Abstract
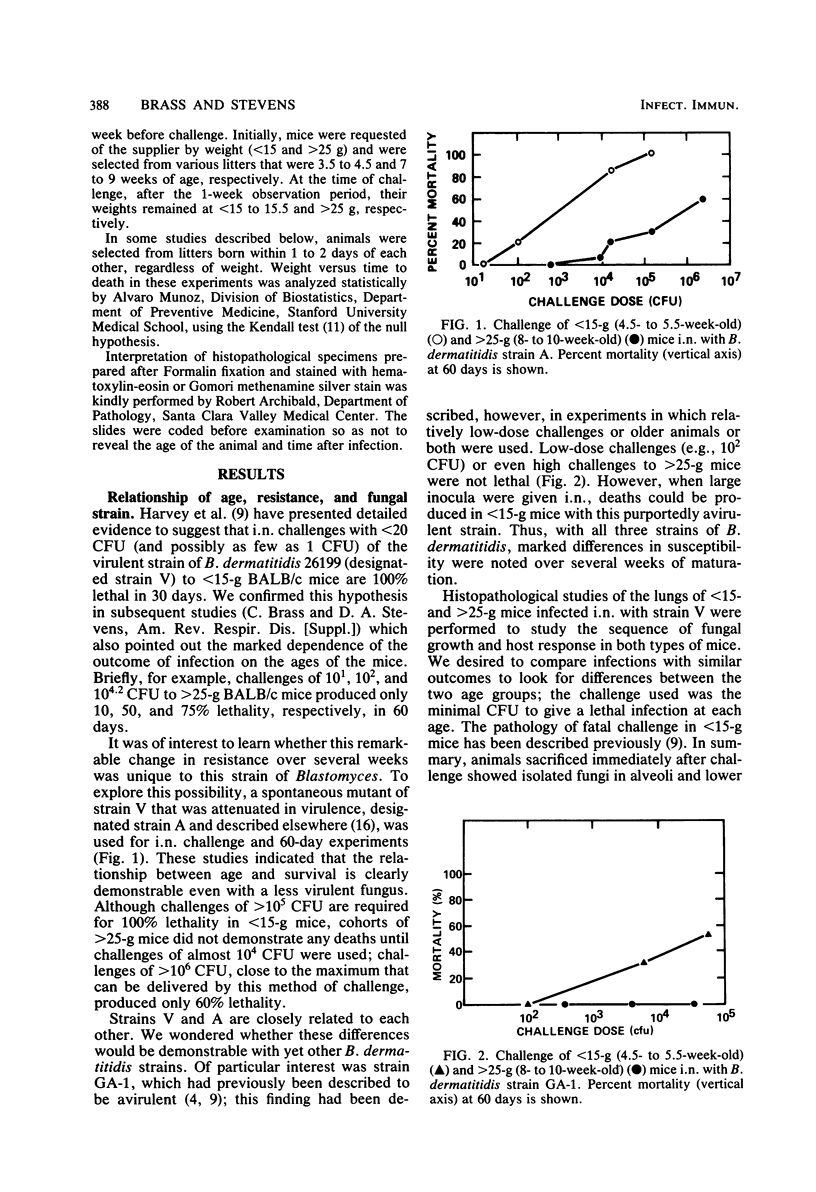
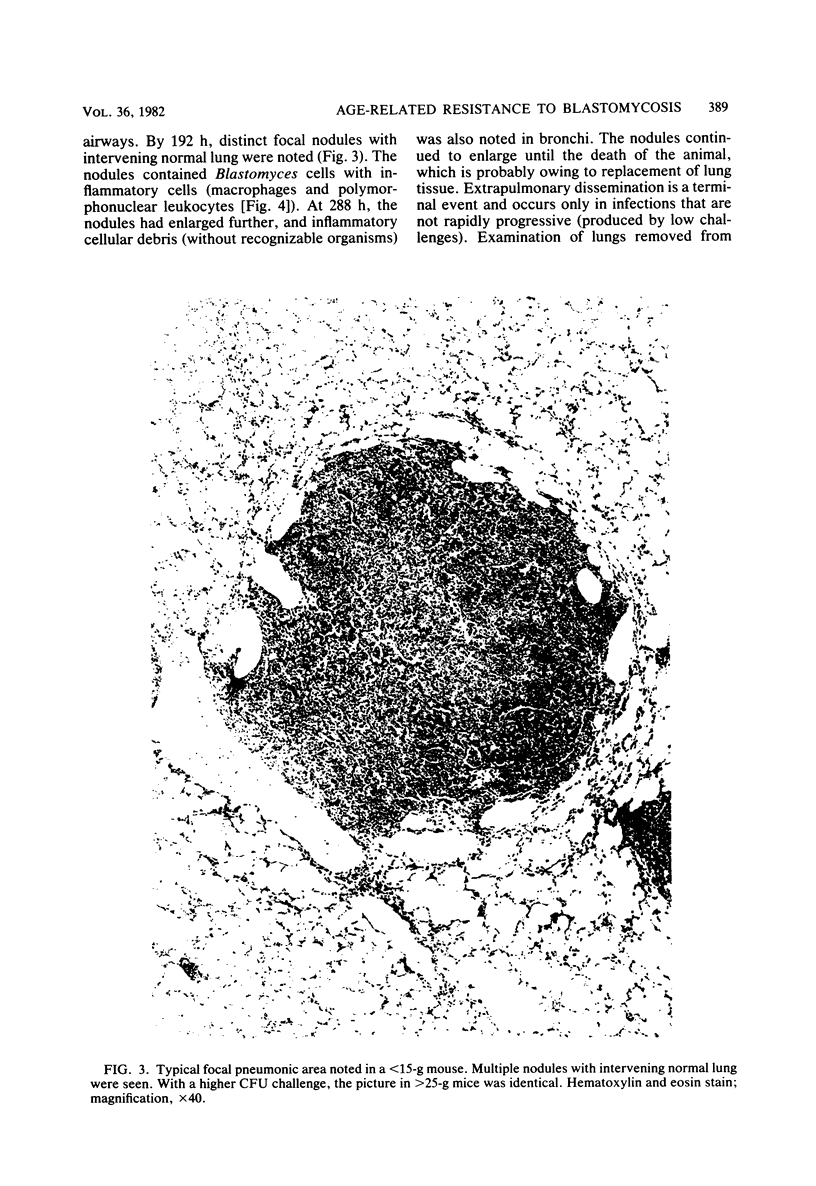
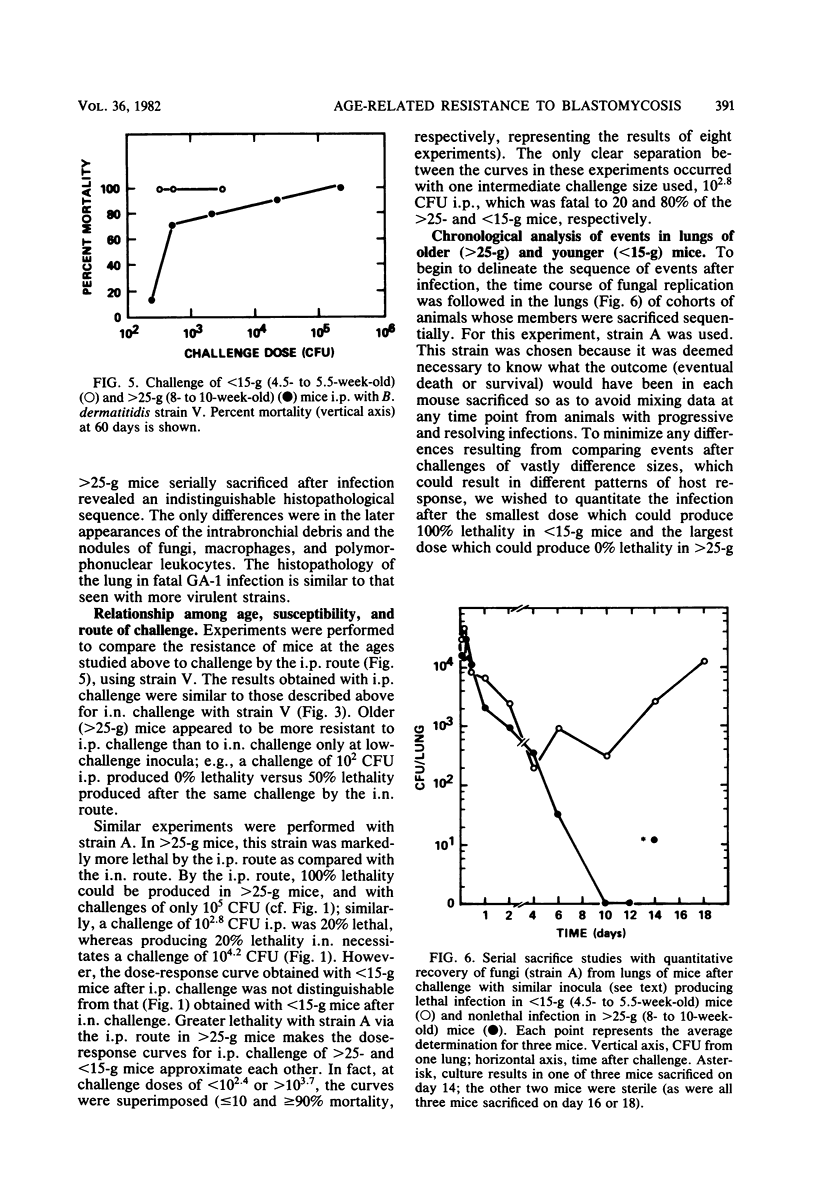
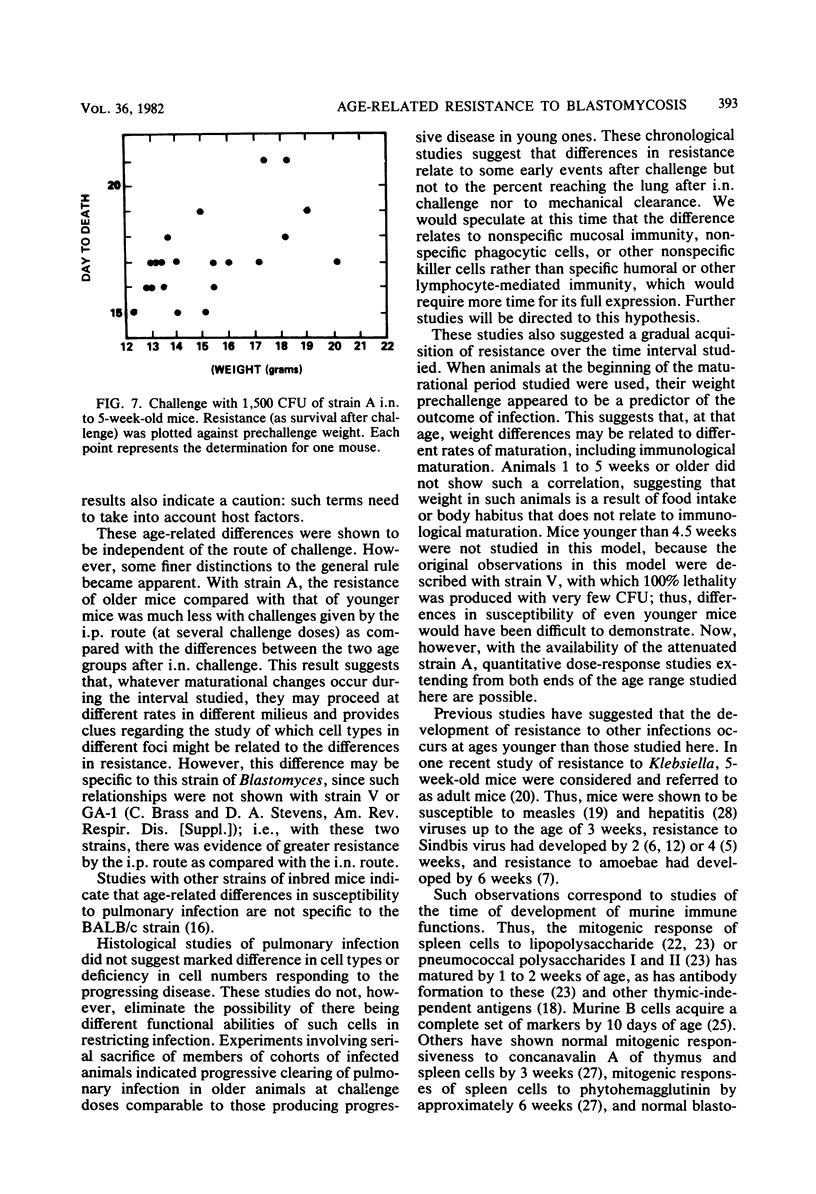
Marked resistance of 9-week-old mice as compared to that of 5-week-old mice was demonstrated after pulmonary challenge with three strains of Blastomyces dermatitidis of various virulences. Quantitative studies with graded doses of the strain that was intermediate in virulence indicated that the difference in resistance between the two age groups was 1,000-fold. Acquisition of resistance appeared to be gradual between the ages of 5 and 9 weeks. Maturational differences among individual mice appeared to be most crucial at 5 weeks of age. With two fungal strains, susceptibility of the younger mice was also demonstrated after intraperitoneal challenge; with one of these strains, the differences between the two groups of mice were much smaller, suggesting that maturation of defenses in the peritoneal cavity may develop faster. Studies with serial sacrifice of different groups of mice given pulmonary challenges (of comparable amounts) indicated that the differences are not due to the amount of challenge reaching the lungs or its clearance. The infection-limiting effect in the lungs of older mice occurred within 4 days after challenge. These differences in resistance over this narrow age interval appear to be unique; resistance appears to occur later than resistance to other infectious agents and at a time when most murine immune functions have matured. This model and these observations provide an opportunity for further studies of the mechanism of resistance and are relevant to clinical observations of susceptibility of infants and children to deep mycoses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argyris B. F. Further studies on suppressor cell activity in the spleen of neonatal mice. Cell Immunol. 