Abstract
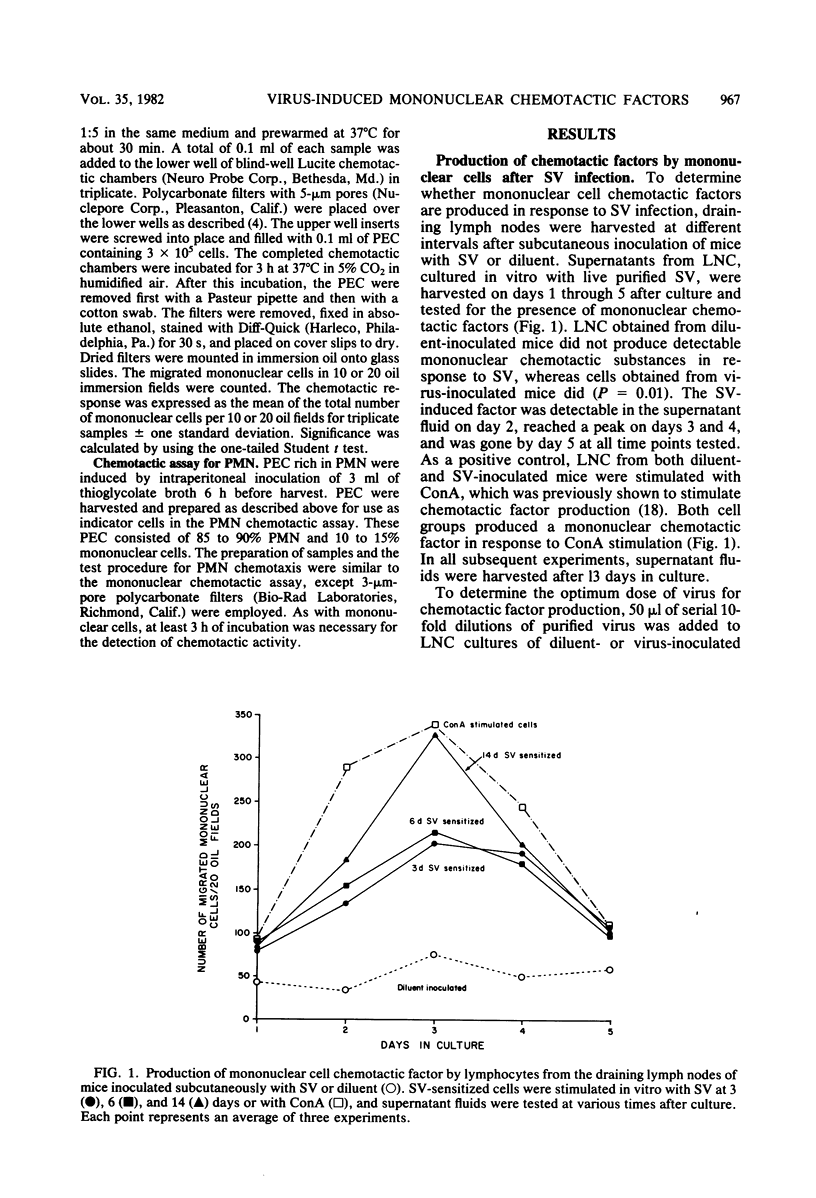
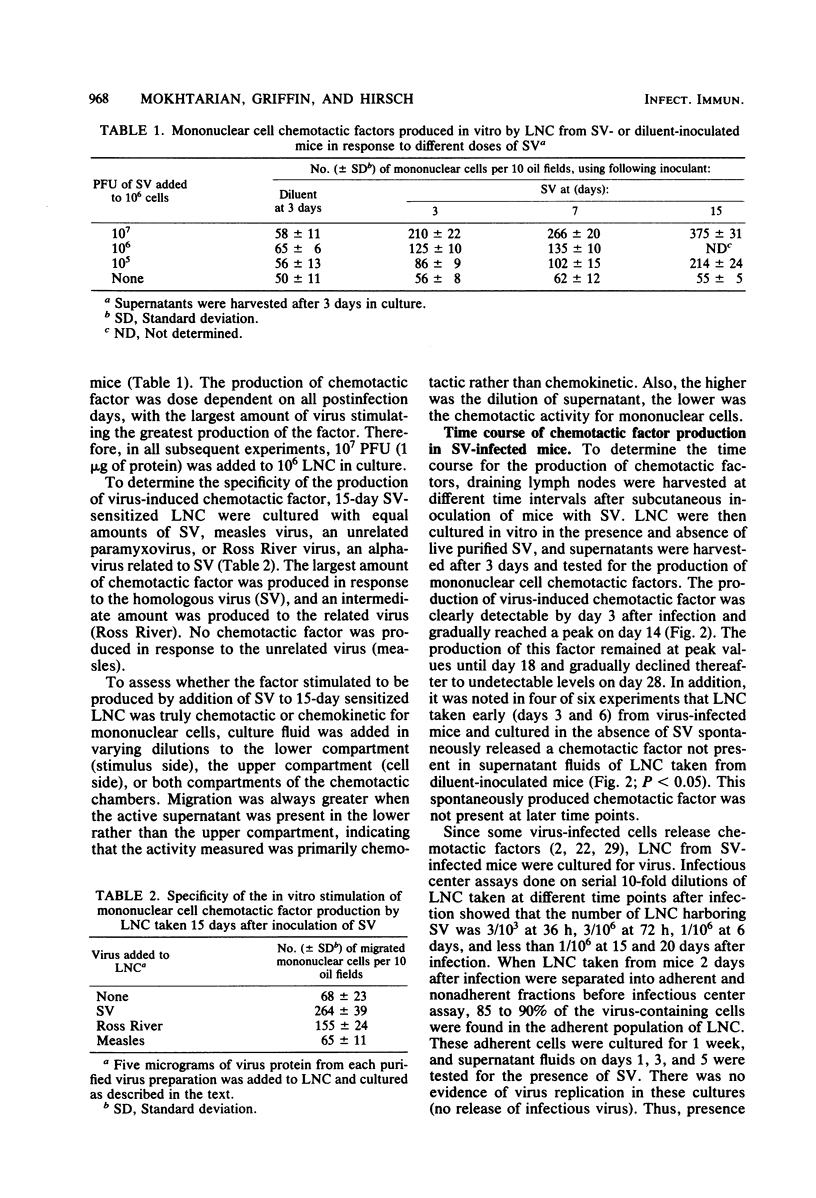
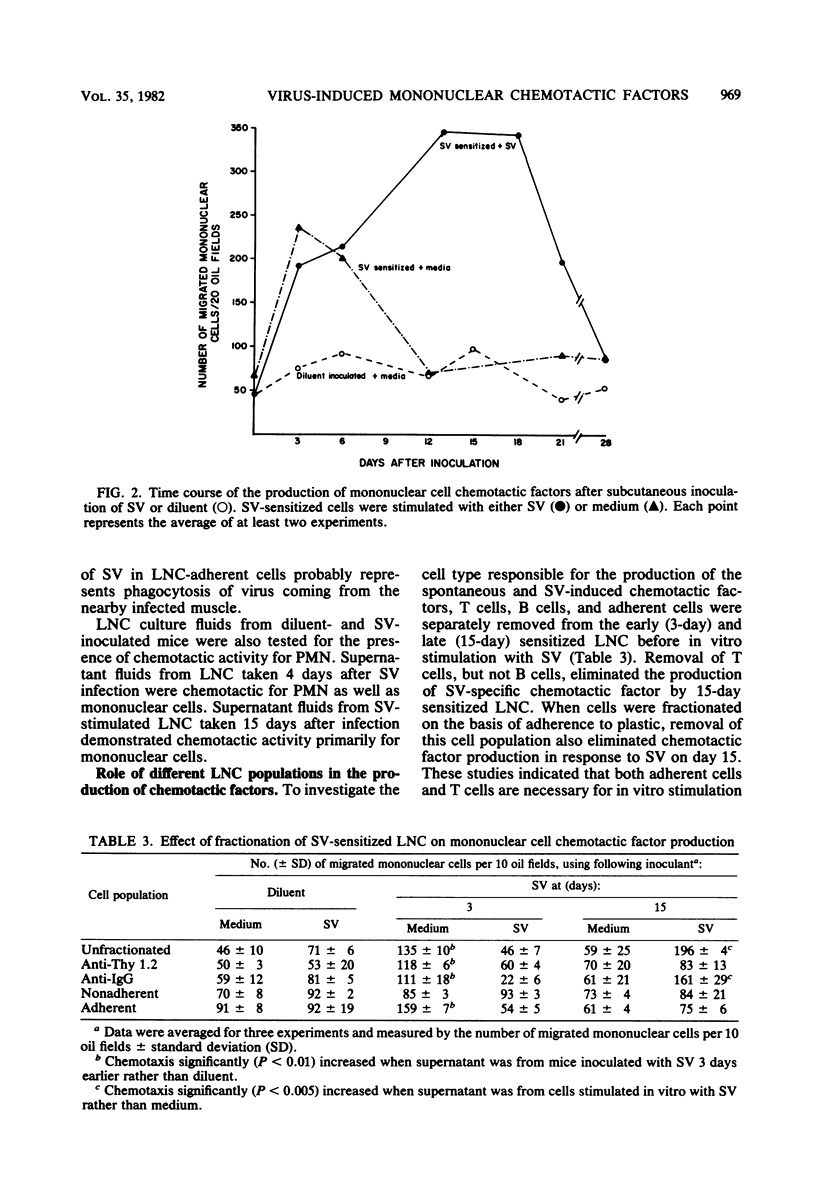
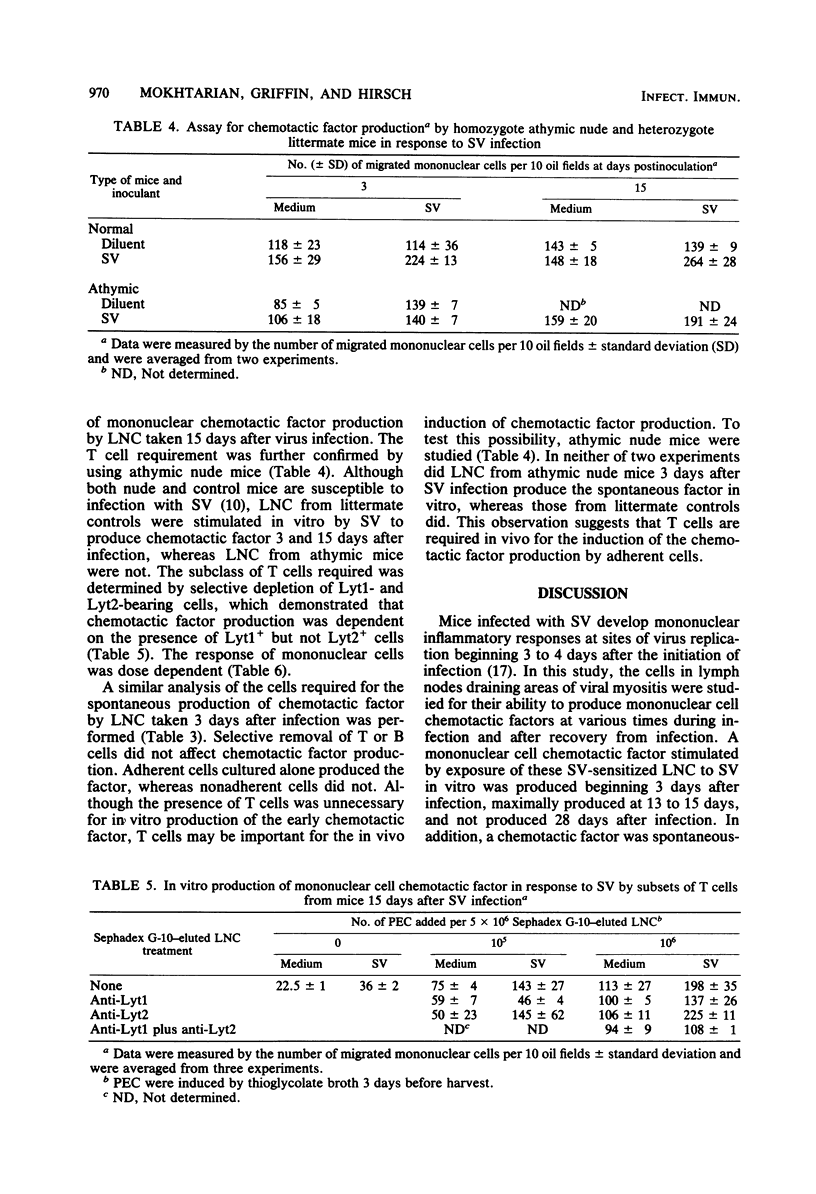
Draining lymph node cells of mice infected subcutaneously with Sindbis virus (SV) produced two mononuclear chemotactic factors in vitro. One factor did not require the addition of SV in vitro and was only detectable during the first week after infection. A second factor, resembling lymphocyte-derived chemotactic factor, required the addition of SV in vitro, was first detectable at 3 days, reached a peak at 15 to 18 days, and was gone by 29 days after infection. The production of this factor was virus specific. Diluent-inoculated mice produced no detectable mononuclear chemotactic factors in response to SV. In vitro production of the virus-specific chemotactic factor was dependent on both adherent cells and sensitized Lyt1+ T cells. In vitro production of the spontaneous factor was associated only with adherent cells but also appeared to be T cell dependent, since the lymph node cells from SV-infected athymic nude mice failed to produce either factor. Infectious center assays showed that adherent cells contained infectious SV without replicating it, suggesting the engulfment of virus by macrophages in the lymph node draining the area of virus replication. These cells probably process virus as antigen for presentation to T cells, resulting in local production of chemotactic factors as well as production in more distant sites of viral replication after leaving the lymph node. These virus-stimulated, mononuclear cell-produced chemotactic factors are likely to be of importance in generating the mononuclear inflammatory response.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman L. C., Snyderman R., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. A human mononuclear leukocyte chemotactic factor: characterization, specificity and kinetics of production by homologous leukocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):801–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Gaffney J., Jimenez L. Dissociation of MIF production and cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1972 Dec;109(6):1395–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boetcher D. A., Meltzer M. S. Mouse mononuclear cell chemotaxis: description of system. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Mar;54(3):795–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brier A. M., Snyderman R., Mergenhagen S. E., Notkins A. L. Inflammation and herpes simplex virus: release of a chemotaxis-generating factor from infected cells. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1104–1106. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornely H. P. Reversal of chemotaxis in vitro and chemotactic activity of leukocyte fractions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):831–835. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C. Quantitative studies of the inflammatory process in fatal viral meningoencephalitis. Am J Pathol. 1973 Dec;73(3):607–622. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Shen F. W., Gershon R. K., Ruddle N. H. Lymphotoxin production by subsets of T cells. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1199–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. Cellular immune response to viral infection: in vitro studies of lymphocytes from mice infected with Sindbis virus. Cell Immunol. 1973 Dec;9(3):426–434. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E. Role of the immune response in age-dependent resistance of mice to encephalitis due to Sindbis virus. J Infect Dis. 1976 Apr;133(4):456–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.4.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. H., Ward P. A. C3 leukotactic factors produced by a tissue protease. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):505–518. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. L., Griffin D. E. The pathogenesis of Sindbis virus infection in athymic nude mice. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1215–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. T. VIRUS INVASION OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: A STUDY OF SINDBIS VIRUS INFECTION IN THE MOUSE USING FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY. Am J Pathol. 1965 Jun;46:929–943. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T. Inflammatory response to viral infection. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1971;49:305–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., McFarland H. F., Levy S. E. Age-dependent resistance to viral encephalitis: studies of infections due to Sindbis virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):257–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühner A. L., Cantor H., David J. R. Ly phenotype of lymphocytes producing murine migration inhibitory factor (MIF). J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1117–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ly I. A., Mishell R. I. Separation of mouse spleen cells by passage through columns of sephadex G-10. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLUSKEY R. T., BENACERRAF B., MCCLUSKEY J. W. STUDIES ON THE SPECIFICITY OF THE CELLULAR INFILTRATE IN DELAYED HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS. J Immunol. 1963 Mar;90:466–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland H. F., Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. Specificity of the inflammatory response in viral encephalitis. I. Adoptive immunization of immunosuppressed mice infected with Sindbis virus. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):216–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S. Chemotactic response of mouse macrophages to culture fluids mitogen-stimulated spleen cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Sep;6(2):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Jones E. E., Boetcher D. A. Increased chemotactic responses of macrophages from BCG-infected mice. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):268–276. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Kang A. H. Latent lymphokines: isolation of guinea pig latent lymphocyte-derived chemotactic factor for monocytes. Its activation by trypsin and a soluble factor from macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):561–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E. Production of migration inhibitory factor by non-dividing lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):674–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. L., Snyderman R., Notkins A. L. Production of chemotactic factor and lymphotoxin by human leukocytes stimulated with Herpes simplex virus. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):111–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.111-115.