Abstract
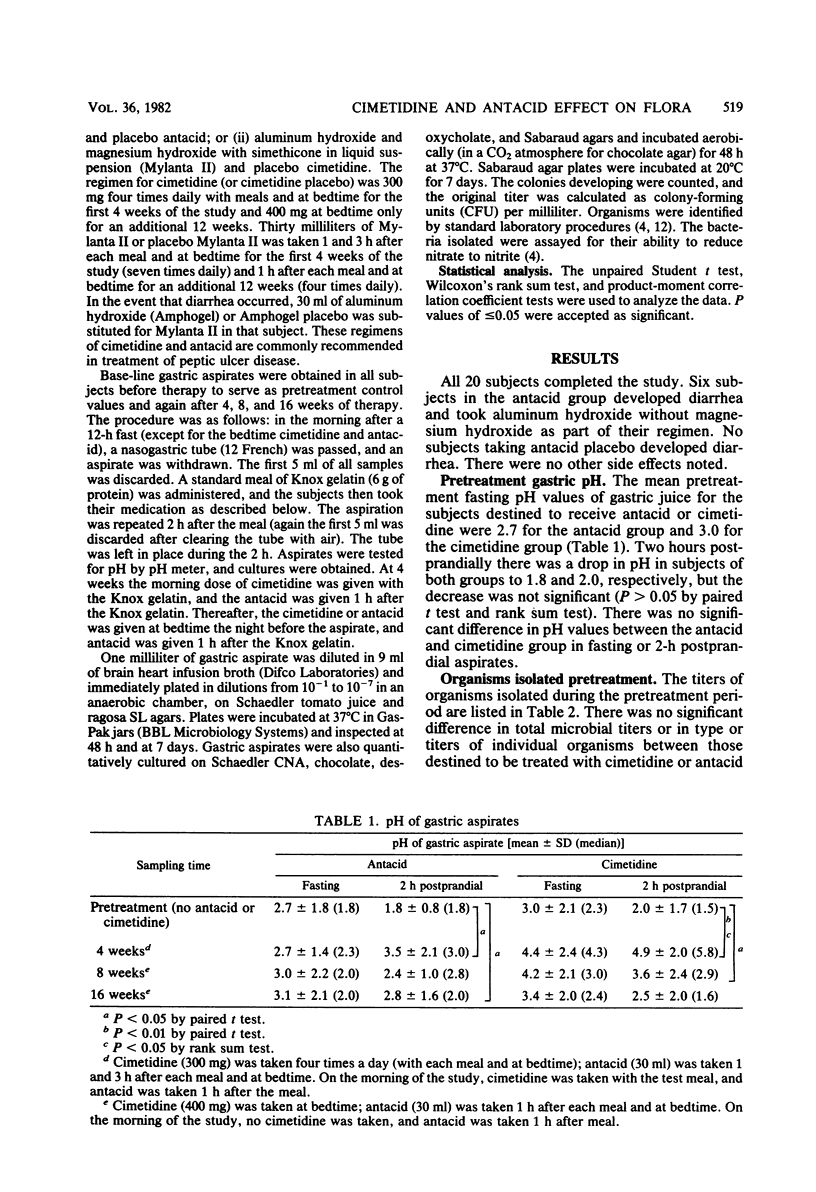
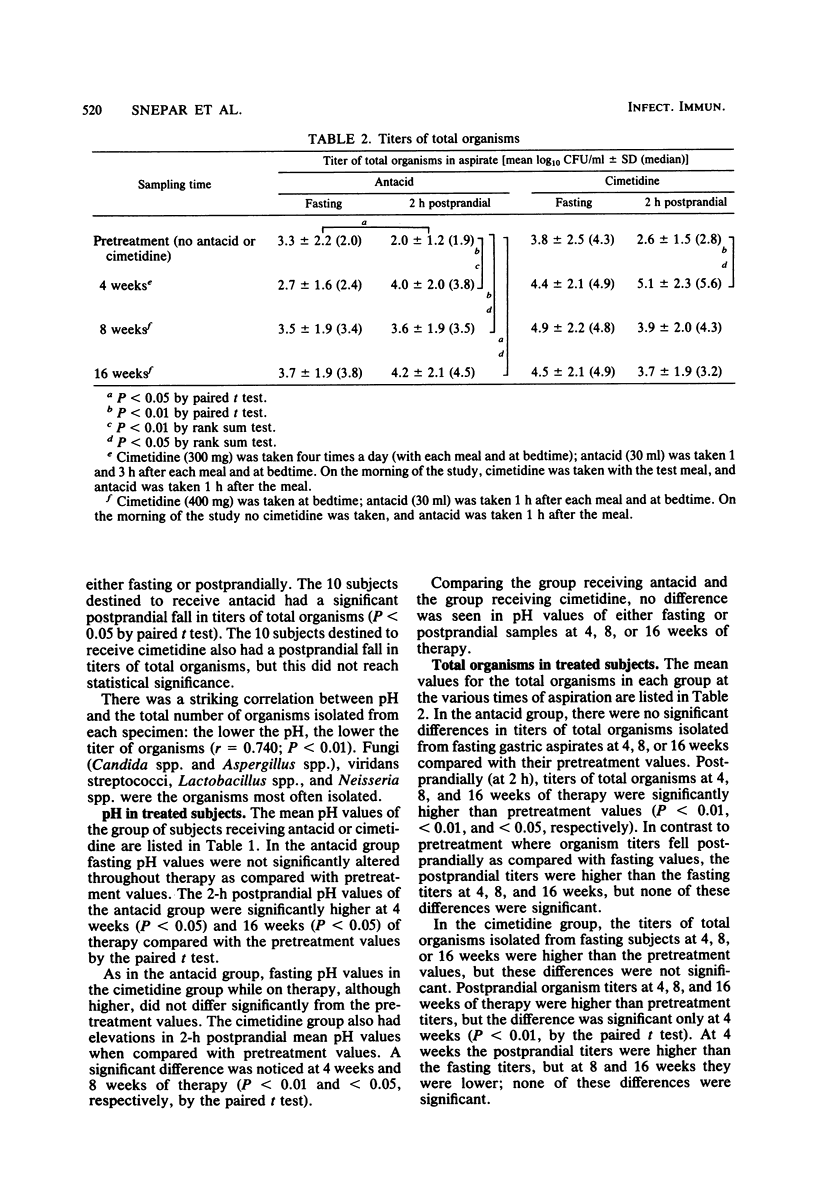
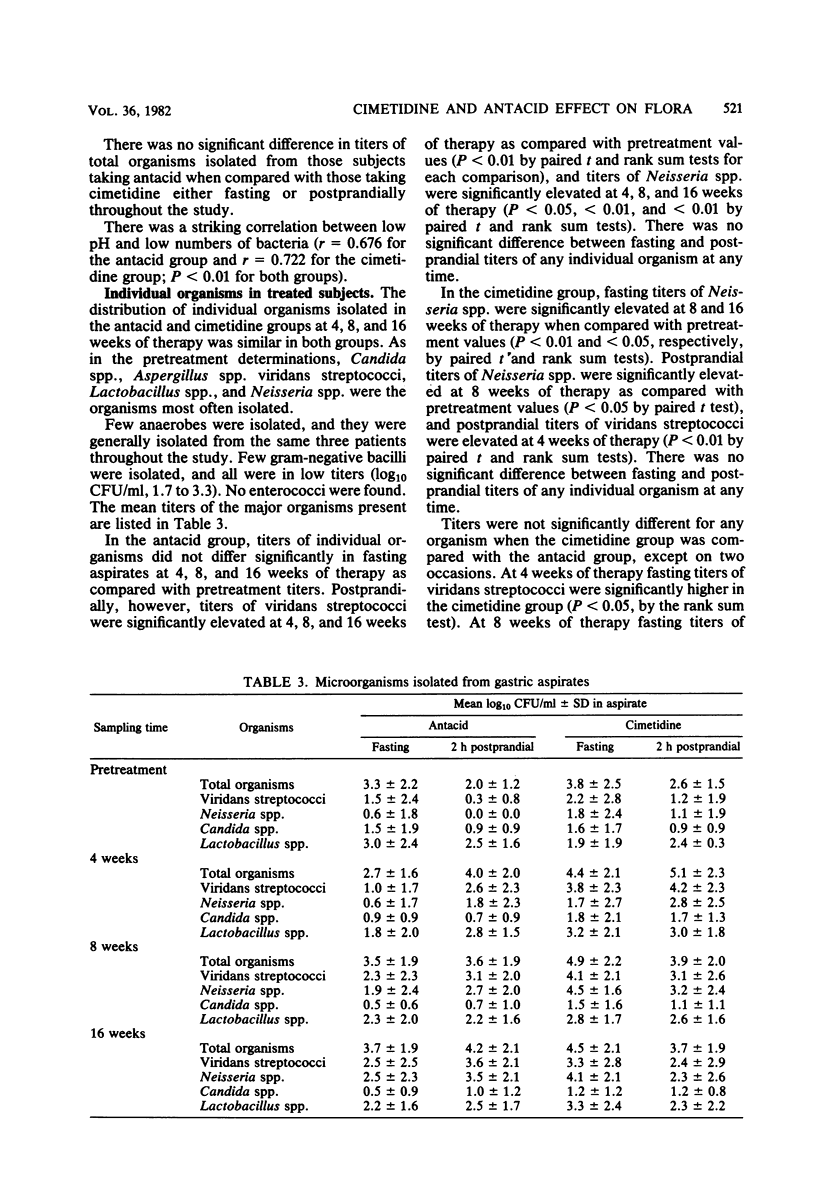
The effect of a standard regimen of cimetidine on the gastric flora of 20 male volunteers was studied in a double-blind manner and compared with the effects of a standard antacid regimen. Postprandial microbial titers in gastric aspirates were significantly higher at 4, 8, and 16 weeks of therapy in subjects taking antacids and at 4 weeks in subjects taking cimetidine when compared with their pretreatment titers. Although not significant, there was a tendency for fasting microbial titers to be higher in subjects receiving cimetidine as compared with pretreatment titers. The higher titers were primarily related to increases in survival of mouth flora (viridans streptococci and Neisseria spp.); Enterobacteriaceae and other nitrate-reducing organisms were unusual isolates. There was no significant difference in the total titers or types of organisms isolated when subjects taking cimetidine were compared with those taking antacid.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drasar B. S., Shiner M., McLeod G. M. Studies on the intestinal flora. I. The bacterial flora of the gastrointestinal tract in healthy and achlorhydric persons. