animals. Although the model described herein for the induction of immune responses in murine cryptococcosis has at least one drawback, viz., the presence of cryptococci in the skin lesion of many animals throughout the duration of the experiment, it does have the advantage that the immune responses were stimulated by a virulent strain and only minimal dissemination occurred. Therefore, lymphocytes could be removed from animals that were not contaminated with cryptococci for in vitro and in vivo transfer.
Full text
PDF


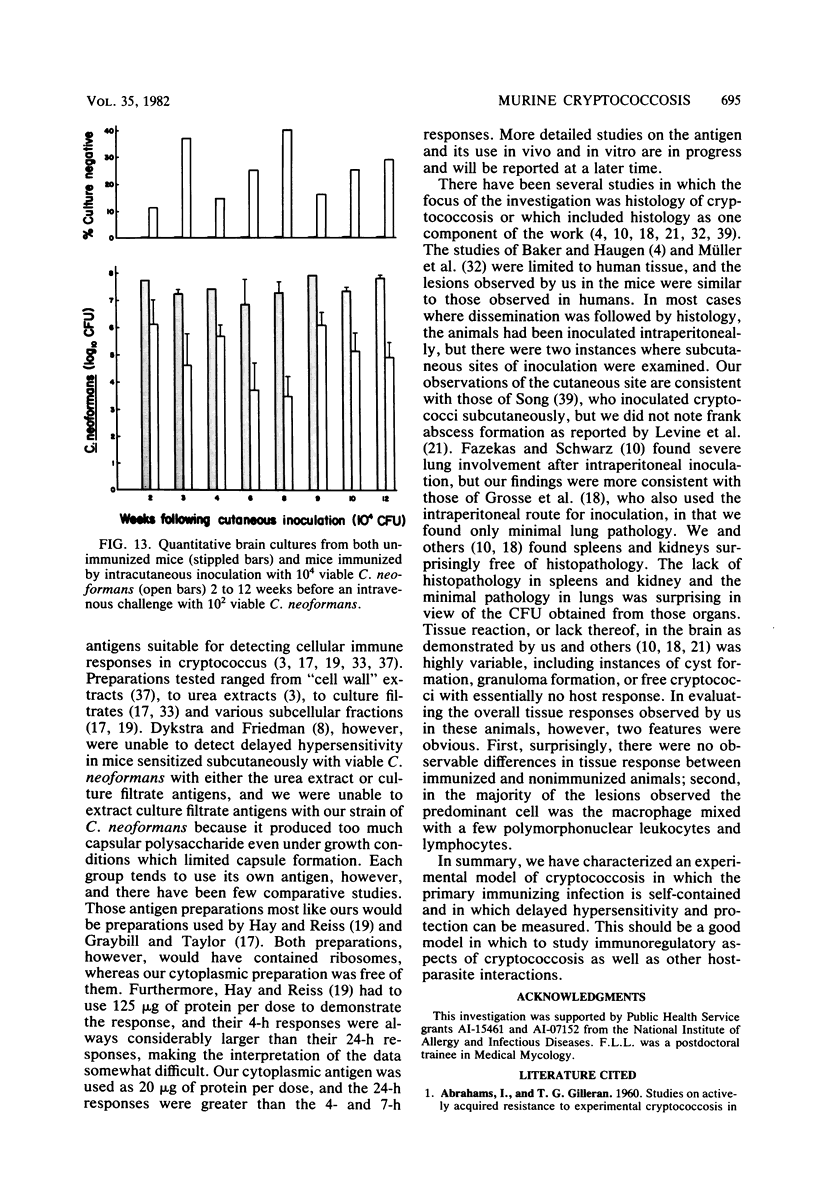

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson D. M., Cozad G. C. Effect of antilymphocyte serum on animals experimentally infected with Histoplasma capsulatum or Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1271–1276. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1271-1276.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson A. J., Jr, Bennett J. E. Experience with a new skin test antigen prepared from Cryptococcus neoformans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Apr;97(4):637–643. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.97.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER R. D., HAUGEN R. K. Tissue changes and tissue diagnosis in cryptococcosis; a study of 26 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1955 Jan;25(1):14–24. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/25.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauley L. K., Murphy J. W. Response of congenitally athymic (nude) and phenotypically normal mice to Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):644–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.644-651.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer J. E. In vivo and in virto cellular responses to cytoplasmic and cell wall antigens of Histoplasma capsulatum in artificially immunized or infected guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):790–799. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.790-799.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra M. A., Friedman L., Murphy J. W. Capsule size of Cryptococcus neoformans: control and relationship to virulence. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):129–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.129-135.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra M. A., Friedman L. Pathogenesis, lethality, and immunizing effect of experimental cutaneous cryptococcosis. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):446–455. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.446-455.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAZEKAS G., SCHWARZ J. Histology of experimental murine cryptococcosis. Am J Pathol. 1958 May-Jun;34(3):517–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A., Blackstock R., Hall N. K., Bulmer G. S. Immunization of mice with an avirulent pseudohyphal form of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycopathologia. 1979 Sep 28;68(3):179–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00578527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giger D. K., Domer J. E., McQuitty J. T., Jr Experimental murine candidiasis: pathological and immune responses to cutaneous inoculation with Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):499–509. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.499-509.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J. Host defense in cryptococcosis. II. Cryptococcosis in the nude mouse. Cell Immunol. 1978 Oct;40(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Mitchell L. Cyclophosphamide effects on murine cryptococcosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):674–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.674-677.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Mitchell L., Drutz D. J. Host defense in cryptococcosis. III. Protection of nude mice by thymus transplantation. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):546–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Mitchell L. Host defense in Cryptococcosis. III. In vivo alteration of immunity. Mycopathologia. 1979 Dec 28;69(3):171–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00452831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Taylor R. L. Host defense in cryptococcosis. I. An in vivo model for evaluating immune response. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;57(2):101–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosse G., Mishra S. K., Staib F. Selective involvement of the brain in experimental murine cryptococcosis. II. Histopathological observations. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975 Sep;233(1):106–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. J., Reiss E. Delayed-type hypersensitivity responses in infected mice elicited by cytoplasmic fractions of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):72–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.72-79.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Gulley W. F., Cazin J., Jr Immune response to Cryptococcus neoformans soluble polysaccharide: immunological unresponsiveness. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):701–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.701-707.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., ZIMMERMAN H. M., SCORZA A. Experimental cryptococcosis (torulosis). Am J Pathol. 1957 May-Jun;33(3):385–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim T. S., Murphy J. W., Cauley L. K. Host-etiological agent interactions in intranasally and intraperitoneally induced Cryptococcosis in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):633–641. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.633-641.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim T. S., Murphy J. W. Transfer of immunity to cryptococcosis by T-enriched splenic lymphocytes from Cryptococcus neoformans-sensitized mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):5–11. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.5-11.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. V., Schneidau J. D., Jr A simple and reliable assimilation test for the identification of candida species. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Jun;53(6):875–879. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.6.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monga D. P., Kumar R., Mohapatra L. N., Malaviya A. N. Experimental cryptococcosis in normal and B-cell-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):1–3. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.1-3.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser S. A., Domer J. E. Effects of cyclophosphamide on murine candidiasis. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):376–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.376-386.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Cozad G. C. Immunological unresponsiveness induced by cryptococcal capsular polysaccharide assayed by the hemolytic plaque technique. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.896-901.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Gregory J. A., Larsh H. W. Skin testing of guinea pigs and footpad testing of mice with a new antigen for detecting delayed hypersensitivity to Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):404–409. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.404-409.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Schorre W., Suchenwirth R., Zitz H. M., Konorza G. A case of fatal cryptococcus meningitis with intraventricular granuloma. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1978;44(3-4):223–235. doi: 10.1007/BF01402064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss F., Alture-Werber E. Immunization of mice with a mutant of Cryptococcus neoformans. Characterization of the mutant, actively acquired resistance to experimental cryptococcosis in mice. Dermatologica. 1976;152(1):16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo-Moreno A., Schneidau J. D., Jr Nature of the skin-reactive principle in culture filtrates prepared from Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1741–1748. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1741-1748.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALVIN S. B., SMITH R. F. An antigen for detection of hypersensitivity to Cryptococcus neoformans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Nov;108:498–501. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-26977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields A. B., Ajello L. Medium for selective isolation of Cryptococcus neoformans. Science. 1966 Jan 14;151(3707):208–209. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3707.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song M. M. Experimental cryptococcosis of the skin. Sabouraudia. 1974 Jul;12(2):133–137. doi: 10.1080/00362177485380191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Krick J. A., Remington J. S. Pulmonary infection in the compromised host: part I. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Aug;114(2):359–394. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]