Abstract
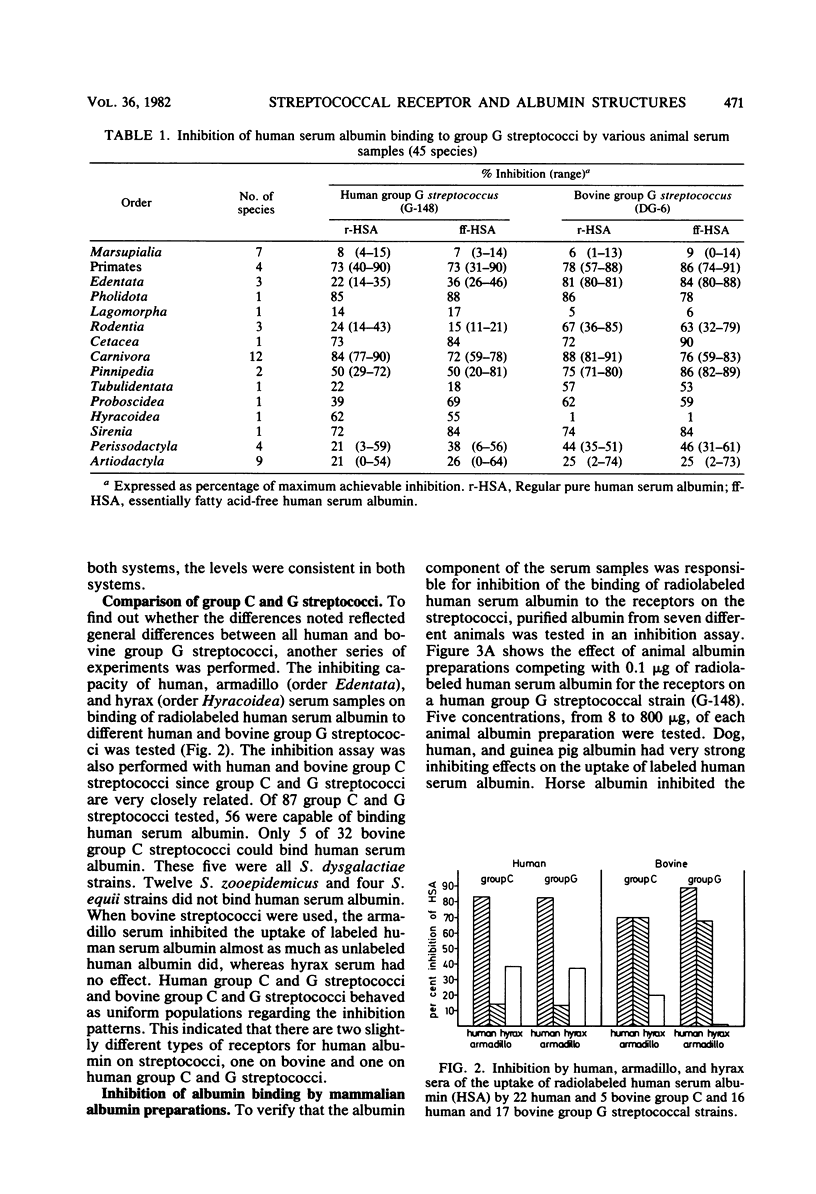
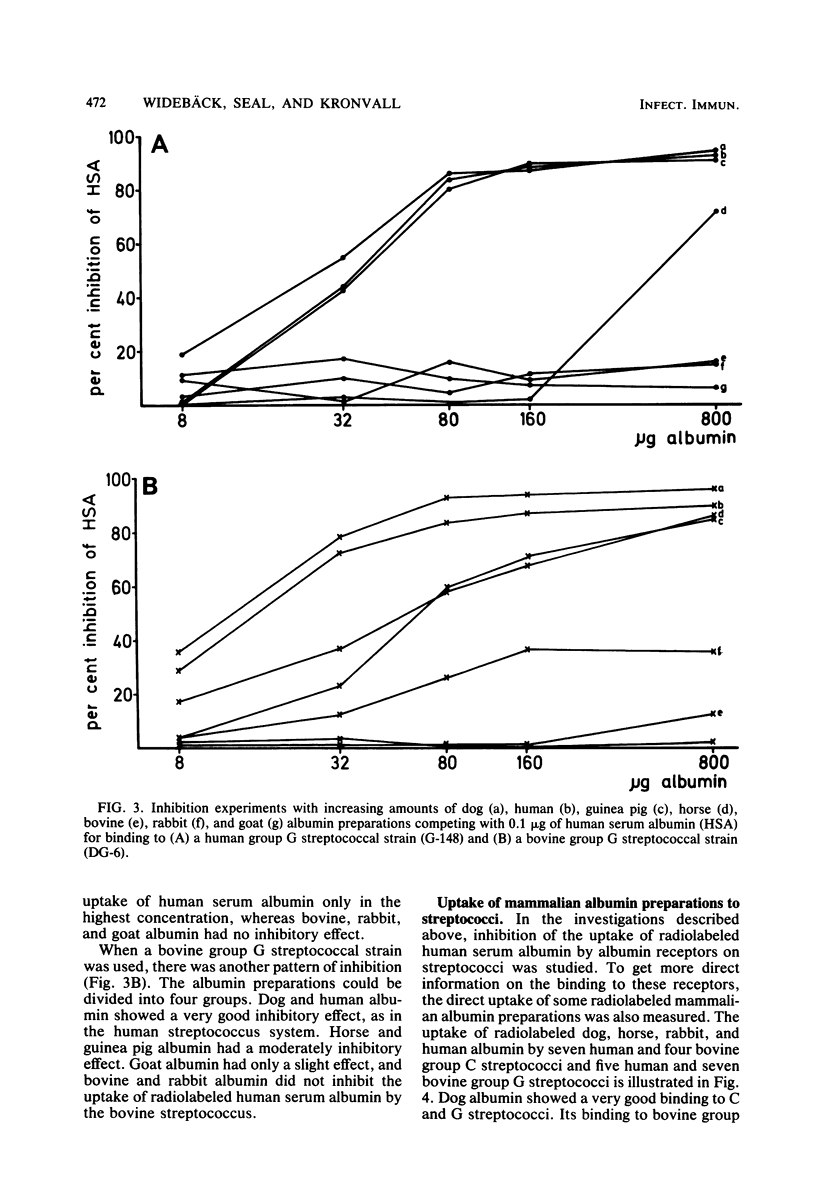
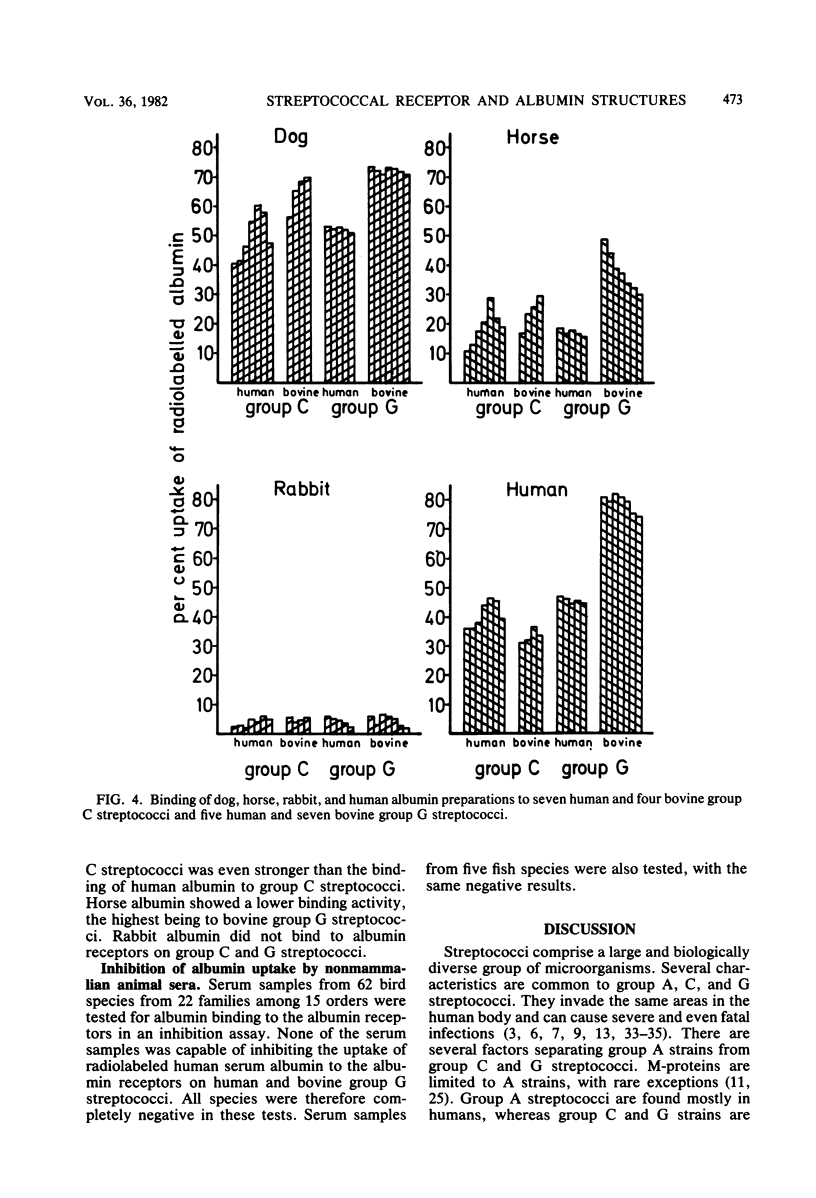
The presence of albumin structures with the capacity to bind to a surface receptor in group C and G streptococci was studied in serum samples from 45 mammalian species representing 15 different orders, using an inhibition assay. The ability of animal sera to inhibit the uptake of radiolabeled human serum albumin by the streptococci indicated the presence of such albumin structures. Positive reactions were found in species of most orders tested, with Marsupialia as a notable exception. All Carnivora sera tested were strongly positive. In some orders such as Artiodactyla both positive and negative species were identified. Serum samples from 62 bird species representing 15 orders and from 5 fish species were also tested in the inhibition assay. None of these serum samples was capable of inhibiting the uptake of human serum albumin by streptococci. Some differences were also noted in the results obtained with group C and G streptococci from human and bovine sources, respectively, indicating the presence of two types of receptors. The present studies suggest a phylogenetic origin of albumin structures with affinity for the streptococcal receptor to a period after the divergence of Marsupialia from the other mammalian orders.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Air G. M., Thompson E. O., Richardson B. J., Sharman G. B. Amino-acid sequences of kangaroo myoglobin and haemoglobin and the date of marsupial-eutherian divergence. Nature. 1971 Feb 5;229(5284):391–394. doi: 10.1038/229391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ankerst J., Christensen P., Kjellén L., Kronvall G. A rountine diagnostic test for IgA and IgM antibodies to rubella virus: absorption of IgG with Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):268–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Blevins A., Louria D. B., Henkel J. S., Moody M. D., Sukany M. Groups B, C, and G streptococcal infections in a cancer hospital. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):511–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnum D. A., Fuller D. S. Report on an Outbreak of Chronic Mastitis in Cattle Caused by a Streptococcus Of Langefield'S Group - G. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1953 Nov;17(11):465–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Kahlmeter G., Jonsson S., Kronvall G. New method for the serological grouping of Streptococci with specific antibodies adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):881–885. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.881-885.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunniff H., Bump C. M. Extrarespiratory non-group A, non-group D isolates of streptococci. Am J Med Technol. 