Abstract
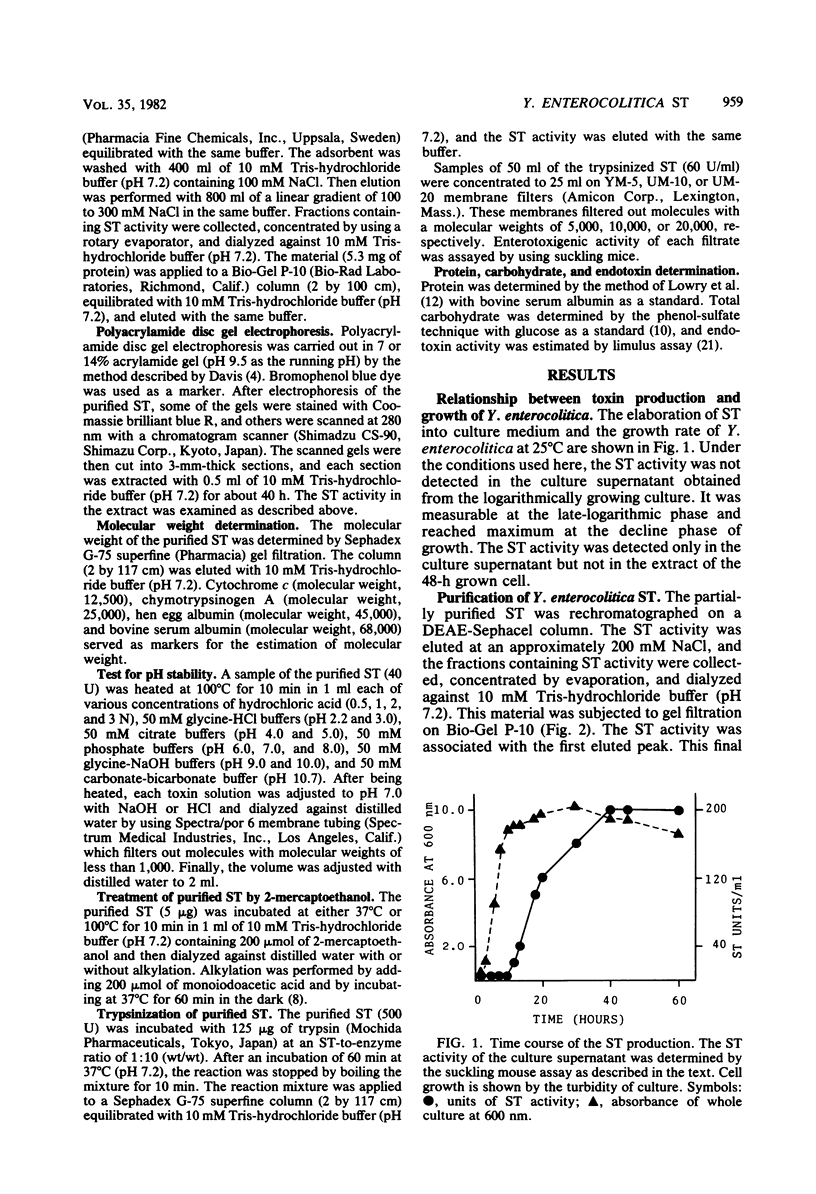
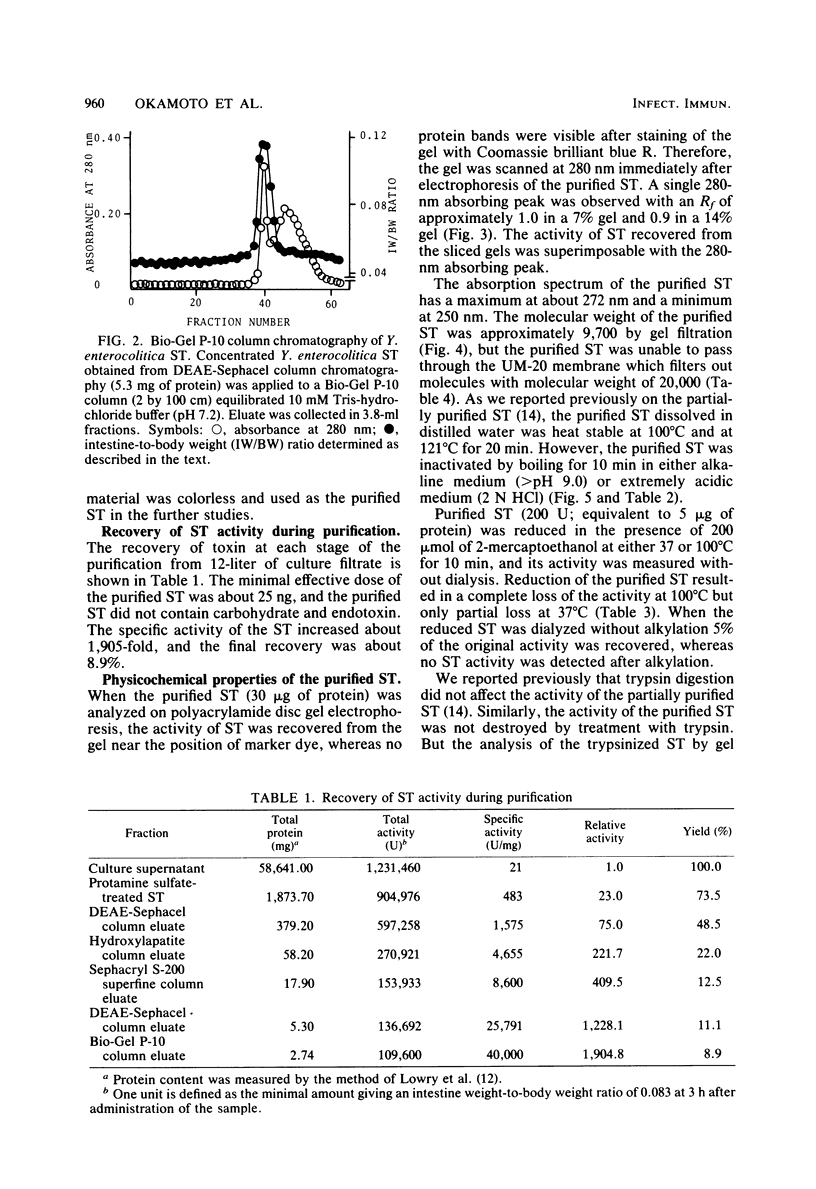
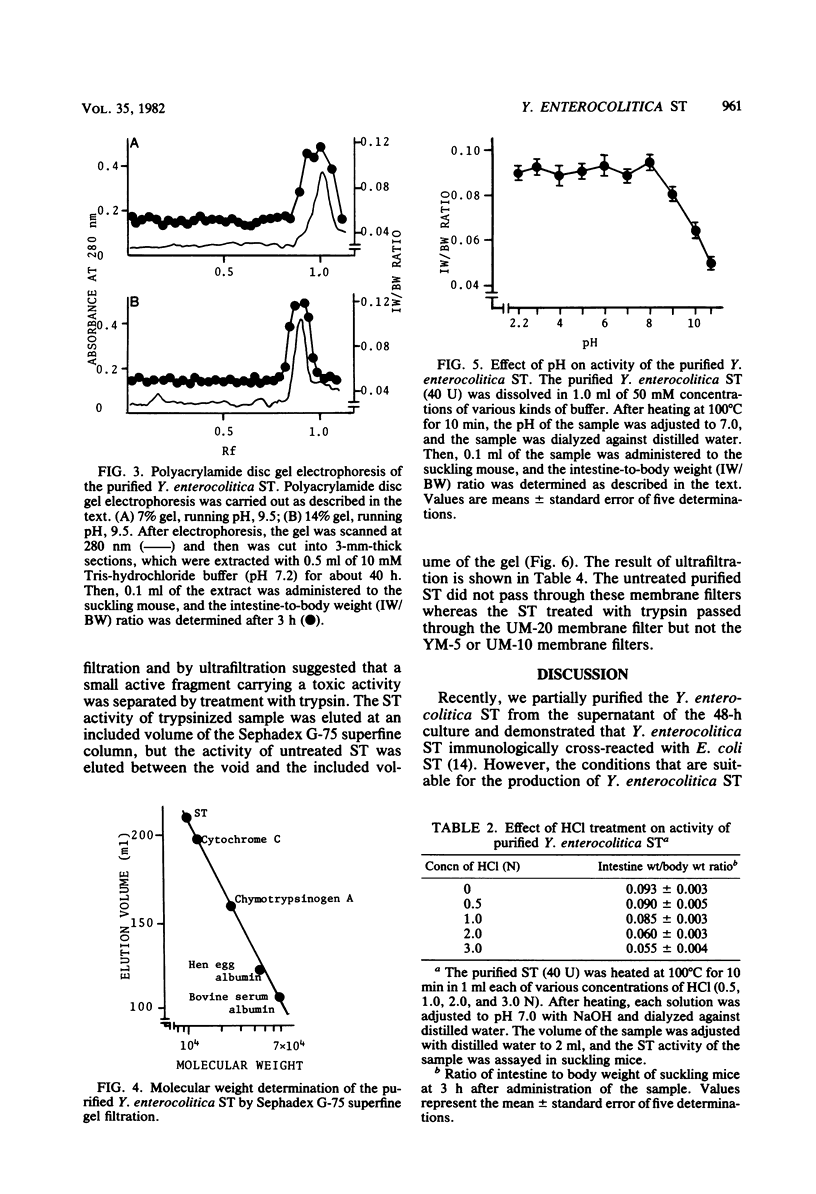
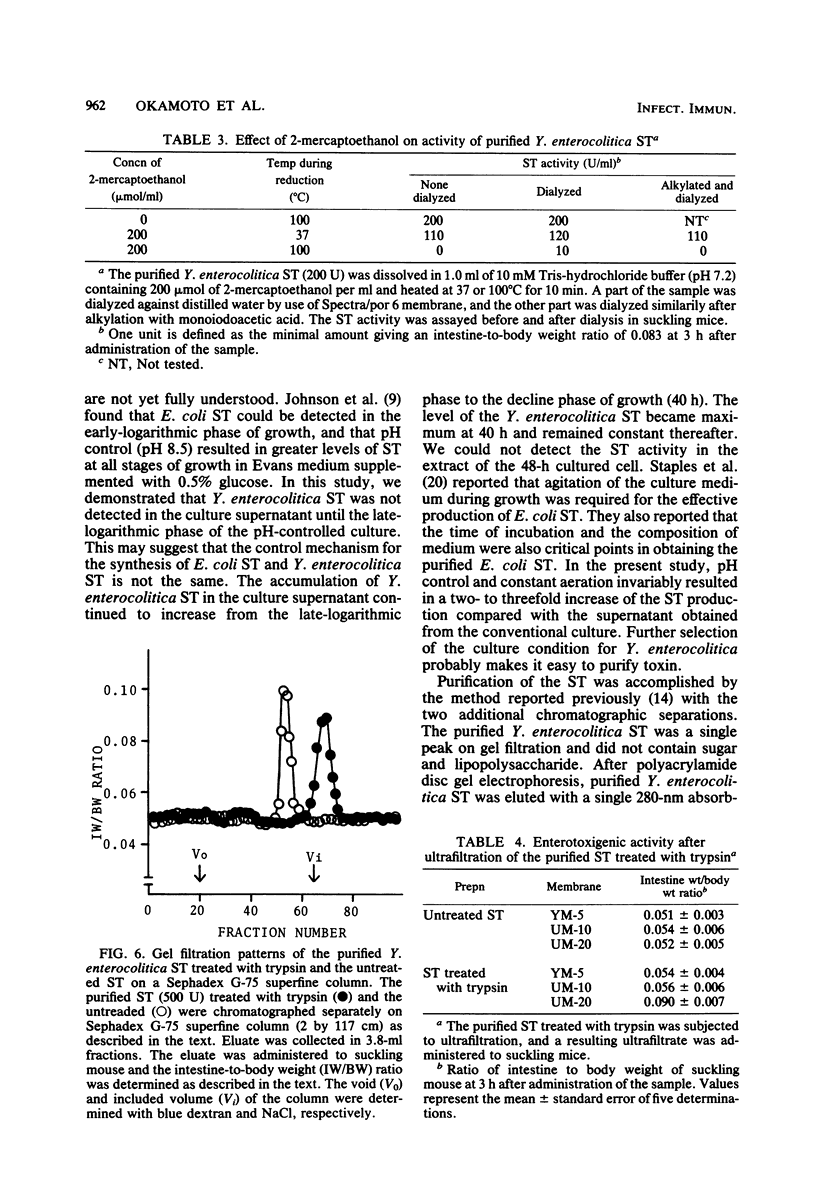
Heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) of Yersinia enterocolitica was produced under defined conditions. It was first detected in the culture supernatant of the late-logarithmic phase of growth and increased lineally during the the stationary phase of growth. The ST level became maximum at the decline phase of growth, and the ST was not detected in the lysate of bacteria obtained from the decline phase of growth. The ST was extensively purified from the culture supernatant, and about a 1,905-fold purification was achieved with a yield of 8.9%. The minimal effective dose of the purified ST was approximately 25 ng in the suckling mouse assay. The purified ST gave a single 280-nm absorbing peak on polyacrylamide disc gel electrophoresis and had a maximum absorption at 272 nm, and its molecular weight was 9,700 by Sephadex G-75 superfine gel filtration. The biological activity