Abstract
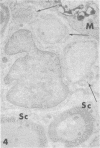
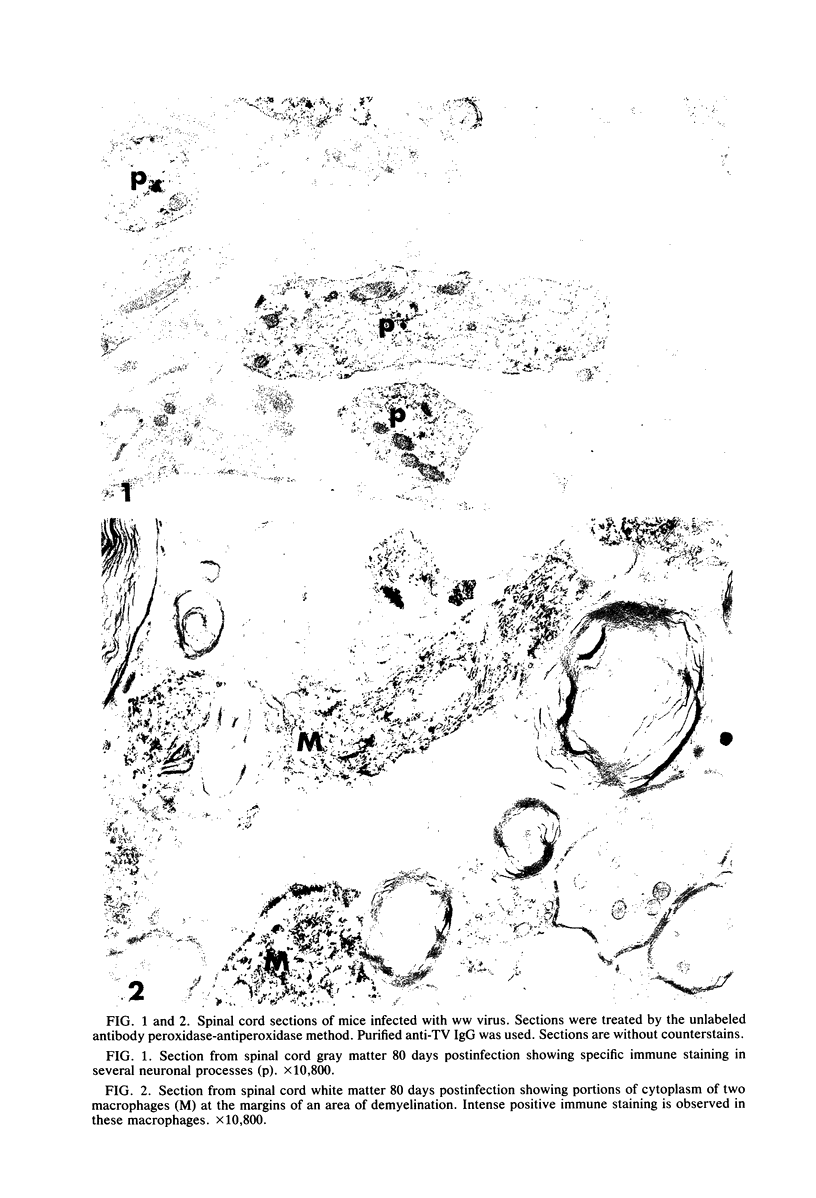
Theiler's virus infection in mice produces a chronic demyelinating disease which appears to be based on an immune pathogenesis rather than on direct viral destruction of myelin-supporting cells. The purpose of the present study is to ascertain whether viral antigen is present in the cytoplasm of such cells in areas of demyelination. Because of the difficulty of identifying oligodendrocytes in tissues rich in infiltrating mononuclear cells and fixed for immunohistochemistry, I turned to a recently described form of Theiler's virus encephalomyelitis which follows inoculation with the attenuated ww strain and is characterized by extensive spinal cord remyelination by invading Schwann cells and by recurrent demyelination of Schwann cell-remyelinated axons. The unlabeled antibody peroxidase-antiperoxidase technique was employed to study whether such spinal cord Schwann cells were primarily infected by virus at the time when recurrent demyelination was occurring. Whereas other types of cells, including neurons, astrocytes, and macrophages, contained abundant viral antigen, no positive immune reaction was observed in Schwann cells. These results correlate with our previous studies which had suggested that demyelination in this viral model is not dependent on primary viral attack on myelinating cells but is probably dependent on the host immune response.