1976 Jun;42(6):195–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. The action of fibrinogen on certain pathogenic cocci. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Oct;13(2):383–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Stagg N. L., Kunz L. J. Extrarespiratory streptococcal infections. Importance of the various serologic groups. N Engl J Med. 1966 Aug 18;275(7):356–361. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196608182750704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. A., Stark D. M. Occurrence and characterization of Lancefield group G streptococci in bovine mastitis. Am J Vet Res. 1970 Feb;31(2):397–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Caldwell G. G., Wilson E., Hager D., Zimmerman R. A. Epidemic of pharyngitis due to streptococci of Lancefield group G. Lancet. 1969 Aug 16;2(7616):371–374. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92713-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A surface component in group A, C, and G streptococci with non-immune reactivity for immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Myhre E. B., Björck L., Berggård I. Binding of aggregated human beta2-microglobulin to surface protein structure in group A, C, and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):136–142. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.136-142.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Schönbeck C., Myhre E. Fibrinogen binding structures in beta-hemolytic streptococci group A, C, and G. Comparisons with receptors for IgG and aggregated beta 2-microglobulin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Oct;87(5):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Seal U. S., Finstad J., Williams R. C., Jr Phylogenetic insight into evolution of mammalian Fc fragment of gamma G globulin using staphylococcal protein A. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Seal U. S., Svensson S., Williams R. C., Jr Phylogenetic aspects of staphylococcal protein A-reactive serum globulins in birds and mammals. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Feb;82(1):12–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Simmons A., Myhre E. B., Jonsson S. Specific absorption of human serum albumin, immunoglobulin A, and immunoglobulin G with selected strains of group A and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.1-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler W., Prokop O. Relationship between haptoglobin and Streptococcus pyogenes T4 antigens. Nature. 1978 Jan 26;271(5643):373–373. doi: 10.1038/271373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallinson H., Roberts C., Bruce White G. B. Staphylococcal protein A; its preparation and an application to rubella serology. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Nov;29(11):999–1002. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.11.