Abstract
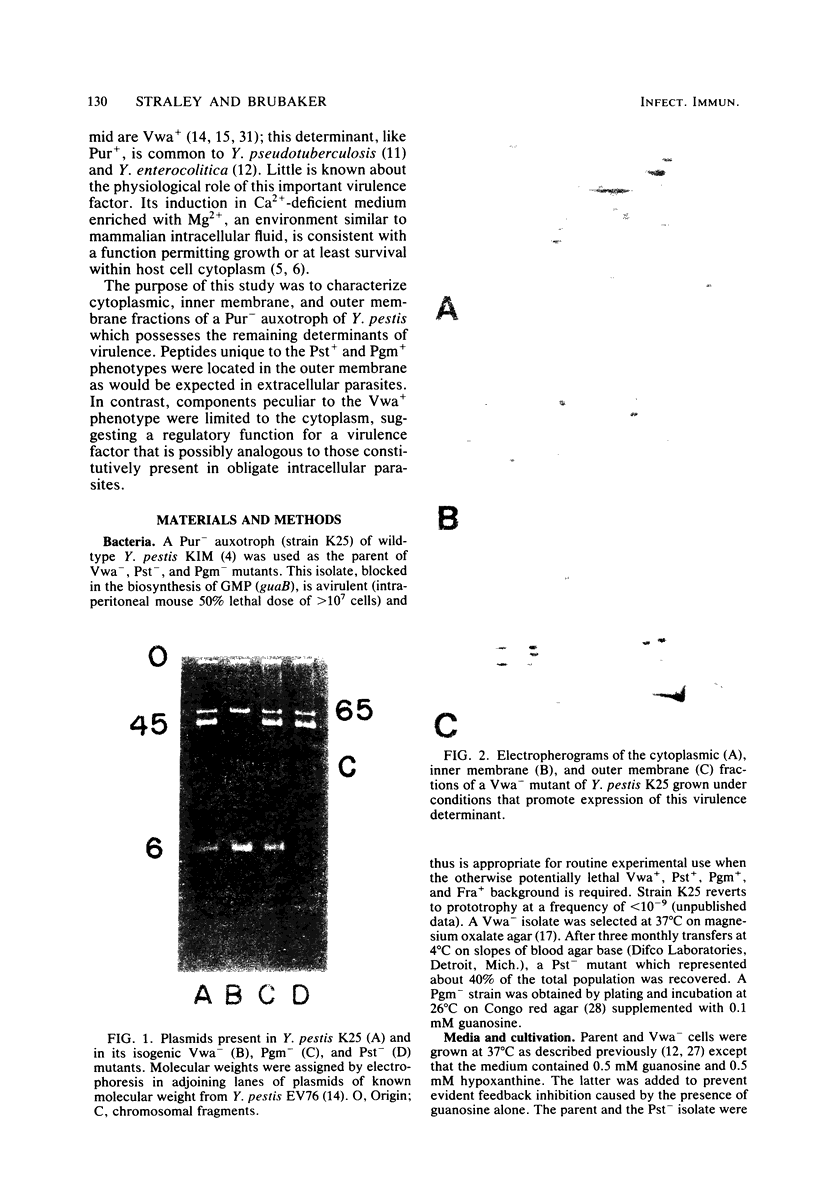
An avirulent guanine auxotroph of wild-type Yersinia pestis was used to select isogenic mutants lacking invasive determinants of virulence including V and W antigens (Vwa-), genetically linked fibrinolysin, coagulase, and pesticin activities (Pst-), and the capacity to absorb exogenous pesticin and pigments including hemin (Pgm-). After growth in environments known to favor expression of these factors by the parent, cells were converted to spheroplasts and disrupted to obtain preparations of cytoplasm; particulate matter was separated into inner and outer membranes by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Peptides present in these fractions were then solubilized and compared by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Components unique to Vwa+ cells, including V antigen, were restricted to the cytoplasmic fraction. In contrast, peptides possibly corresponding to fibrinolysin and coagulase were located primarily within the outer membrane of the Pst+ parent; pesticin was not identified. Similarly, a major outer membrane peptide, possibly representing the pesticin and pigment receptor, was peculiar to the Pgm+ parent. Accordingly, two of the virulence factors examined (Pst+ and Pgm+) can interact directly with host cells or fluids by virtue of their location on the bacterial surface. The remaining cytoplasmic Vwa+ determinant remains a candidate for a regulatory system whose role in pathogenicity is expression of functions required for intracellular survival.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACON G. A., BURROWS T. W., YATES M. The effects of biochemical mutation on the virulence of Bacterium typhosum; the loss of virulence of certain mutants. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):85–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. Pesticins. I. Pesticinbacterium interrelationships, and environmental factors influencing activity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:940–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.940-949.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. An antigen determining virulence in Pasteurella pestis. Nature. 1956 Mar 3;177(4505):426–427. doi: 10.1038/177426b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. V and W antigens in strains of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Feb;41:38–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The pigmentation of Pasteurella pestis on a defined medium containing haemin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):570–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. VIRULENCE OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS AND IMMUNITY TO PLAGUE. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1963;37:59–113. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-36742-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley E. D., Brubaker R. R., Janssen W. A., Surgalla M. J. Pesticins. 3. Expression of coagulase and mechanism of fibrinolysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):19–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.19-26.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R., Beesley E. D., Surgalla M. J. Pasteurella pestis: Role of Pesticin I and Iron in Experimental Plague. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Interconversion of Purine Mononucleotides in Pasteurella pestis. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):446–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.446-454.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Mutation rate to nonpigmentation in Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1404–1406. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1404-1406.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The genus Yersinia: biochemistry and genetics of virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;57:111–158. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65297-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Zahorchak R. J., Brubaker R. R. Plague virulence antigens from Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):638–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.638-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Shipley P. L. Plasmid-mediated factors associated with virulence of bacteria to animals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:465–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Głosnicka R., Gruszkiewicz E. Chemical composition and biological activity of the Yersinia pestis envelope substance. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.506-512.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Brubaker R. R. Characterization of pesticin. Separation of antibacterial activities. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4749–4753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWTON W. D., ERDMAN R. L., SURGALLA M. J. BIOSYNTHESIS AND PURIFICATION OF V AND W ANTIGEN IN PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:179–184. doi: 10.21236/ad0299868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Accumulation of iron by yersiniae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1290-1298.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Ito K., Yura T. Membrane proteins of Escherichia coli K-12: two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of inner and outer membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):557–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surgalla M. J., Beesley E. D. Congo red-agar plating medium for detecting pigmentation in Pasteurella pestis. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):834–837. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.834-837.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahorchak R. J., Charnetzky W. T., Little R. V., Brubaker R. R. Consequences of Ca2+ deficiency on macromolecular synthesis and adenylate energy charge in Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):792–799. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.792-799.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]