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jan;56(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein W., Isselbacher K. J. Drug therapy: Cimetidine. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 2;299(18):992–996. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811022991806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Broitman S. A., Zamcheck N. Gastric acid barrier to ingested microorganisms in man: studies in vivo and in vitro. Gut. 1972 Apr;13(4):251–256. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.4.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Plaut A. G., Nahas L., Weinstein L., Spanknebel G., Levitan R. Studies of intestinal microflora. II. Microorganisms of the small intestine and their relations to oral and fecal flora. Gastroenterology. 1967 Dec;53(6):856–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawksworth G. M., Hill M. J. Bacteria and the N-nitrosation of secondary amines. Br J Cancer. 1971 Sep;25(3):520–526. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1971.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heathcote J. G., Washington R. Amino-acids and peptides in human gastric juice with particular reference to pernicious anaemia: a review. Nature. 1965 Aug 28;207(5000):941–944. doi: 10.1038/207941a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee P. N., Barnes J. M. Carcinogenic nitroso compounds. Adv Cancer Res. 1967;10:163–246. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscroft T. J., Youngs D. J., Burdon D. W., Keighley M. R. Cimetidine is unlikely to increase formation of intragastric N-nitroso-compounds in patients taking a normal diet. Lancet. 1981 Feb 21;1(8217):408–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91791-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscroft T. J., Youngs D., Burdon D. W., Keighley M. R. Cimetidine and the potential risk of postoperative sepsis. Br J Surg. 1981 Aug;68(8):557–559. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800680812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddell W. S., Bone E. S., Hill M. J., Blendis L. M., Walters C. L. Gastric-juice nitrite. A risk factor for cancer in the hypochlorhydric stomach? Lancet. 1976 Nov 13;2(7994):1037–1039. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90962-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddell W. S., Bone E. S., Hill M. J., Walters C. L. Pathogenesis of gastric cancer in pernicious anaemia. Lancet. 1978 Mar 11;1(8063):521–523. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90550-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


