Abstract
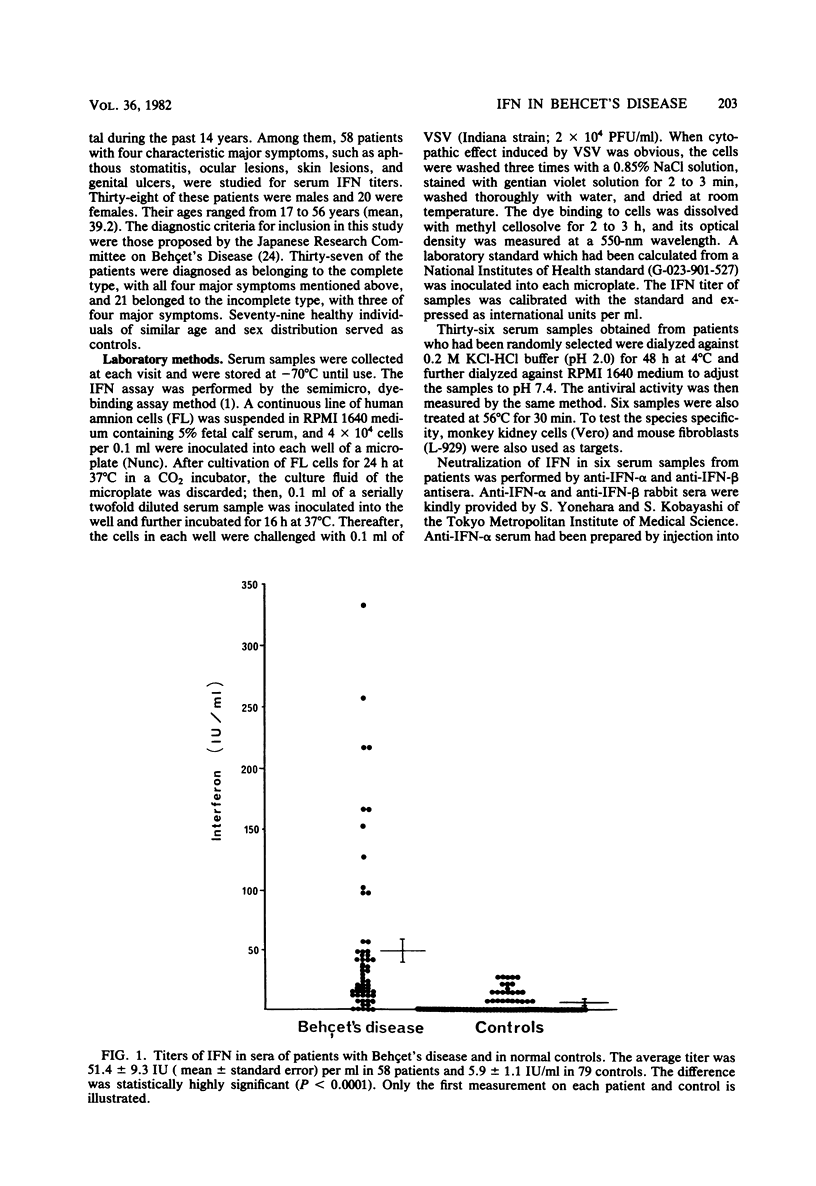
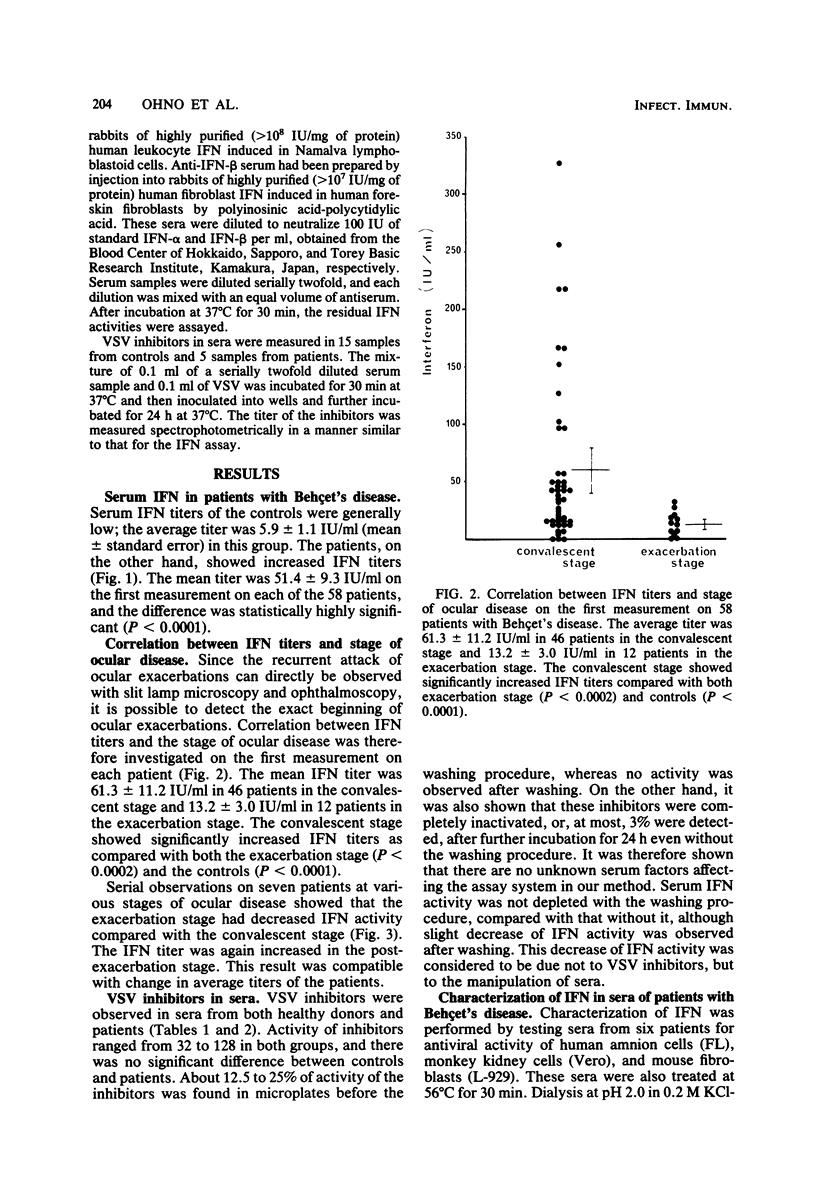
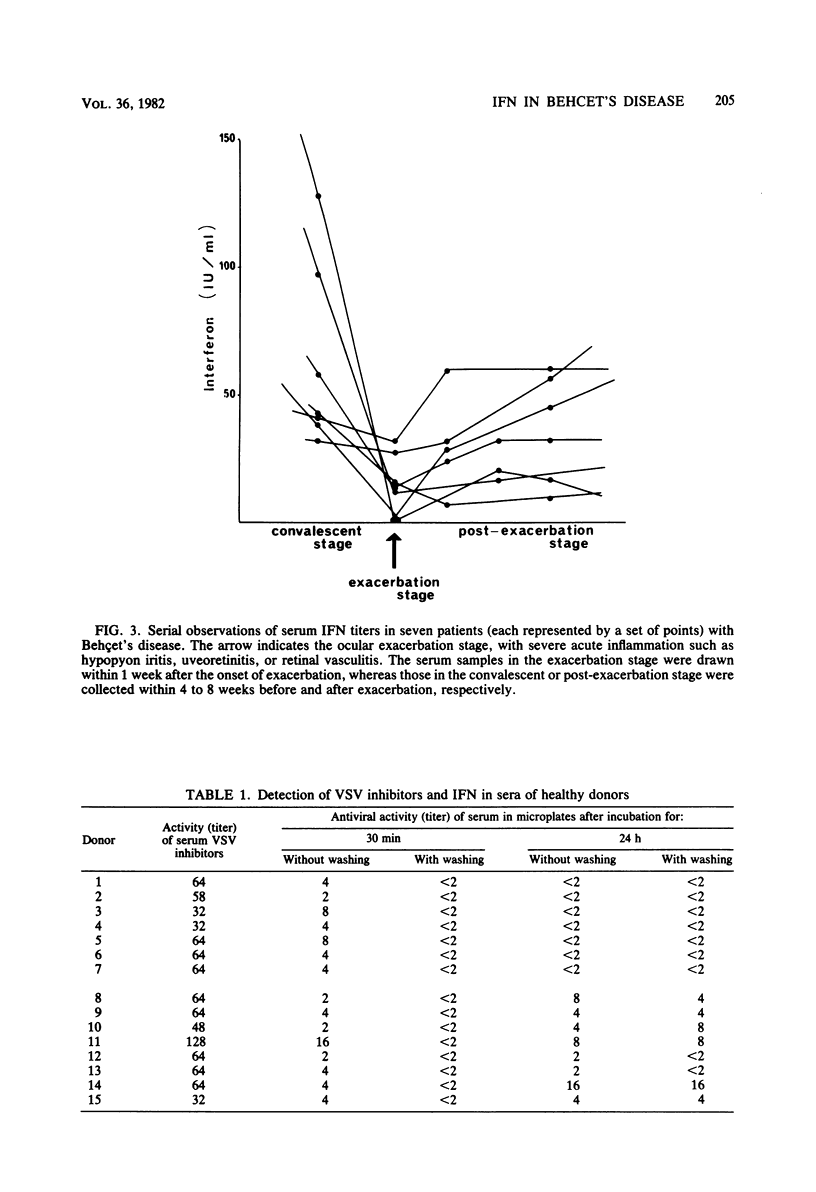
The serum levels of interferon (IFN) in 58 patients with Behçet's disease were significantly higher than those in 79 normal controls (P less than 0.0001). The average IFN titer was 51.4 +/- 9.3 IU/ml in the patients and 5.9 +/- 1.1 IU/ml in the controls. The patients were then divided into two groups according to the stage of ocular disease. Forty-six patients in the ocular convalescent stage had higher IFN levels (61.3 +/- 11.2 IU/ml) than did 12 patients in the exacerbation stage (13.2 +/- 3.0 IU/ml). Moreover, the kinetics of the IFN level in the circulation of seven patients showed a significant decrease of IFN in the exacerbation stage. IFN activity in sera from patients was destroyed by acid treatment and heating at 56 degrees C for 30 min and was not neutralized with anti-human IFN-alpha and -beta sera. In addition, it was demonstrated that vesicular stomatitis virus inhibitors detected in sera from both the patients and the controls had no effect on our IFN assay. Therefore, antiviral activity detected in sera of patients seems to be due to gamma interferon (IFN-gamma). IFN-gamma may play a significant role in the pathophysiology of Behçet's disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A. Semi-micro, dye-binding assay for rabbit interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):723–725. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.723-725.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur B. R., Merigan T. C. Suppressive effect of interferon on the humoral immune response to sheep red blood cells in mice. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1319–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani F., Monahan T. M., Scupham A., Zucca M. Enzymatic induction of interferon production by galactose oxidase treatment of human lymphoid cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):879–882. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.879-882.