1979 Dec;48(2):398–406. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIE A. The disease spectrum of human histoplasmosis. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Sep;49(3):544–555. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-49-3-544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calkins C. E., Stutman O. Changes in suppressor mechanisms during postnatal development in mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):87–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E. Role of the immune response in age-dependent resistance of mice to encephalitis due to Sindbis virus. J Infect Dis. 1976 Apr;133(4):456–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.4.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackbarth S. A., Reinarz A. B., Sagik B. P. Age-dependent resistance of mice to sindbis virus infection: reticuloendothelial role. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 Nov;14(5):405–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty R. M., John D. T. Innate resistance of mice to experimental infection with Naegleria fowleri. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):73–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.73-77.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Schmid E. S., Carrington C. C., Stevens D. A. Mouse model of pulmonary blastomycosis: utility, simplicity, and quantitative parameters. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Apr;117(4):695–703. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.4.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Lavrin D. H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic acid allogeneic tumors. I. Distribution of reactivity and specificity. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):216–229. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., McFarland H. F., Levy S. E. Age-dependent resistance to viral encephalitis: studies of infections due to Sindbis virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):257–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi P. A., Halpern J. W., Stevens D. A. Susceptibility differences of inbred strains of mice to blastomycosis. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):160–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.160-168.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Prescott B., Cross S. S., Stashak P. W., Baker P. J. Regulation of the antibody response to type III pneumococcal polysaccharide. V. Ontogeny of factors influencing the magnitude of the plaque-forming cell response. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):279–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Johnson B. M. Ontogeny of mouse lymphocyte function. II. Development of the ability to produce antibody is modulated by T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):216–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neighbour P. A., Rager-Zisman B., Bloom B. R. Susceptibility of mice to acute and persistent measles infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):764–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.764-770.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parant M., Parant F., Chedid L. Enhancement of the neonate's nonspecific immunity to Klebsiella infection by muramyl dipeptide, a synthetic immunoadjuvant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3395–3399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. A., Schuit K. E. Acute pulmonary blastomycosis in children: clinical course and follow-up. Pediatrics. 1979 May;63(5):736–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz S. G. Comparative mitogenic responses of T-cells and B-cells in spleens of mice of varying age. Immunol Commun. 1975;4(1):63–79. doi: 10.3109/08820137509055762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz S. G. Measurement and comparison of the proliferative and antibody response of neonatal, immature and adult murine spleen cells to T-dependent and T-independent antigens. Cell Immunol. 1976 Feb;21(2):201–216. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo A., Robledo M., Giraldo R., Hernández H., Sierra F., Gutiérrez F., Londoño F., López R., Calle G. The gamut of paracoccidioidomycosis. Am J Med. 1976 Jul;61(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Unanue E. R. Development of B lymphocytes. I. Cell populations and a critical event during ontogeny. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1730–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowron-Cendrzak A., Ptak W. Splenic suppressor cells in fetal and newborn mice. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1978;26(1-6):1091–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]