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Altman L. C., Hausman M. S., Mergenhagen S. E. Human mononuclear leukocyte chemotaxis: a quantitative assay for humoral and cellular chemotactic factors. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):857–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Shin H., Dannenberg A. M., Jr Macrophage proteinase and inflammation: the production of chemotactic activity from the fifth complement by macrophage proteinase. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):896–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel J. D., Gallin J. I. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte and monocyte chemoattractants produced by human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):609–618. doi: 10.1172/JCI109343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Wilton J. M., Rosenstreich D. L., Oppenheim J. J. The role of macrophages in the production of lymphokines by T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1296–1301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. H. Immunoglobulins and lymphokines as mediators of inflammatory cell mobilization and target cell killing. Cell Immunol. 1976 Dec;27(2):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Cohen S., Flanagan T. D. Leukotactic factors elaborated by virus-infected tissues. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1095–1103. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Remold H. G., David J. R. The production by antigen-stimulated lymphocytes of a leukotactic factor distinct from migration inhibitory factor. Cell Immunol. 1970 Jul;1(2):162–174. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Tracey D. E., Henney C. S. BCG-induced murine effector cells. II. Characterization of natural killer cells in peritoneal exudates. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1152–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Gallin J. I. A functional differentiation of human neutrophil granules: generation of C5a by a specific (secondary) granule product and inactivation of C5a by azurophil (primary) granule products. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1068–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


