Abstract
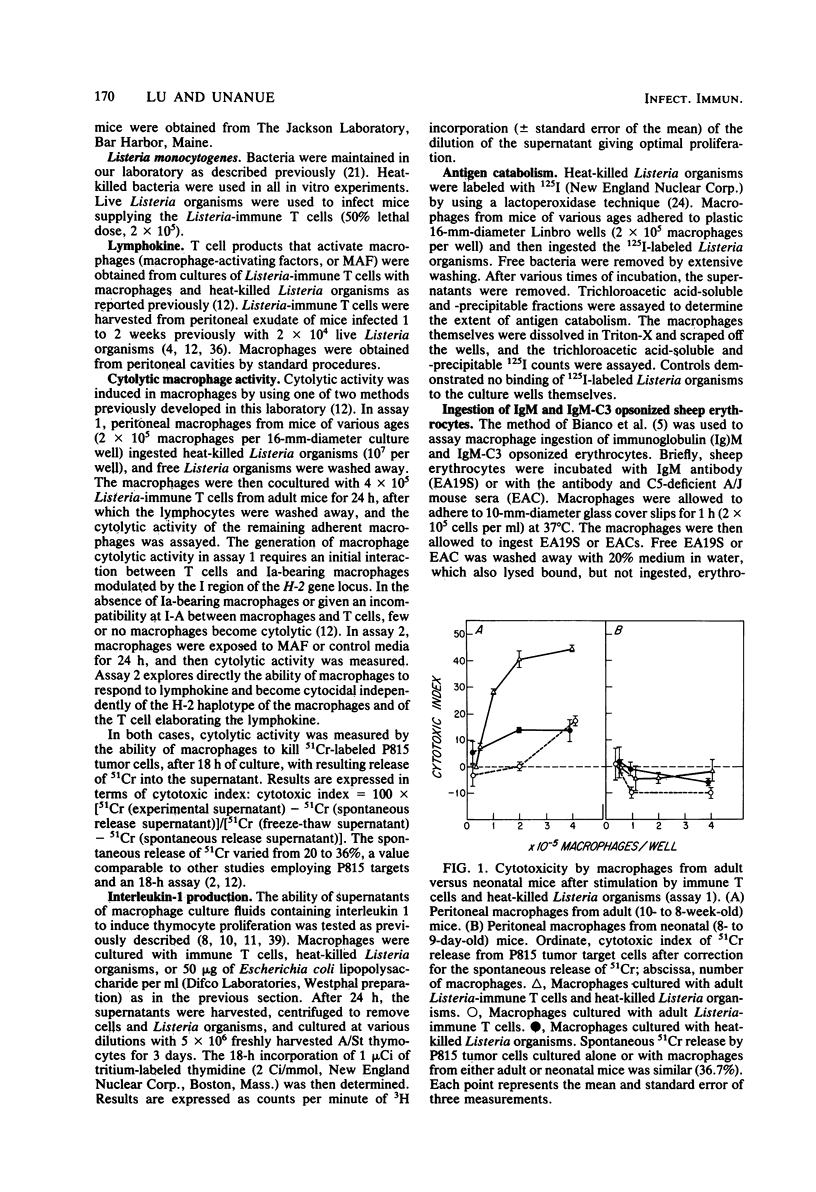
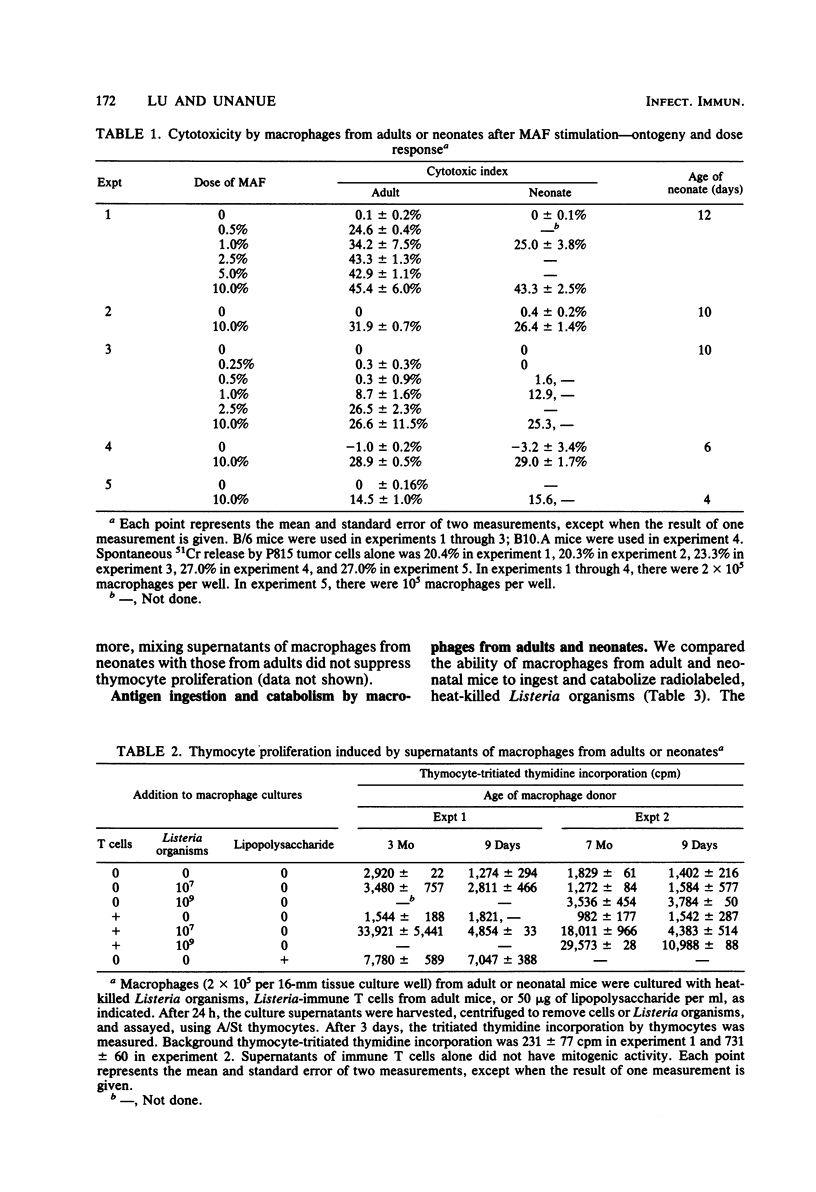
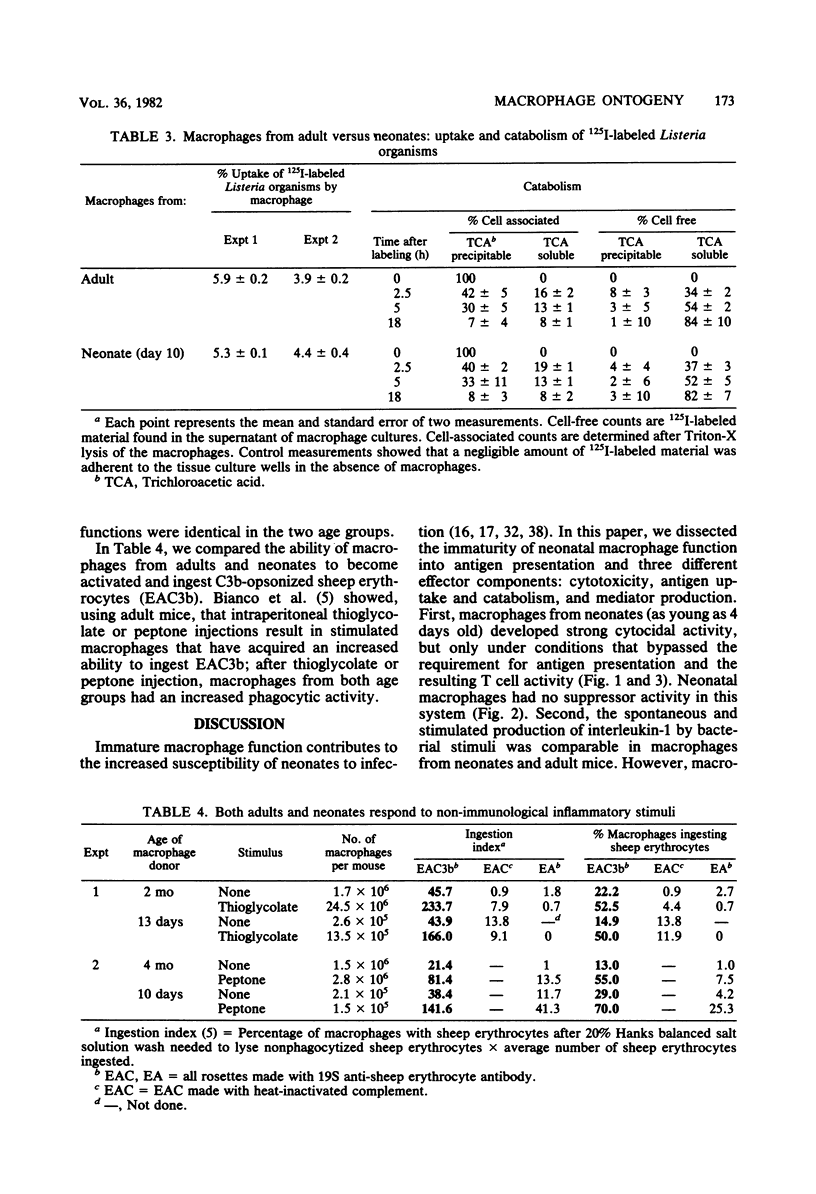
Macrophage function in neonates was dissected into four components: antigen uptake and catabolism, cytotoxicity, antigen presentation, and the production of the lymphostimulatory molecule interleukin-1 (also called thymocyte mitogenic protein or lymphocyte-activating factor). The uptake and catabolism of 125I-labeled Listeria monocytogenes was equivalent in macrophages from adult and neonatal mice. However, interactions between macrophages from neonates, heat-killed Listeria organisms, and immune T lymphocytes were impaired, and no cytocidal macrophages capable of killing tumor cells were generated. Previous studies with cells from adult mice had established that the development of cytocidal macrophages required Ia-bearing, antigen-presenting macrophages and histocompatibility at I-A between macrophages and T cells. To circumvent this requirement for antigen-presenting macrophages, an assay was used in which lymphokine was added directly to the macrophages from neonates. Strong cytocidal activity resulted. Thus, our studies confirmed that macrophages from neonates present antigen poorly but can acquire cytocidal function provided that the need for antigen-presenting function is bypassed. Similar conclusions were reached for the secretion of interleukin-1. Macrophages from neonates spontaneously secreted as much mediator as macrophages from adults, and the secretion was increased after the ingestion of heat-killed Listeria organisms or endotoxin. However, the marked increase in interleukin-1 production that follows antigen-macrophage-lymphocyte interaction was best seen in macrophages from adults. Macrophages from neonates could be activated to ingest C3b-coated sheep erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Marino P. A. Evidence for a multistep mechanism of cytolysis by BCG-activated macrophages: the interrelationship between the capacity for cytolysis, target binding, and secretion of cytolytic factor. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):981–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argyris B. F. Role of macrophages in immunological maturation. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):459–467. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Regulation of macrophage populations. I. Preferential induction of Ia-rich peritoneal exudates by immunologic stimuli. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1426–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Griffin F. M., Jr, Silverstein S. C. Studies of the macrophage complement receptor. Alteration of receptor function upon macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1278–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burakoff S. J., Finberg R., Glimcher L., Lemonnier F., Benacerraf B., Cantor H. The biologic significance of alloreactivity. The ontogeny of T-cell sets specific for alloantigens or modified self antigens. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1414–1422. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderon J., Kiely J. M., Lefko J. L., Unanue E. R. The modulation of lymphocyte functions by molecules secreted by macrophages. I. Description and partial biochemical analysis. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):151–164. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiscon M. Q., Golub E. S. Functional development of the interacting cells in the immune response. I. Development of T cell and B cell function. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1379–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., Dorf M. E., Unanue E. R. Secretion of mediators following T lymphocyte-macrophage interaction is regulated by the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3542–3546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Macrophage-T cell interactions involving Listeria monocytogenes--role of the H-2 gene complex. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2395–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr A. G., Wechter W. J., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Induction of cytocidal macrophages after in vitro interactions between Listeria-immune T cells and macrophages--role of H-2. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2405–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Activation in vitro of mouse macrophages by syngeneic, allogeneic, or xenogeneic lymphocyte supernatants. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Nov;55(5):1159–1163. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.5.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowles R. E., Fajardo I. M., Leibowitch J. L., David J. R. The enhancement of macrophage bacteriostasis by products of activated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):952–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. II. The cellular source of potentiating mediator(s). J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):143–155. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy B., Globerson A., Danon D. Ontogenic development of the reactivity of macrophages to antigenic stimulation. Cell Immunol. 1973 Nov;9(2):282–288. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Zisman B., Allison A. C. Macrophages and age-dependent resistance to Herpes simplex virus in mice. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1160–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Adachi T. Generation of specific helper cells and suppressor cells in vitro for the IgE and IgG antibody responses. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):40–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landahl C. A. Ontogeny of adherent cells. I. Distribution and ontogeny of A cells participating in the response to sheep erythrocytes in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Feb;6(2):130–134. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane F. C., Unanue E. R. Requirement of thymus (T) lymphocytes for resistance to listeriosis. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1104–1112. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C. Y., Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. During ontogeny, Ia-bearing accessory cells are found early in the thymus but late in the spleen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1597–1601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C. Y., Calamai E. G., Unanue E. R. A defect in the antigen-presenting function of macrophages from neonatal mice. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):327–329. doi: 10.1038/282327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler P. I., Klingenstein R. J., Hodes R. J. Ontogeny of murine accessory cells: Ia antigen expression and accessory cell function in in vitro primary antibody responses. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):914–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Pike B. L. Evidence for the clonal abortion theory of B-lymphocyte tolerance. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):904–917. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piessens W. F., Churchill W. H., Jr, David Macrophages activated in vitro with lymphocyte mediators kill neoplastic but not normal cells. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Owen J. J., Cooper M. D., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Megson M., Gathings W. E. Differences in susceptibility of mature and immature mouse B lymphocytes to anti-immunoglobulin-induced immunoglobulin suppression in vitro. Possible implications for B-cell tolerance to self. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1052–1064. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Allison A. C. The role of antibody and host cells in the resistance of mice against infection by coxsackie B-3 virus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;19(3):329–338. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revised nomenclature for antigen-nonspecific T cell proliferation and helper factors. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2928–2929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: induction of tumoricidal macrophages by supernatants of PPD-stimulated Bacillus Calmette-Guérin-immune spleen cell cultures. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):889–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher M. G., Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. Demonstration of a soluble mediator that induces exudates rich in Ia-positive macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1684–1698. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin W. K., Rowlands D. T., Jr Determinants of the hierarchy of humoral immune responsiveness during ontogeny. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1549–1554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Unanue E. R. Receptor-mediated inactivation of early B lymphocytes. Nature. 1975 Sep 11;257(5522):149–151. doi: 10.1038/257149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczuk M. R., Sherr D. H., Siskind G. W. Ontogeny of B lymphocyte function. VI. Ontogeny of thymus cell capacity to facilitate the functional maturation of B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1978 May;8(5):370–373. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu M., Héry C., Dupuy J. M. Neonatal susceptibility to MHV3 infection in mice. II. Role of natural effector marrow cells in transfer of resistance. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):418–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Kiely J. M., Calderon J. The modulation of lymphocyte functions by molecules secreted by macrophages. II. Conditions leading to increased secretion. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):155–166. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Melcher U., McWilliams M., Lamm M. E., Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Uhr J. W. Cell surface immunoglobulin. XI. The appearance of an IgD-like molecule on murine lymphoid cells during ontogeny. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):206–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks B. A., Kavas A. F. Macrophage chemotaxis and phagocytosis in guinea pigs: influence of age and nutrition. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Nov;26(5):501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston W. L., Carson B. S., Barkin R. M., Slater G. D., Dustin R. D., Hecht S. K. Monocyte-macrophage function in the newborn. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Nov;131(11):1241–1242. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120240059011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Skinsnes O. K. Peritoneal macrophage response in neonatal mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 Aug;14(2):181–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler K., Unanue E. R. Identification of a macrophage antigen-processing event required for I-region-restricted antigen presentation to T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1869–1875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


