Abstract
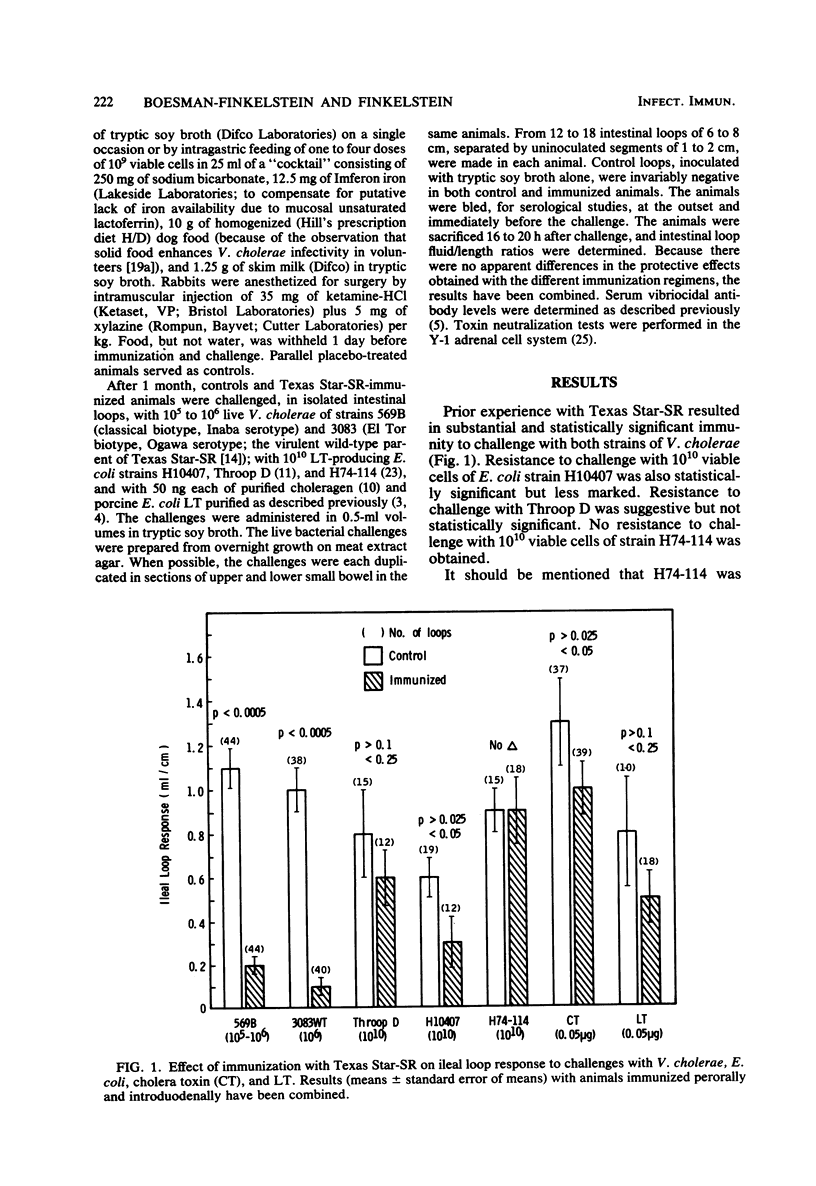
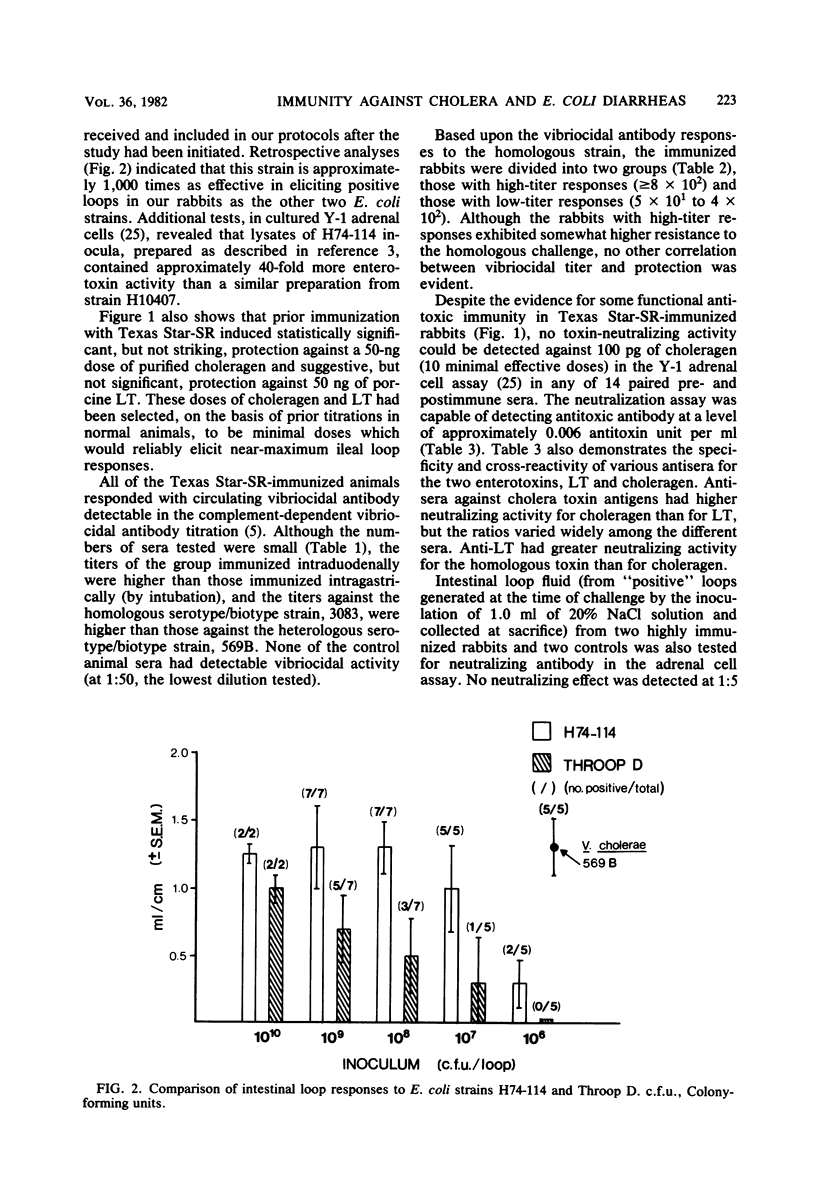
The avirulent, A-B+, streptomycin-resistant mutant designated Texas Star-SR, isolated from a virulent, hypertoxinogenic, colonizing strain of Vibrio cholerae (Ogawa serotype, El Tor biotype) and administered intragastrically or intraduodenally in adult rabbits, has been found to induce substantial immunity to subsequent challenge (in ligated intestinal loops) with virulent wild-type cholera vibrios (of both homologous and heterologous biotype and serotype). Significant resistance to challenge with one strain of human heat-labile enterotoxin (LT)-producing Escherichia coli was also demonstrated, but resistance against two other human LT-producing strains was either nil or marginal under these experimental conditions. Significant, but not striking, resistance against challenge with purified choleragen was obtained, whereas protection against a bolus challenge of purified porcine LT was not statistically significant.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological cross-reactivity between a heat-labile enterotoxin(s) of Escherichia coli and subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1036-1039.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Yancey R. J., Finkelstein R. A. Properties of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):91–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.91-97.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R. The serologic character of cholera Vibrio mucinase. J Infect Dis. 1955 Nov-Dec;97(3):238–245. doi: 10.1093/infdis/97.3.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera. Preparation and isolation of choleragen and choleragenoid. J Exp Med. 1969 Jul 1;130(1):185–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Monospecific equine antiserum against cholera exo-enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Dec;2(6):691–697. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.6.691-697.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Vasil M. L., Jones J. R., Anderson R. A., Barnard T. Clinical cholera caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Mar;3(3):382–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.3.382-384.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary S. J., Marchlewicz B. A., Finkelstein R. A. Comparison of heat-labile enterotoxins from porcine and human strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.215-220.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Finkelstein R. A. Selection and characteristics of a Vibrio cholerae mutant lacking the A (ADP-ribosylating) portion of the cholera enterotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2052–2056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. Composition and immunochemical properties of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):382–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.382-389.