Abstract
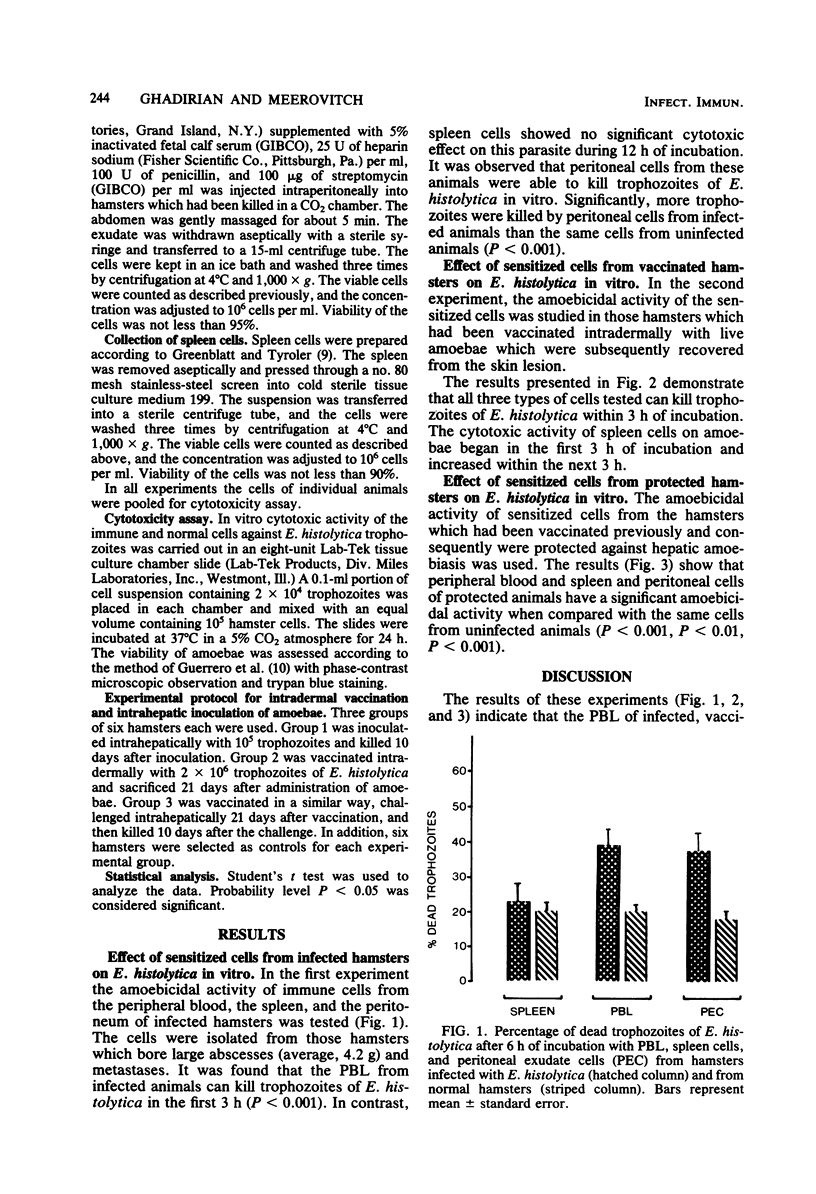
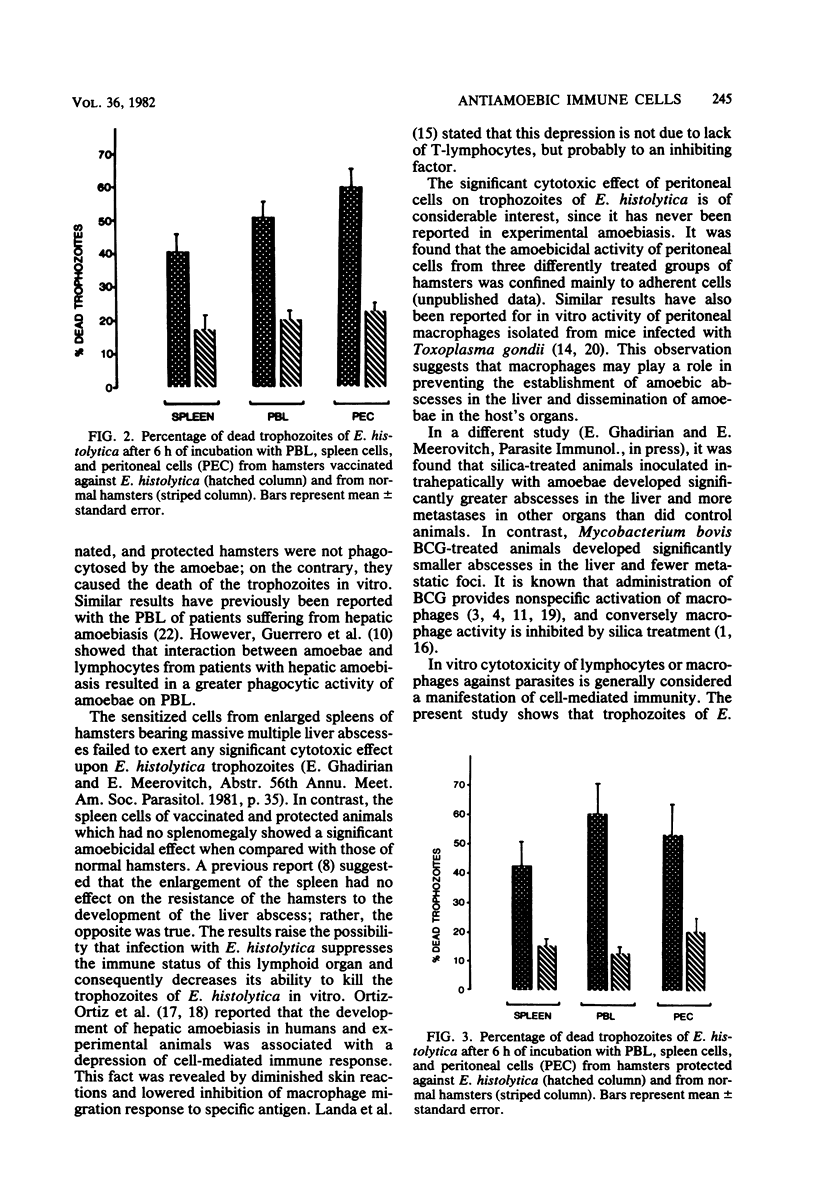
The amoebicidal activity of peripheral blood lymphocytes and spleen and peritoneal cells from hamsters vaccinated against or protected from hepatic amoebiasis and from those with hepatic amoebiasis was investigated. Peripheral blood lymphocytes and peritoneal and spleen cells from vaccinated or protected animals can kill trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica in vitro. In contrast, spleen cells from infected hamsters showed no significant cytotoxic effect on the parasite. These data suggest that cellular immunity plays an important role in host defense against hepatic amoebiasis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos H. J., van de Griend R. J. Virulence and toxicity of axenic Entamoeba histolytica. Nature. 1977 Jan 27;265(5592):341–343. doi: 10.1038/265341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Allison A. C., Cox F. E. Protection of mice against Babesia and Plasmodium with BCG. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):309–311. doi: 10.1038/259309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland R. P., Meltzer M. S., Zbar B. Tumor cytotoxicity in vitro by macrophages from mice infected with mycobacterium bovis strain BCG. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jun;52(6):1887–1895. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.6.1887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Techniques of axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae. J Parasitol. 1968 Oct;54(5):1047–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Behavior of axenic IP-106 strain of Entamoeba histolytica in the golden hamster. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Mar;27(2 Pt 1):241–247. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Effect of immunosuppression on the size and metastasis of amoebic liver abscesses in hamsters. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Winter;3(4):329–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E., Hartmann D. P. Protection against amebic liver abscess in hamsters by means of immunization with amebic antigen and some of its fractions. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Sep;29(5):779–784. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Vaccination against hepatic amebiasis in hamsters. J Parasitol. 1978 Aug;64(4):742–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt C. L., Tyroler E. Trypanosoma lewisi: in vitro behavior of rat spleen cells. Exp Parasitol. 