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Potter E. V. The presence of type 12 M-protein antigen in group G streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):119–125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. J., McDonald J. S. Streptococci isolated from bovine intramammary infections. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Apr;37(4):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Holmberg O., Kronvall G. Immunoglobulin-binding structure on bovine group G streptococci different from type III Fc receptors on human group G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.1-7.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Demonstration of specific binding sites for human serum albumin in group C and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):6–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.6-14.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Heterogeneity of nonimmune immunoglobulin Fc reactivity among gram-positive cocci: description of three major types of receptors for human immunoglobulin G. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):475–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.475-482.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLAS W. C., STEELE C. P. Occurrence of groupable beta-hemolytic streptococci. Study among school children in Bismarck, N.D. JAMA. 1962 Jul 21;181:197–205. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050290019004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T., Ball L. C. Streptococci and aerococci associated with systemic infection in man. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Aug;9(3):275–302. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-3-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock H. M., Dahlgren B. J. Distribution of streptococcal groups in clinical specimens with evaluation of bacitracin screening. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):141–143. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.141-143.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Binding of streptococcal lipoteichoic acid to the fatty acid binding sites on serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6092–6097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Fatty acid binding sites of serum albumin as membrane receptor analogs for streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):119–122. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.119-122.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaug K., Tjotta E. Diagnosis of recent Herpes simplex infections. A modified immunofluorescent test for the detection of specific Herpes simplex IgM antibodies after staphylococcal adsorption of IgG. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):323–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