Full text
PDF

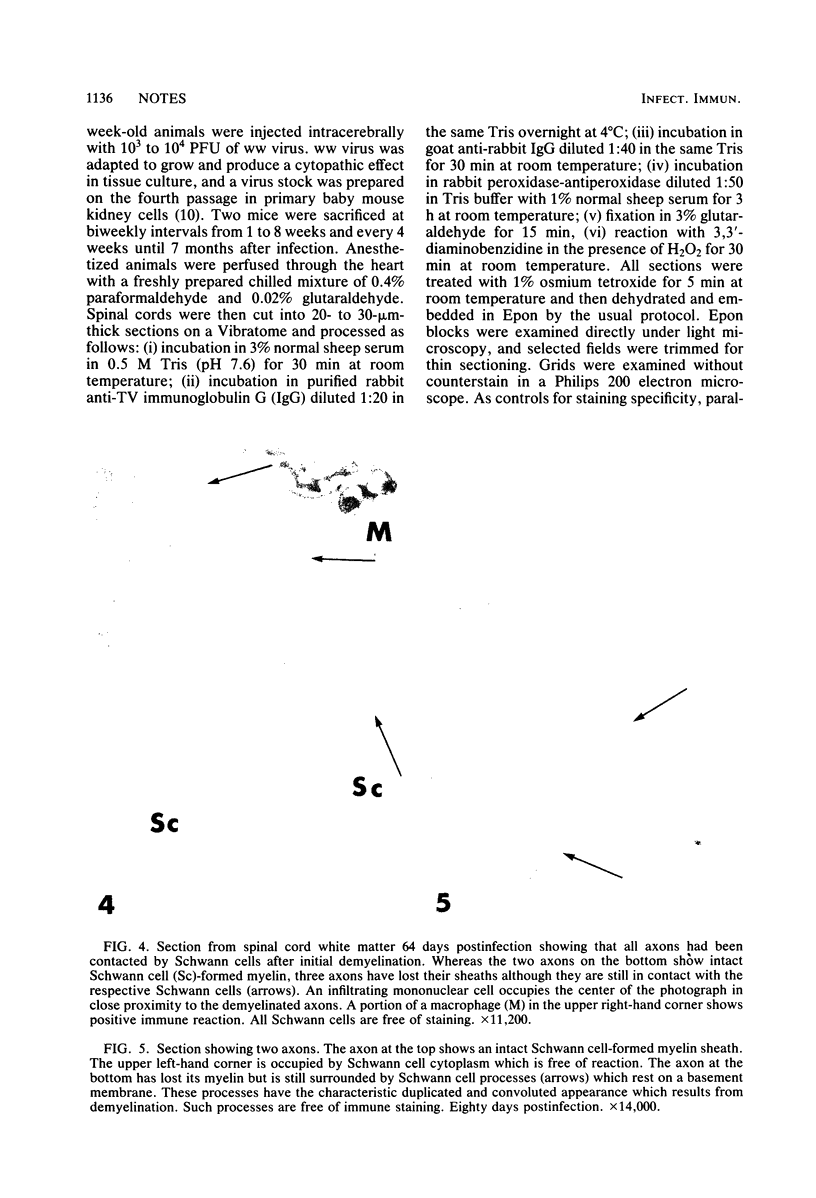


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dal Canto M. C., Lipton H. L. Multiple sclerosis. Animal model:Theiler's virus infection in mice. Am J Pathol. 1977 Aug;88(2):497–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canto M. C., Lipton H. L. Primary demyelination in Theiler's virus infection. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1975 Dec;33(6):626–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canto M. C., Lipton H. L. Schwann cell remyelination and recurrent demyelination in the central nervous system of mice infected with attenuated Theiler's virus. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jan;98(1):101–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canto M. C., Lipton H. L. Ultrastructural immunohistochemical localization of virus in acute and chronic demyelinating Theiler's virus infection. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jan;106(1):20–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. T. THE PATHOGENESIS OF HERPES VIRUS ENCEPHALITIS. II. A CELLULAR BASIS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF RESISTANCE WITH AGE. J Exp Med. 1964 Sep 1;120:359–374. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Sims J. K., Kniazeff A. J. Mechanism of demyelination in JHM virus encephalomyelitis. Electron microscopic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1973 Mar 30;24(1):76–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00691421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. The TO strains of Theiler's viruses cause "slow virus-like" infections in mice. Ann Neurol. 1979 Jul;6(1):25–28. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. Theiler's virus-induced demyelination: prevention by immunosuppression. Science. 1976 Apr 2;192(4234):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.176726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Theiler's virus infection in mice: an unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1147–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1147-1155.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penney J. B., Jr, Wolinsky J. S. Neuronal and oligodendroglial infection by the WW strain of Theiler's virus. Lab Invest. 1979 Mar;40(3):324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P. Pathogenesis of demyelination induced by a mouse hepatitis. Arch Neurol. 1973 May;28(5):298–303. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490230034003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewska Z., Gilden D. H., Wellish M., Rorke L. B., Warren K. G., Wolinsky J. S. Virus-specific intracytoplasmic inclusions in mouse brain produced by a newly isolated strain of Theiler virus. I. Virologic and morphologic studies. Lab Invest. 1977 Dec;37(6):595–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewska Z., Kim S. U., Sheffield W. D., Gilden D. H. Growth of the WW strain of Theiler virus in mouse central nervous system organotypic culture. Acta Neuropathol. 1979 Jun 15;47(1):13–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00698267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]