1971 Dec;30(3):363–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(71)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna M. G., Jr, Zbar B., Rapp H. J. Histopathology of tumor regression after intralesional injection of Mycobacterium bovis. I. Tumor growth and metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 May;48(5):1441–1455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. G., Bray R. S. Cellular sensitivity in amoebiasis--preliminary results of lymphocytic transformation in response to specific antigen and to mitogen in carrier and disease states. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1976;70(4):340–343. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(76)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARUMILINTA R., KRADOLFER F. THE TOXIC EFFECT OF ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA ON LEUCOCYTES. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1964 Sep;58:375–381. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1964.11686259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. In vitro induction of nonspecific resistance in macrophages by specifically sensitized lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):337–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.337-343.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. H., Wheelock E. F. Effects of intravenous silica on immune and non-immune functions of the murine host. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):41–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Garmilla C., Tanimoto-Weki M., Zamacona-Ravelo G. Hipersensibilidad celular en amibiasis. I. Reacciones en hamsters inoculados con E. histolytica. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1973;(Suppl):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Zamacona G., Sepúlveda B., Capín N. R. Cell-mediated immunity in patients with amebic abscess of the liver. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratzan K. R., Musher D. M., Keusch G. T., Weinstein L. Correlation of increased metabolic activity, resistance to infection, enhanced phagocytosis, and inhibition of bacterial growth by macrophages from Listeria- and BCG-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):499–504. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.499-504.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Krahenbuhl J. L., Mendenhall J. W. A role for activated macrophages in resistance to infection with Toxoplasma. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):829–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.829-834.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savanat T., Viriyanond P., Nimitmongkol N. Blast transformation of lymphocytes in amebiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1973 Nov;22(6):705–710. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1973.22.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemberger H. Zytolytische Immunreaktionen in vitro gegen Trophozoiten von E. histolytica. Immun Infekt. 1978 Apr;6(2):71–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



