Abstract
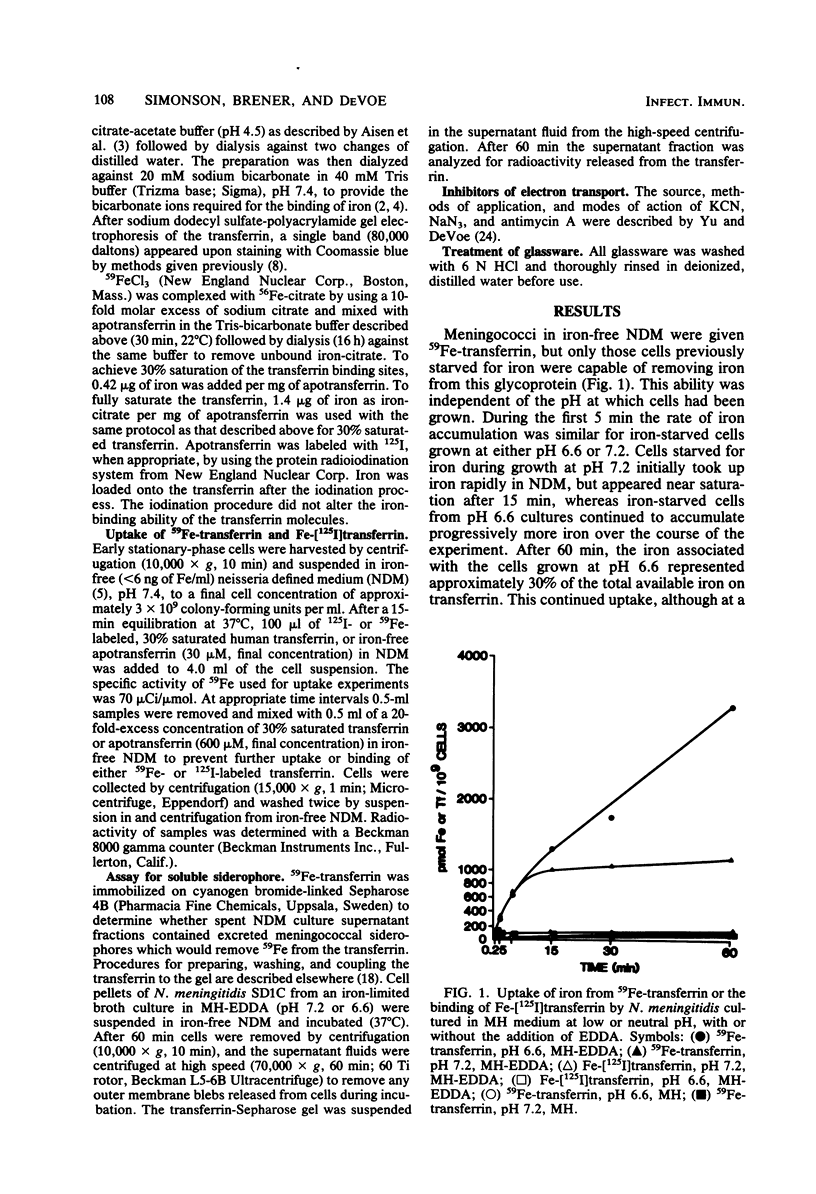
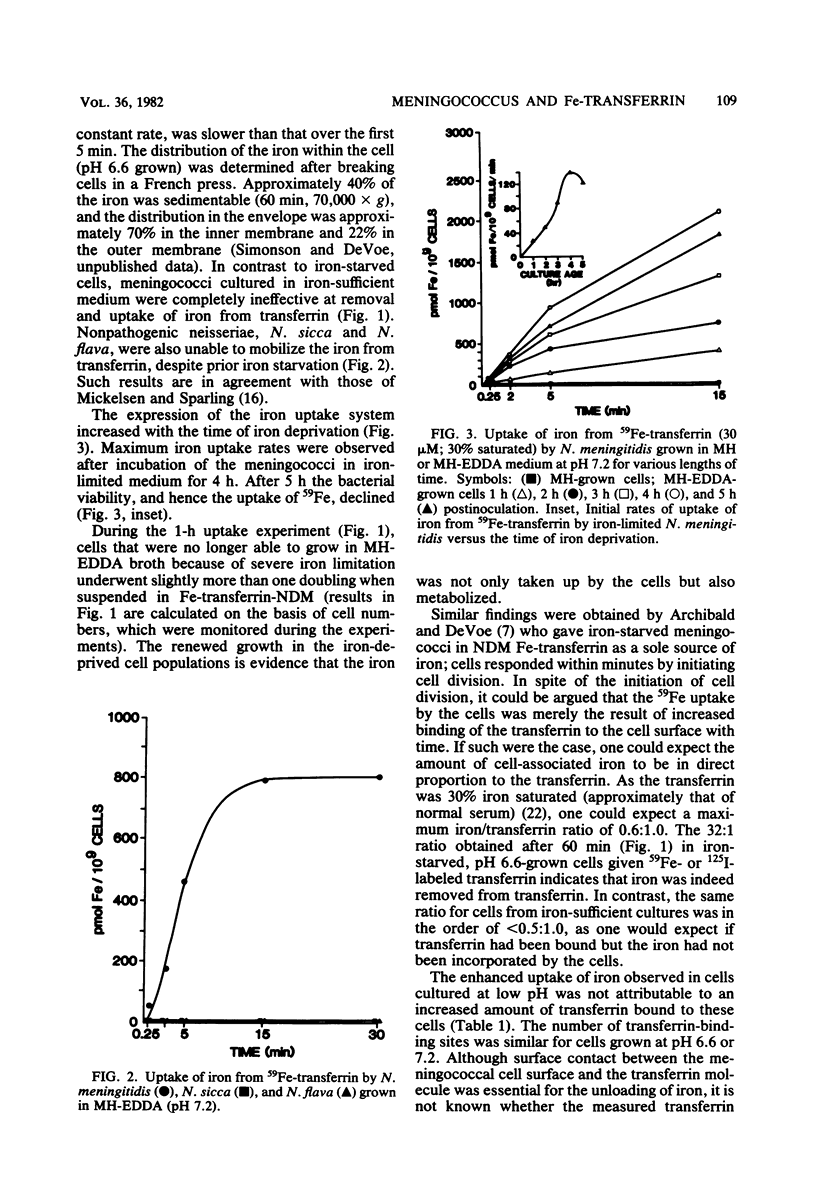
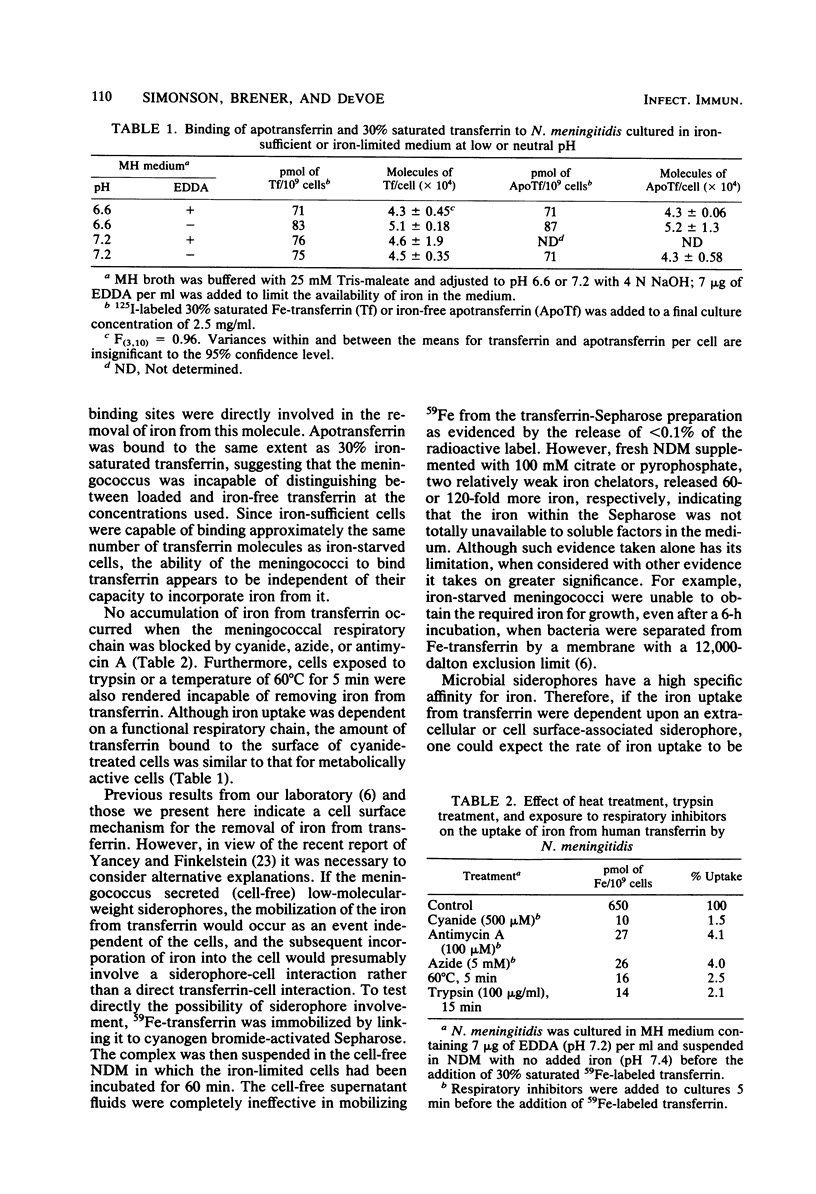
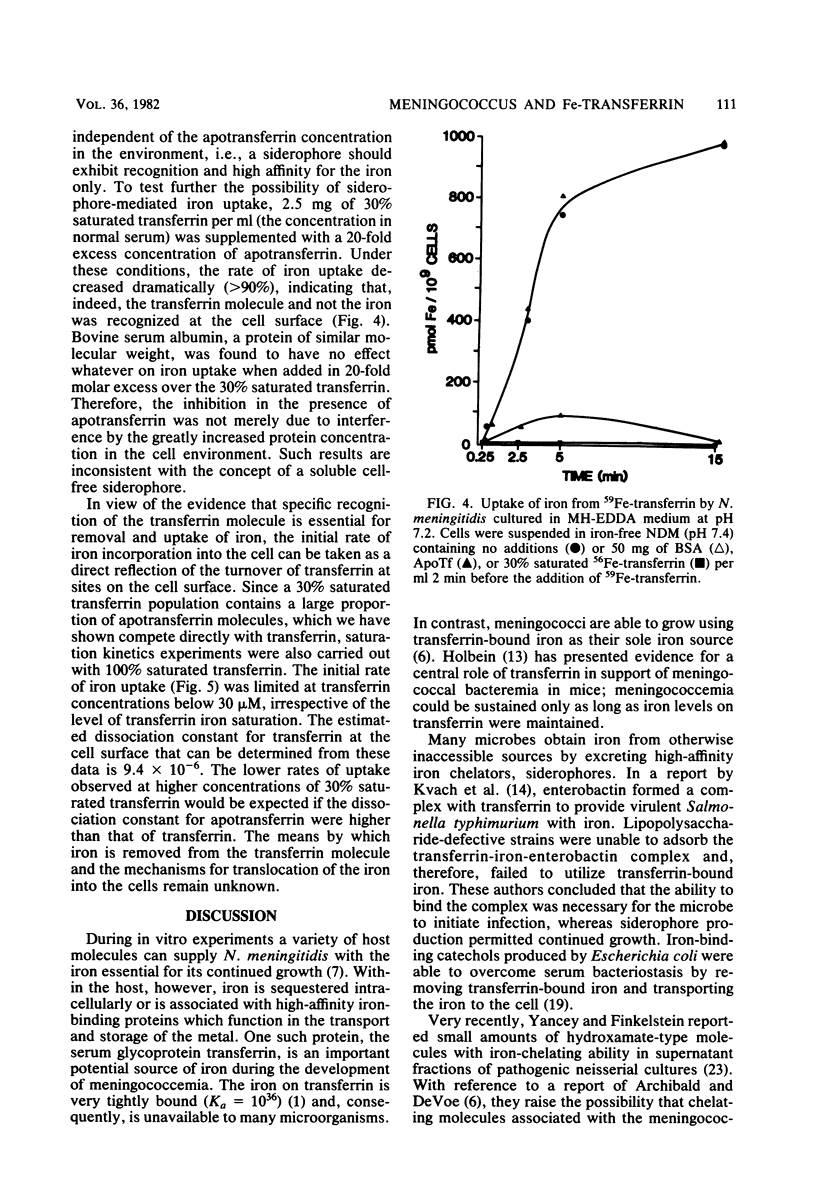
Iron-starved meningococci grown at either pH 7.2 or 6.6 were capable of removing and incorporating iron from human transferrin by a saturable, cell surface mechanism that specifically recognized transferrin rather than iron. The maximum expression of the iron uptake system occurred after 4 h of iron starvation. The uptake of the iron was dependent upon a functioning electron transport chain and was sensitive to 60 degrees C and trypsin. Cells grown under iron-sufficient conditions were incapable of accumulating iron from transferrin. No evidence was found for a primary role for cell-free soluble siderophores in the removal of iron from transferrin. The nonpathogenic neisseriae, Neisseria flava and N. sicca, were unable to utilize iron on transferrin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Leibman A. The role of the anion-binding site of transferrin in its interaction with the reticulocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 28;304(3):797–804. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90226-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisen P., Leibman A., Zweier J. Stoichiometric and site characteristics of the binding of iron to human transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1930–1937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisen P., Listowsky I. Iron transport and storage proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:357–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald F. S., DeVoe I. W. Iron acquisition by Neisseria meningitidis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):322–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.322-334.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald F. S., DeVoe I. W. Iron in Neisseria meningitidis: minimum requirements, effects of limitation, and characteristics of uptake. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):35–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.35-48.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brener D., DeVoe I. W., Holbein B. E. Increased virulence of Neisseria meningitidis after in vitro iron-limited growth at low pH. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.59-66.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J., Rogers H. J., Griffiths E. Role of iron in bacterial infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W. Egestion of degraded meningococci by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):258–266. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.258-266.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W., Gilchrist J. E. Piliation and colonial morphology among laboratory strains of meningococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):379–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.379-384.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Wada H. G., Sussman H. H. Identification of transferrin receptors on the surface of human cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6406–6410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E. Iron-controlled infection with Neisseria meningitidis in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):886–891. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.886-891.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvach J. T., Wiles T. I., Mellencamp M. W., Kochan I. Use of transferrin-iron enterobactin complexes as the source of iron by serum-exposed bacteria. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):439–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.439-445.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod M. N., DeVoe I. W. Localization of carbonic anhydrase in the cytoplasmic membrane of Neisseria sicca (strain 19). Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jan;27(1):87–92. doi: 10.1139/m81-014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.555-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Accumulation of iron by yersiniae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1290-1298.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Trivett T., DeVoe I. W. Energy-independent uptake of iron from citrate by isolated outer membranes of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):547–553. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.547-553.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Finkelstein R. A. Siderophore production by pathogenic Neisseria spp. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):600–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.600-608.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu E. K., DeVoe I. W. L-cysteine oxidase activity in the membrane of Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):280–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.280-287.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bockxmeer F. M., Morgan E. H. Identification of transferrin receptors in reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 1;468(3):437–450. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


