Abstract
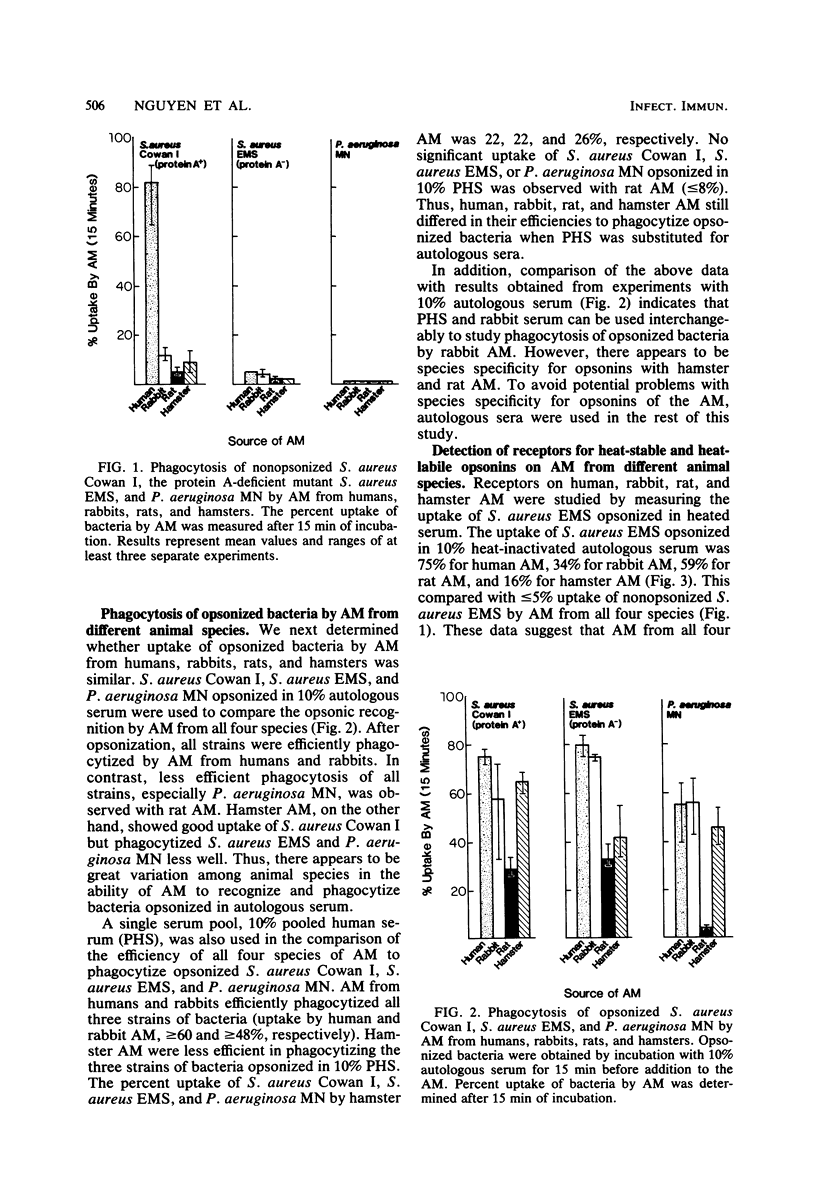
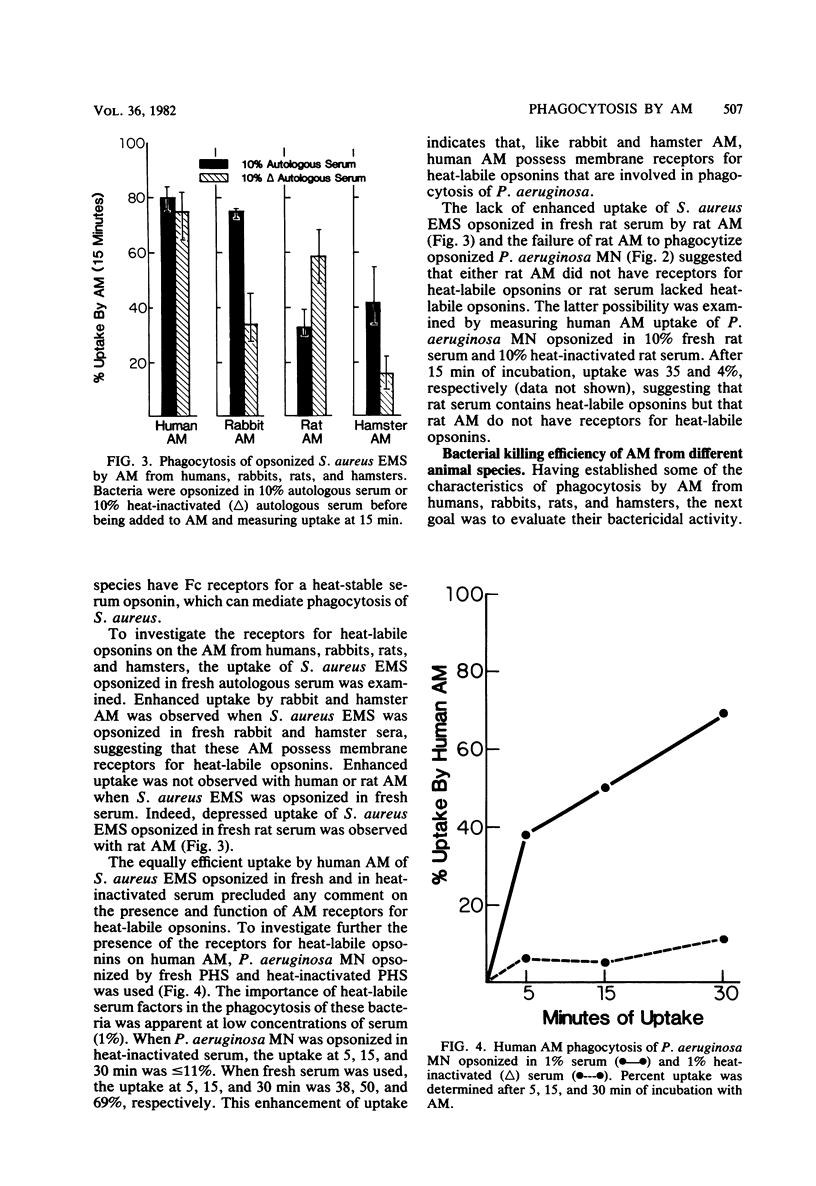
Phagocytosis and killing by alveolar macrophages from humans, rabbits, rats, and hamsters, were compared in vitro. In the absence of serum opsonins, human alveolar macrophages could phagocytize Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I (protein A positive), but not S. aureus EMS (protein A negative) or Pseudomonas aeruginosa MN. In contrast, rabbit, rat, and hamster alveolar macrophages did not phagocytize S. aureus Cowan I or other nonopsonized bacteria. Human alveolar macrophages, but not other species, stained positively with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated protein A. When opsonized bacterial were studied, phagocytosis by human, rabbit, and hamster alveolar macrophages was found to be mediated by both Fc and C3 receptors. However, only Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis of bacteria was demonstrated for rat alveolar macrophages. Differences were also found in the kinetics of bacterial killing by alveolar macrophages from different species. Human and rabbit alveolar macrophages rapidly killed opsonized S. aureus Cowan I. However, bacterial killing by hamster alveolar macrophages proceeded at a slower rate, and rat alveolar macrophages completely failed to kill S. aureus. These significant differences in the function of alveolar macrophages from four different species emphasize the need to document the appropriateness of animal models before using them to predict the biological activities of human alveolar macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berken A., Benacerraf B. Properties of antibodies cytophilic for macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):119–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Hansen J. A., Bloomfield C. D., Good R. A. B lymphocytes in untreated patients with malignant lymphoma and Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3064–3073. doi: 10.1172/JCI107505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W. Kinetics and function of the human alveolar macrophage. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Sep;22(3):223–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Lippert W., Warshauer D. Pulmonary alveolar macrophage. Defender against bacterial infection of the lung. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):519–528. doi: 10.1172/JCI107788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking W. G., Golde D. W. The pulmonary-alveolar macrophage (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Sep 13;301(11):580–587. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197909133011104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hof D. G., Repine J. E., Peterson P. K., Hoidal J. R. Phagocytosis by human alveolar macrophages and neutrophils: qualitative differences in the opsonic requirements for uptake of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jan;121(1):65–71. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R., Beall G. D., Rasp F. L., Jr, Holmes B., White J. G., Repine J. E. Comparison of the metabolism of alveolar macrophages from humans, rats, and rabbits: phorbol myristate acetate. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Nov;92(5):787–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R., Schmeling D., Peterson P. K. Phagocytosis, bacterial killing, and metabolism by purified human lung phagocytes. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):61–71. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R., White J. G., Repine J. E. Influence of cationic local anesthetics on the metabolism and ultrastructure of human alveolar macrophages. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 May;93(5):857–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juers J. A., Rogers R. M., McCurdy J. B., Cook W. W. Enhancement of bactericidal capacity of alveolar macrophages by human alveolar lining material. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):271–275. doi: 10.1172/JCI108468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaForce F. M., Kelly W. J., Huber G. L. Inactivation of staphylococci by alveolar macrophages with preliminary observations on the importance of alveolar lining material. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Oct;108(4):784–790. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.4.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey S. A., Root R. K., Schreiber A. D. The role of antibody and complement in phagocytosis by rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):896–903. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Kinetics of phagocytosis and bacterial killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):502–509. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Douglas S. D., Quie P. G., Verhoef J. The key role of peptidoglycan in the opsonization of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):597–609. doi: 10.1172/JCI108971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Kazmierowski J. A., Newball H. H. Specificity of opsonic antibodies to enhance phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by human alveolar macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):376–385. doi: 10.1172/JCI108102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Territo M. C., Golde D. W. The function of human alveolar macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Jan;25(1):111–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I. R. Macrophage-cytophilic antibodies and the functions of macrophage-bound immunoglobulins. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Dec;35(4):365–378. doi: 10.1128/br.35.4.365-378.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