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. A., Van Heyningen W. E. Deactivation of cholera toxin by a sialidase-resistant monosialosylganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):639–647. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. E., Saier M. H., Jr Genetic dissection of catalytic activities of the Salmonella typhimurium mannitol enzyme II. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1106–1109. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1106-1109.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Cisneros L., Nalin D. R., Young C. R. Duration of infection-derived immunity to cholera. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):818–820. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nalin D. R., Craig J. P., Hoover D., Bergquist E. J., Waterman D., Holley H. P., Hornick R. B., Pierce N. P., Libonati J. P. Immunity of cholera in man: relative role of antibacterial versus antitoxic immunity. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(1):3–9. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nalin D. R., Hoover D. L., Bergquist E. J., Hornick R. B., Young C. R. Immunity to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):729–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.729-736.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley W. H., Benenson A. S., Barui R. A serological survey for cholear antibodies in rural east Pakistan. 1. The distribution of antibody in the control population of a cholera-vaccine field-trial area and the relation of antibody titre to the pattern of endemic cholera. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(3):327–334. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick I. G., Ford C. W., Shackleford G. M., Berry L. J. Improved protection against cholera in adult rabbits with a combined flagellar-toxoid vaccine. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):375–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.375-380.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. R., Parker C. D. Isolation and characterization of protease-deficient mutants of vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):143–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel S. P., Finkelstein R. A., Parker C. D. Ability of an avirulent mutant of Vibrio cholerae to colonize in the infant mouse upper bowel. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):474–479. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.474-479.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. Synergistic protective effect in rabbits of immunization with Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide and toxin/toxoid. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):735–740. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.735-740.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Willis D. L., Berry L. J. Flagella-induced immunity against experimental cholera in adult rabbits. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):220–228. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.220-228.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