of the purified ST was lost by treatment with 2-mercaptoethanol, suggesting that the ST contained disulfide bridges in the molecule which were required for the development of toxic activity. The purified ST was heat stable at 100 degrees C for 10 min between pH 2.2 and 8.0, but not at pH values greater than 9.0 or in 2 N HCl. The treatment of the ST with trypsin resulted in a retarded elution of the ST activity by Sephadex F-75 superfine gel filtration and a passage through a UM-20 membrane filter.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M., Evans E. J., Jr, Evans D. G., DuPont H. L. Production of heat-stable, methanol-soluble enterotoxin by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):532–537. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.532-537.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Bennett P. M., Grinsted J. Properties of pGC1, a lac plasmid orginating in Yersinia enterocolitica 842. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1058–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1058-1062.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H., Johnson K. G. Heat-stable enterotoxin from Escherichia coli: factors involved in growth and toxin production. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):352–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.352-359.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Jacobson J. A., Nahmias A. Yersinia enterocolitica infections in children. J Pediatr. 1976 Jul;89(1):77–79. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80932-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Ichikawa H., Kawamoto Y., Miyama A., Yoshii S. Heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from patients. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(5):401–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Inoue T., Ichikawa H., Kawamoto Y., Miyama A. Partial purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):554–559. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.554-559.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V. Production of enterotoxin by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):908–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.908-911.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. C., Guandalini S., Laird W. J., Field M. Effects of heat-stable enterotoxin of Yersinia enterocolitica on ion transport and cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate metabolism in rabbit ileum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):875–878. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.875-878.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Still C. S., Miliotis M. D., Koornhof H. J. Mechanism of action of Yersinia enterocolitica enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):680–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.680-684.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Heffron F., McCarthy B. J. The E. coli gene encoding heat stable toxin is a bacterial transposon flanked by inverted repeats of IS1. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):453–456. doi: 10.1038/277453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


