Abstract
Coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V (T14V) and Streptococcus sanguis 34 (Ss34) depends upon specific reaction between lectin on T14V and carbohydrate on Ss34. Studies on coaggregation inhibition by sugars related to D-galactose, beta-galactosides, and amphipathic molecules revealed: (i) D-fucose, D-talose approximately equal to D-galactose, which was 0.2 potency of lactose. No other hexoses or pentoses inhibited at 0.1 M. (ii) Gal beta (1 leads to 3)GalNAc alpha OCH2C6H5 was the most potent beta-galactoside inhibitor; it had 20 times the potency of lactose. (iii) Anionic nonaromatic amphipathic compounds were good inhibitors; sodium deoxycholate (I) was equal to lactose; sodium dodecyl sulfate (II) had 15 times the potency of lactose; there was 90 to 100% irreversible inhibition when T14V was treated with 0.005 M (II). Treatment of Ss34 with II had no effect. (iv) Synergism of inhibition was observed between lactose and I or lactose and II, e.g., inhibition by 0.01 M lactose = 5%; inhibition by 0.01 M I = 9%; inhibition by 0.01 M lactose + 0.01 M I = 87%. (v) The irreversible inhibition by II was prevented when 0.25 M lactose or 0.25 M I was present during treatment of T14V with 0.005 M II. (vi) Synergism and prevention by lactose or by I of irreversible inhibition by II suggest that all three react at the same site on T14V lectin. We hypothesize that the T14V lectin combining site for Ss34 carbohydrate has specific affinity for beta-galactosides and for anionic nonaromatic amphipathic molecules. This site can be saturated by either kind of reagent to exclude the other reagent or to inhibit coaggregation.
Full text
PDF




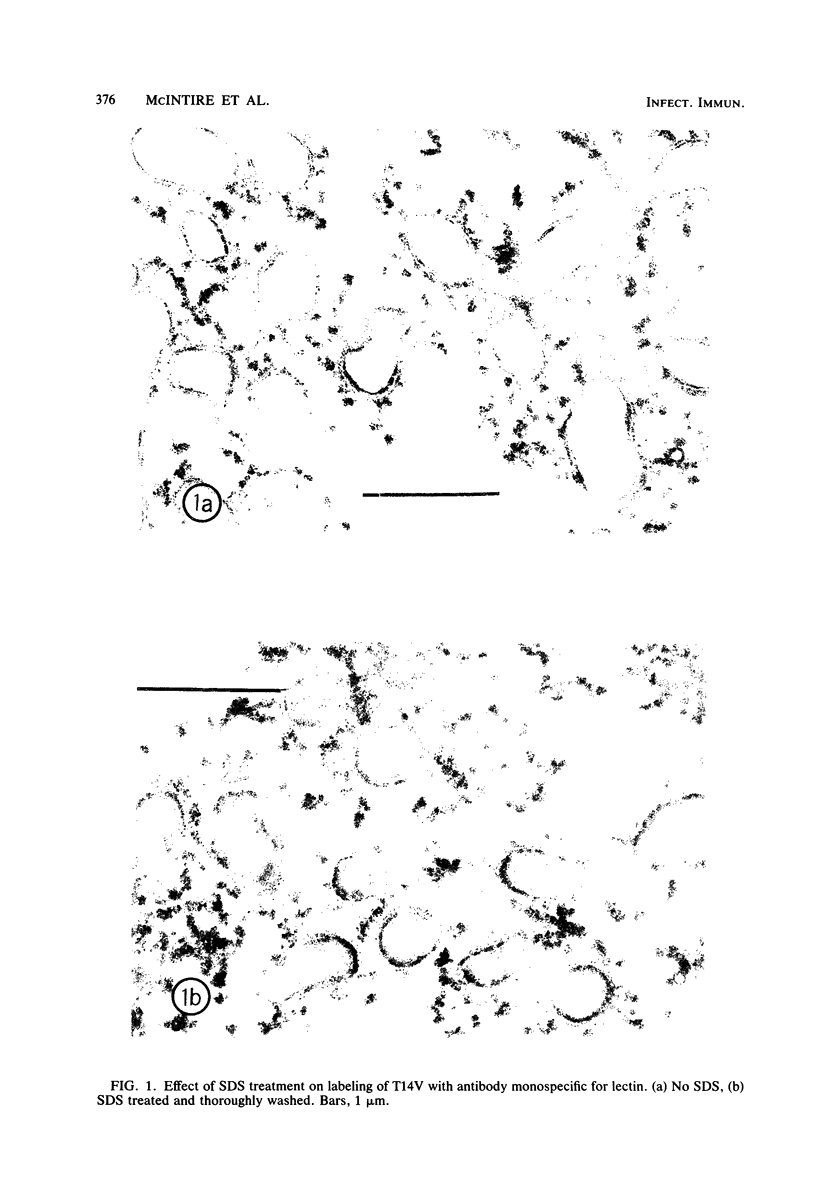


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cisar J. O., Barsumian E. L., Curl S. H., Vatter A. E., Sandberg A. L., Siraganian R. P. Detection and localization of a lectin on Actinomyces viscosus T14V by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1318–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Kolenbrander P. E., McIntire F. C. Specificity of coaggregation reactions between human oral streptococci and strains of Actinomyces viscosus or Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):742–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.742-752.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Nygaard M. Interbacterial aggregation of plaque bacteria. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Dec;15(12):1397–1400. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Schauer S. V., Bloomquist C. G. Compounds which affect the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans to hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res. 1978 Feb;57(2):373–379. doi: 10.1177/00220345780570023901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOVITZ A. Isolation of D-talomethylose (6-deoxy-Dtalose) and D-rhamnose (6-deoxy-D-mannose) from capsular polysaccharide of a gram-negative bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1767–1771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Vatter A. E., Baros J., Arnold J. Mechanism of coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Streptococcus sanguis 34. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):978–988. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.978-988.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