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Cline M. J., Merigan T. C. The interaction of human macrophages and lymphocytes in the phytohemagglutinin-stimulated production of interferon. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):744–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI106545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Cooper H. L. Stimulation of interferon production in human lymphocytes by mitogens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jul;125(3):901–905. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujibayashi T., Hooks J. J., Notkins A. L. Production of interferon by immune lymphocytes exposed to herpes simplex virus-antibody complexes. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1191–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron I., Berg K., Cantell K. Regulatory effect of interferon on T cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1370–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Geis S. A., Stahl N. I., Decker J. L., Notkins A. L. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):5–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M. Differentiation of the immunosuppressive and antiviral effects of interferon. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 15;36(2):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawachi-Takahashi S., Tanaka K., Takahashi M., Kawashima T., Shimada K. Determination of serum C9 level by immunodiffusion. Elevation in patients with infectious or allergic skin diseases. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(2):161–170. doi: 10.1159/000231302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Georgiades J. A., Stanton G. J., Dianzani F., Johnson H. M. Large-scale production and physicochemical characterization of human immune interferon. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.36-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Asanuma T., Sugiura S., Wakisaka A., Aizawa M., Itakura K. HLA-Bw51 and Behçet's disease. JAMA. 1978 Aug 11;240(6):529–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S., Nakayama E., Sugiura S., Itakura K., Aoki K. Specific histocompatibility antigens associated with Behçet's disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1975 Oct;80(4):636–641. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(75)90394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Manejias R. E., Russo M., Abbey E. E. Increased spreading of macrophages from mice treated with interferon inducers. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 1;29(1):86–95. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Kogure M., Kawashima T., Nishioka K. Reduction of complement in Behçet's disease and drug allergy. Med Biol. 1974 Aug;52(4):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Ehrlich G. E., Inaba G., Hayashi K. Behçet disease (Behçet syndrome). Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1979 May;8(4):223–260. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld G., Mandel A. D., Merigan T. C. The immunosuppressive effect of type II mouse interferon preparations on antibody production. Cell Immunol. 1977 Dec;34(2):193–206. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura S. [Some observations on uveitis in Japan, with special reference to Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada and Behçet diseases (author's transl)]. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1976 Nov 10;80(11):1285–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valle M. J., Bobrove A. M., Strober S., Merigan T. C. Immune specific production of interferon by human T cells in combined macrophage-lymphocyte cultures in response to Herpes simplex antigen. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):435–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Salvin S. B. Production and properties of migration inhibitory factor and interferon in the circulation of mice with delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1914–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



